Abstract
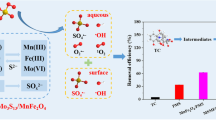
Persulfate-based advanced oxidation process (PS-AOPs) is a promising technique for removing antibiotic contaminants from water. Magnetic MoS2/CoFe2O4 nanocomposites were synthesized by a hydrothermal method and first used to activate peroxydisulfate (PDS) to degrade tetracycline (TC). The optimal MoS2/CoFe2O4-20 catalyst achieved 96.2% degradation efficiency of TC (20 mg L−1) in the presence of PDS (1.5 g L−1) after 80 min, which was significantly higher than that of pure MoS2 and CoFe2O4. Moreover, MoS2/CoFe2O4 catalysts exhibited a better catalytic activity for TC removal by activating PDS than that of recently reported ferrite-based catalysts. The influence of initial pH, PDS dosage and inorganic anions on the removal of TC in MoS2/CoFe2O4-20/PDS oxidation system was studied. The quenching experiments and electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) experiments show that the free radical (O2·−, SO4·− and ·OH) and non-radical (1O2) oxidation pathways collectively led to TC degradation in MoS2/CoFe2O4/PDS system. The exposed Mo(IV) sites on the surface of MoS2 can accelerate the cycle ≡ X(III)/ ≡ X(II) (X = Co or Fe) and the decomposition of PDS to generate the reactive species, thus enhancing the removal efficiency of TC. Cycling test confirms that as-synthesized MoS2/CoFe2O4 can be easily recovered and effectively reused. Besides, the removal of TC from various water matrices was also studied.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors declare that all data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article.
References
H. Kim, Y. Hong, J.-E. Park, V.K. Sharma, S.I. Cho, Sulfonamides and tetracyclines in livestock wastewater. Chemosphere 91, 888 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.02.027
P. Kovalakova, L. Cizmas, T.J. McDonald, B. Marsalek, M. Feng, V.K. Sharma, Occurrence and toxicity of antibiotics in the aquatic environment: a review. Chemosphere 251, 126351 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126351
R. Pulicharla, K. Hegde, S.K. Brar, R.Y. Surampalli, Tetracyclines metal complexation: significance and fate of mutual existence in the environment. Environ. Pollut. 221, 1 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.12.017
M.C. Danner, A. Robertson, V. Behrends, J. Reiss, Antibiotic pollution in surface fresh waters: occurrence and effects. Sci. Total. Environ. 664, 793 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.01.406
P. Chen, Y.J. Gou, J.M. Ni, Y.M. Liang, B.Q. Yang, F.F. Jia, S.X. Song, Efficient ofloxacin degradation with Co(II)-doped MoS2 nano-flowers as PMS activator under visible-light irradiation. Chem. Eng. J. 401, 125978 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.125978
L. Yang, X. Bai, J. Shi, X.Y. Du, L. Xu, P.K. Jin, Visible-light activation of persulfate by TiO2/g-C3N4 photocatalyst toward efficient degradation of micropollutants. Chem. Eng. J. 384, 123245 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.123245
A. Hassani, P. Eghbali, B. Kakavandi, K.-Y.A. Lin, F. Ghanbari, Acetaminophen removal from aqueous solutions through peroxymonosulfate activation by CoFe2O4/mpg-C3N4 nanocomposite: insight into the performance and degradation kinetics. Environ. Technol. Innovation. 20, 101127 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2020.101127
Q. Yang, Y.H. Ma, F. Chen, F.B. Yao, J. Sun, S.N. Wang, K.X. Yi, L.H. Hou, X.M. Li, D.B. Wang, Recent advances in photo-activated sulfate radical-advanced oxidation process (SR-AOP) for refractory organic pollutants removal in water. Chem. Eng. J. 378, 122149 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.122149
R.M. Li, H.W. Hu, Y.Y. Ma, X.Y. Liu, L.T. Zhang, S.R. Zhou, B.Y. Deng, H. Lin, H. Zhang, Persulfate enhanced photocatalytic degradation of bisphenol A over wasted batteries-derived ZnFe2O4 under visible light. J. Clean. Prod. 276, 124246 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.124246
S. Wacławek, H.V. Lutze, K. Grübel, V.V.T. Padil, M. Černík, D.D. Dionysiou, Chemistry of persulfates in water and wastewater treatment: a review. Chem. Eng. J. Molybdenum Disulfide 330, 44 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.07.132
A.S. Sethulekshmi, J.S. Jayan, S. Appukuttan, K. Joseph, MoS2: advanced nanofiller for reinforcing polymer matrix. Phys. E. 132, 114716 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physe.2021.114716
