Abstract
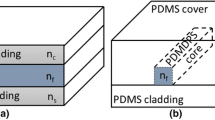
The paper reports on the properties of polydimethylsiloxane bulk samples and optical multimode channel waveguides doped with yellow dye fabricated by the microdispensing method. The spectral characteristics of the doped polymer bulk samples showed that the transmission of the edge of the spectra shifted towards longer wavelengths and significantly increased the absorption. The refractive index measured by dark mode spectroscopy did not confirm any change in the refractive index depending on the amount of the dye. The optical losses of the channel waveguides were measured by the cut-back method. The measurement showed that the waveguides with the dye-doped core containing 0.01 wt% of the dye had the lowest losses at 850 and 1300 nm, where the average losses were −1.18 dB (at 850 nm) and − 1.06 dB (at 1300 nm). In comparison with undoped samples, dye-doping caused an increase in optical losses by 0.5–1.0 dB/cm.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available on request from the corresponding author V. Prajzler. The data are not publicly available due to restrictions, e.g., their containing information that could compromise the privacy of research participants.
References
L. Eldada, L.W. Shacklette, Advances in polymer integrated optics. IEEE J. Sel. Top Quantum Electron 6, 54–68 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1109/2944.826873
R.A.S. Ferreira, P.S. Andre, L.D. Carlos, Organic-inorganic hybrid materials towards passive and active architectures for the next generation of optical networks. Opt. Mat. 32, 1397–1409 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2010.06.019
W. Daum, J. Krauser, P.E. Zamzow, O. Ziemann, Polymer Optical Fibers for Data Communication (Springer, Berlin, 2002)
S. Fengyuan, N. Bamiedakis, P.P. Vasilev, R.V. Penty, I.H. White, D. Chu, Flexible multimode polymer waveguide arrays for versatile high-speed short-reach communication links. J. Lightwave Technol. 36, 2685–2693 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/JLT.2018.2816562
Y. Shi, L. Ma, M. Kaneta, B.X. Xu, X.Y. Fan, Y.D. Zhuang, Z.Y. He, High-speed performance evaluation of ultra-flexible polymer waveguides supporting meter-scale optical interconnects. Opt. Express. 30, 27236–27248 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.460783
I. Parola, E. Arrospide, F. Recart, M.A. Illarramendi, G. Durana, N. Guarrotxena, O. García, J. Zubia, Fabrication and characterization of polymer optical fibers doped with perylene-derivatives for fluorescent lighting applications. Fibers. 5, 28 (2017). https://doi.org/10.3390/fib5030028
Z. Gong, Z. Xiang, X. OuYang, J. Zhang, N. Lau, J. Zhou, C.C. Chan, Wearable fiber optic technology based on smart textile: a review. Materials. 12, 3311 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12203311
K. Jakubowski, C.S. Huang, L.F. Boesel, R. Hufenus, M. Heuberger, Recent advances in photoluminescent polymer optical fibers. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 25, 100912 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cossms.2021.100912
J. Guo, B. Zhou, C. Yang, Q. Dai, L. Kong, Stretchable and upconversion—luminescent polymeric optical sensor for wearable multifunctional sensing. Opt. Lett. 44, 5747–5750 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1364/OL.44.005747
S. Nizamoglu, M.C. Gather, M. Humar, M. Choi, S. Kim, K.S. Kim, S.K. Hahn, G. Scarcelli, M. Randolph, R.W. Redmond, S.H. Yun, Bioabsorbable polymer optical waveguides for deep-tissue photomedicine. Nat. Comm. 7, 10374 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms10374
Y. Wang, Y. Huang, H.Y. Bai, G.Q. Wang, X.H. Hu, S. Kumar, R. Min, Biocompatible and biodegradable polymer optical fiber for biomedical application: a review. Biosensors (Basel) 11, 472 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11120472
A. Dupuis, N. Guo, Y. Gao, N. Godbout, S. Lacroix, C. Dubois, M. Skorobogatiy, Prospective for biodegradable microstructured optical fibers. Opt. Lett. 32, 109–111 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1364/OL.32.000109
M. Choi, J.W. Choi, S. Kim, S. Nizamoglu, S.K. Hahn, S.H. Yun, Light-guiding hydrogels for cell-based sensing and optogenetic synthesis in vivo. Nat. Photonics. 7, 987–994 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/NPHOTON.2013.278
S.T. Parker, P. Domachuk, J. Amsden, J. Bressner, J.A. Lewis, D.L. Kaplan, F.G. Omenetto, Biocompatible silk printed optical waveguides. Adv. Mater. 21, 2411–2415 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.200801580