H.Y. Zhou, L.D. Lai, Y.J. Wan, Y.G. He, G. Yao, B. Lai, Molybdenum disulfide (MoS2): a versatile activator of both peroxymonosulfate and persulfate for the degradation of carbamazepine. Chem. Eng. J. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.123264
X.M. Song, J.Y. Tian, J.X. Ma, J.X. Ni, D.M. Liu, W. Wang, W.X. Shi, Y.X. Yuan, F.Y. Cui, Z. Chen, Peroxydisulfate activation by a versatile ball-milled nZVI@MoS2 composite: performance and potential activation mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.139830
Y. Tan, C.Q. Li, Z.M. Sun, R.Z. Bian, X.B. Dong, X.W. Zhang, S.L. Zheng, Natural diatomite mediated spherically monodispersed CoFe2O4 nanoparticles for efficient catalytic oxidation of bisphenol A through activating peroxymonosulfate. Chem. Eng. J. 388, 124386 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.124386
J. Li, M.J. Xu, G. Yao, B. Lai, Enhancement of the degradation of atrazine through CoFe2O4 activated peroxymonosulfate (PMS) process: kinetic, degradation intermediates, and toxicity evaluation. Chem. Eng. J. 348, 1012 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.05.032
S. Feng, M.G. Yu, T.P. Xie, T. Li, D.S. Kong, J.W. Yang, C.L. Cheng, H.Y. Chen, J.K. Wang, MoS2/CoFe2O4 heterojunction for boosting photogenerated carrier separation and the dominant role in enhancing peroxymonosulfate activation. Chem. Eng. J. 433, 134467 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.134467
X.M. Peng, Z.H. Yang, F.P. Hu, C.Q. Tan, Q.Y. Pan, H.L. Dai, Mechanistic investigation of rapid catalytic degradation of tetracycline using CoFe2O4@MoS2 by activation of peroxymonosulfate. Sep. Purif. Technol. 287, 120525 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2022.120525
G.S. Wang, F. Zhou, Z.W. Lu, Y.Y. Ma, X.G. Li, Y. Tong, X.F. Dong, Controlled synthesis of CoFe2O4/MoS2 nanocomposites with excellent sedimentation stability for magnetorheological fluid. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 70, 439 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2018.11.006
J. Kiwi, S. Rtimi, Insight into the interaction of magnetic photocatalysts with the incoming light accelerating bacterial inactivation and environmental cleaning. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 281, 119420 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2020.119420
H. Zhang, Y. Zhou, Y. Zhang, Z. Hu, X. Gao, X. Wang, Z. Wu, Two-dimensional MoS2 lattice constrained Cu(I) enables high activity and superior stability in visible-light-assisted peroxymonosulfate activation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 315, 123671 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2023.123671
C. Nethravathi, J. Prabhu, S. Lakshmipriya, M. Rajamathi, Magnetic Co-doped MoS2 nanosheets for efficient catalysis of nitroarene reduction. ACS Omega 2, 5891 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.7b00848
T. Zhang, C.J. Li, J. Ma, H. Tian, Z.M. Qiang, Surface hydroxyl groups of synthetic α-FeOOH in promoting OH generation from aqueous ozone: property and activity relationship. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 82, 131 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2008.01.008
L.J. Luo, J.H. Li, J.H. Dai, L.H. Xia, C.J. Barrow, H.B. Wang, J. Jegatheesan, M. Yang, Bisphenol A removal on TiO2–MoS2-reduced graphene oxide composite by adsorption and photocatalysis. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 112, 274 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2017.04.032
K. Srinivas, Y. Chen, Z. Su, B. Yu, M. Karpuraranjith, F. Ma, X.Q. Wang, W.L. Zhang, D.X. Yang, Heterostructural CoFe2O4/CoO nanoparticles-embedded carbon nanotubes network for boosted overall water-splitting performance. Electrochim. Acta 404, 139745 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2021.139745
K. Dou, Y.K. Lu, R.C. Wang, H.P. Cao, C. Yao, J.L. Liu, N. Tsidaeva, W. Wang, (1T/2H)-MoS2/CoFe2O4 heterojunctions with a unique grape bunch structure for photocatalysis of organic dyes driven by visible light. Appl. Surf. Sci. 605, 154751 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2022.154751
Y.F. Jia, H.X. Ma, C.L. Liu, Au nanoparticles enhanced Z-scheme Au-CoFe2O4/MoS2 visible light photocatalyst with magnetic retrievability. Appl. Surf. Sci. 463, 854 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.09.008
Y.W. Zhong, K.M. Shi, Z.H. Diao, G. Song, M.H. Su, L.A. Hou, D.Y. Chen, L.J. Kong, Peroxymonosulfate activation through LED-induced ZnFe2O4 for levofloxacin degradation. Chem. Eng. J. 417, 129225 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.129225
S.N. Nguyen, T.K. Truong, S.J. You, Y.F. Wang, T.M. Cao, V.V. Pham, Investigation on photocatalytic removal of NO under visible light over Cr-doped ZnO nanoparticles. ACS Omega 4, 12853 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.9b01628
M.Y. Xing, W.J. Xu, C.C. Dong, Y.C. Bai, J.B. Zeng, Y. Zhou, J.L. Zhang, Y.D. Yin, Metal sulfides as excellent co-catalysts for H2O2 decomposition in advanced oxidation processes. Chem 4(6), 1359–1372 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chempr.2018.03.002
Y. Li, Y. Feng, B. Yang, Z. Yang, K. Shi, Activation of peroxymonosulfate by molybdenum disulfide-mediated traces of Fe(III) for sulfadiazine degradation. Chemosphere 283, 131212 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131212
R. Chen, W. Wang, X.R. Zhao, Y.J. Zhang, S.Z. Wu, F. Li, Rapid hydrothermal synthesis of magnetic CoxNi1−xFe2O4 nanoparticles and their application on removal of Congo red. Chem. Eng. J. 242, 226 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.12.016
Y.K. Lu, B.Y. Ren, S.C. Chang, W.B. Mi, J. He, W. Wang, Achieving effective control of the photocatalytic performance for CoFe2O4/MoS2 heterojunction via exerting external magnetic fields. Mater. Lett. 260, 126979 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2019.126979
X.Y. Meng, Q.B. He, T.T. Song, M. Ge, Z.X. He, C.S. Guo, Activation of peroxydisulfate by magnetically separable rGO/MnFe2O4 toward oxidation of tetracycline: efficiency, mechanism and degradation pathways. Sep. Purif. Technol. 282, 120137 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2021.120137
Z.H. Xie, C.S. He, H.Y. Zhou, L.L. Li, Y. Liu, Y. Du, W. Liu, Y. Mu, B. Lai, Effects of molecular structure on organic contaminants’ degradation: efficiency and dominant ROS in the advanced oxidation process with multiple ROS. Environ. Sci. Technol. 56(12), 8784–8795 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.2c00464
T. Ye, Z. Wei, R. Spinney, C.J. Tang, S. Luo, R. Xiao, D.D. Dionysiou, Chemical structure-based predictive model for the oxidation of trace organic contaminants by sulfate radical. Water Res. 116, 106–115 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2017.03.015
Z.M. Liu, Z.M. Gao, Q. Wu, Activation of persulfate by magnetic zirconium-doped manganese ferrite for efficient degradation of tetracycline. Chem. Eng. J. 423, 130283 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.130283
S.M. Liu, Y.C. Liu, M.Y. Chen, L.L. Li, W.W. Tu, Z. Huang, CuFe2O4 modified expanded graphite synthesized by urea-assisted hydrothermal method for tetracycline treatment through persulfate activation: characterization, mechanism and degradation intermediates. Chem. Eng. J. 433, 133516 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.133516
S. Tang, M. Zhao, D. Yuan, X. Li, Z. Wang, X. Zhang, T. Jiao, J. Ke, Fe3O4 nanoparticles three-dimensional electro-peroxydisulfate for improving tetracycline degradation. Chemosphere 268, 129315 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.129315
P.H. Guo, Y.Q. Zhou, Y.B. Zhang, Y.K. Li, H.P. Lei, H. Zhang, S.Q. Li, Insights into the well-dispersed nano-Fe3O4 catalyst supported by N-doped biochar prepared from steel pickling waste liquor for activating peroxydisulfate to degrade tetracycline. Chem. Eng. J. 464, 142548 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2023.142548
X.W. Zhang, F. Wang, C.C. Wang, P. Wang, H.F. Fu, C. Zhao, Photocatalysis activation of peroxodisulfate over the supported Fe3O4 catalyst derived from MIL-88A(Fe) for efficient tetracycline hydrochloride degradation. Chem. Eng. J. 426, 131927 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.131927
M. Ge, Z. Hu, J.L. Wei, Q.B. He, Z.X. He, Recent advances in persulfate-assisted TiO2-based photocatalysis for wastewater treatment: performances, mechanism and perspectives. J. Alloys Compd. 888, 161625 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.161625