K.H. Tow, D.M. Chow, F. Vollrath, I. Dicaire, T. Gheysens, L. Thevenaz, Exploring the use of native spider silk as an optical fiber for chemical sensing. J. Lightwave Technol. 36, 1138–1144 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/JLT.2017.2756095
J. Feng, Q. Jiang, P. Rogin, de P.W. Oliveira, A. Campo, Printed soft optical waveguides of PLA copolymers for guiding light into tissue. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 12, 20287–20294 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.0c03903
J. Guo, M. Niu, C. Yang, Highly flexible and stretchable optical strain sensing for human motion detection. Optica. 4, 1285–1288 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1364/OPTICA.4.001285
V. Prajzler, M. Neruda, P. Nekvindova, Flexible multimode polydimethyl–diphenylsiloxane optical planar waveguides. J. Mat. Sci. Mat. El. 29, 5878–5884 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-8560-z
R. Fu, W. Luo, R. Nazempour, D. Tan, H. Ding, K. Zhang, L. Yin, J. Guan, X. Sheng, Implantable and biodegradable poly(L-lactic acid) fibers for optical neural interfaces. Adv. Opt. Mater. 6, 1700941 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1002/adom.201700941
K. Soma, T. Ishigure, Fabrication of a graded-index circular-core polymer parallel optical waveguide using a microdispenser for a high-density optical printed circuit board. IEEE J. Sel. Top Quantum Electron 19, 3600310 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1109/JSTQE.2012.2227688
S. Yakabe, H. Matsui, Y. Kobayashi, Y. Saito, K. Manabe, T. Ishigure, Multi-channel single-mode polymer waveguide fabricated using the mosquito method. J. Light Tech. 39, 547–556 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/JLT.2020.3029395
V. Prajzler, V. Chlupaty, M. Neruda, Circular large core optical elastomer waveguides fabricated by using direct microdispense fabrication method. Optik – International Journal for Light and Electron Optics. 250, 168348 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2021.168348
Advanced Technologies, avantor NuSil, LS 6943 datasheet available: https://www.avantorsciences.com/assetsvc/asset/en_US/id/29018084/contents/en_us_tds_nusils-6943.pdf
DOW Technical Data Sheet available, https://www.farnell.com/datasheets/3154500.pdf
BASF: technical information lumogen F collector dyes available, https://pdf4pro.com/amp/fullscreen/technical-information-lumogen-f-basf-22536a.html
V. Prajzler, P. Nekvindova, J. Spirkova, M. Novotny, The evaluation of the refractive indices of bulk and thick polydimethylsiloxane and polydimethyl-diphenylsiloxane elastomers by the prism coupling technique. J. Mater. Sci: Mater. Electron. 28, 7951–7961 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-6498-1
V. Prajzler, V. Chlupaty, Z. Sarsounova, The effect of gamma-ray irradiation on bulk optical plastic materials. J. Mater. Sci: Mater. Electron. 31, 22599–22615 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-04772-y
V. Prajzler, M. Neruda, P. Jasek, P. Nekvindová, The properties of free-standing epoxy polymer multi-mode optical waveguides. Microsyst. Technol. 25, 257–264 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-018-3960-9
M. Mosca, F. Caruso, L. Zambito, R. Macaluso, C. Cali, E. Feltin, Hybrid LEDs pave way to new lighting applications. Phot. Spect. 47, 60–64 (2013)
M. Grabolle, M. Starke, U. Resch-Genger, Highly fluorescent dye–nanoclay hybrid materials made from different dye classes. Langmuir 32(14), 3506–3513 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.5b04297
Funding
This work was supported by the CTU Grant No. SGS23/181/OHK3/3T/13 as well as by the Centre of Advanced Applied Natural Sciences, Reg. No. CZ.02.1.01/0.0/0.0/16 019/0000778, supported by the Operational Programme Research, Development and Education, co-financed by the European Structural and Investment Funds and the state budget of the Czech Republic and by the specific UCT university research funding, grant No: A1 FCHT 2023 008. The authors thank Karsten Winters from BASF Lampertheim GmbH for technical support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
VP and ML have conceived and designed the experiments; ML have performed the experiments; VP, PV and PN have analysed the data and written the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The authors V. Prajzler, M. Latečka, P. Vařák and P. Nekvindová declare that they have no financial interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Prajzler, V., Latečka, M., Vařák, P. et al. Polydimethylsiloxane multimode optical channel waveguides doped with yellow dye fabricated by microdispensing. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 34, 1907 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-11324-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-11324-7