X. Yuan, S.L. Qu, X.Y. Huang, X.G. Xue, C.L. Yuan, S.W. Wang, L. Wei, P. Cai, Design of core-shelled g-C3N4@ZIF-8 photocatalyst with enhanced tetracycline adsorption for boosting photocatalytic degradation. Chem. Eng. J. 416, 129148 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.129148
J.C. Lyu, M. Ge, Z. Hu, C.S. Guo, One-pot synthesis of magnetic CuO/Fe2O3/CuFe2O4 nanocomposite to activate persulfate for levofloxacin removal: investigation of efficiency, mechanism and degradation route. Chem. Eng. J. 389, 124456 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.124456
J. Lu, Y. Zhou, Y.B. Zhou, Efficiently activate peroxymonosulfate by Fe3O4@MoS2 for rapid degradation of sulfonamides. Chem. Eng. J. 422, 130126 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.130126
H.H. Wang, H. Guo, N. Zhang, Z.S. Chen, B.W. Hu, X.K. Wang, Enhanced photoreduction of U(VI) on C3N4 by Cr(VI) and bisphenol A: ESR, XPS, and EXAFS investigation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 53, 6454 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.129164
C.F. Zhang, Q. Zhuang, H. Wang, X.T. Ying, R.Y. Ji, D.H. Sheng, W. Dong, A.M. Xie, Constructing an acidic microenvironment by MoS2 in heterogeneous Fenton reaction for pollutant control. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 60, 17155 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202105736
X.W. Li, X.T. Liu, C.Y. Lin, H.J. Zhang, Z. Zhou, G.X. Fan, J. Ma, Cobalt ferrite nanoparticles supported on drinking water treatment residuals: an efficient magnetic heterogeneous catalyst to activate peroxymonosulfate for the degradation of atrazine. Chem. Eng. J. 367, 208 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.02.151
Z. Hu, M. Ge, C.S. Guo, Efficient removal of levofloxacin from different water matrices via simultaneous adsorption and photocatalysis using a magnetic Ag3PO4/rGO/CoFe2O4 catalyst. Chemosphere 268, 128834 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128834
G.X. Huang, C.Y. Wang, C.W. Yang, P.C. Guo, H.Q. Yu, Degradation of bisphenol A by peroxymonosulfate catalytically activated with Mn1.8Fe1.2O4 nanospheres: synergism between Mn and Fe. Environ. Sci. Technol. 51, 12611 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.7b03007
Z.H. Hu, B.Y. Guo, H.Q. Wu, F. Zhu, S. Komarneni, J.F. Ma, Activation of Na2S2O8 by MIL-101(Fe)/MoS2 composite for the degradation of tetracycline with visible light assistance. Colloids Surf. A 654, 130202 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2022.130202
S. Li, Y.N. Wu, Y.J. Zheng, T. Jing, J.Z. Tian, H.S. Zheng, N.N. Wang, J. Nan, J. Ma, Free-radical and surface electron transfer dominated bisphenol A degradation in system of ozone and peroxydisulfate co-activated by CoFe2O4-biochar. Appl. Surf. Sci. 541, 147887 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.147887
Q.Y. Yi, J.H. Ji, B. Shen, C.C. Dong, J. Liu, J.L. Zhang, M.Y. Xing, Singlet oxygen triggered by superoxide radicals in a molybdenum cocatalytic Fenton reaction with enhanced redox activity in the environment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 53(16), 9725–9733 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.9b01676
C. Liu, Y.P. Wang, Y.T. Zhang, R.Y. Li, W.D. Meng, Z.L. Song, F. Qi, B.B. Xu, W. Chu, D.H. Yuan, B. Yu, Enhancement of Fe@porous carbon to be an efficient mediator for peroxymonosulfate activation for oxidation of organic contaminants: incorporation NH2-group into structure of its MOF precursor. Chem. Eng. J. 354, 835–848 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.08.060
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province (B2019209373) and Hebei Province High-level Talents Funded Project (No. B2020003030).
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. CZ and JYFperformed the experiments on catalyst synthesis, antibiotic degradation and mechanism study. CZ, MG and QY analyzed the experimental data and wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no conflict of interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, C., Feng, J., Su, Z. et al. Activation of peroxydisulfate by magnetic MoS2/CoFe2O4 composite catalyst for efficient degradation of tetracycline in water. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 34, 1938 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-11357-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-11357-y