Abstract
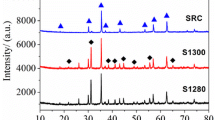
This paper reports on the systematic investigation of the room-temperature magnetoelectric and magnetodielectric coupling coefficients on adding ferromagnetic phase (xCo0.9Ni0.1Fe2O4, where x = 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, and 0.4) to the non-toxic lead-free ferroelectric phase (BaZr0.25Ti0.75O3) prepared via efficient, ultrafast, eco-friendly hybrid microwave sintering at 1100 °C. Rietveld’s refinement of the observed diffraction patterns reflects mixed-phase cubic and tetragonal crystal symmetries with space group Pm3m and P4mm for the ferroelectric phase and cubic Fd-3m for a ferromagnetic phase in each composite which was further verified through micro-Raman spectroscopy. Ferroelectric-ferrite composite at x = 0.2, i.e., 0.8(BaZr0.25Ti0.75O3) − 0.2(Co0.9Ni0.1Fe2O4), had highest magnetoelectric and magnetodielectric coupling coefficients \({\alpha }_{\mathrm{ME}}= 2.71\mathrm{ mV}/\mathrm{cm Oe}\) and MD (%) = 5.19 at 1 kHz applied frequency, respectively. The existence of both ferroelectric and magnetic phases in each composite was confirmed using P–E and M–H hysteresis loops, respectively. This study provides an efficient alternative approach for developing multiferroic composites for various technological applications.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available on reasonable request.
References
D.R. Patil, S.A. Lokare, R.S. Devan, S.S. Chougule, Y.D. Kolekar, B.K. Chougule, Dielectric properties and magnetoelectric effect of (x)NiFe2O4+(1–x)Ba0.8Sr0.2TiO3 composites. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 68, 1522–1526 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2007.03.029
A. Singh, K. Shamim, S. Sharma, R. Rai, P. Kumari, Enhanced electrical and magnetic properties in BZT/NFO multiferroic composites derived by MARH. J. Mater. Sci.-Mater. El. 29, 18221–18230 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-9935-x
Y. Wang, J. Hu, Y. Lin, C.W. Nan, Multiferroic magnetoelectric composite nanostructures. NPG Asia Mater. 2, 61–68 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/asiamat.2010.32
N. Kumar, A. Shukla, N. Kumar, R.N.P. Choudhary, A. Kumar, Structural, electrical, and multiferroic characteristics of lead-free multiferroic: Bi(Co0.5Ti0.5)O3–BiFeO3 solid solution. RSC Adv. 8, 36939–36950 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ra02306a
N.M. Shinde, P.V. Shinde, R.S. Mane, K.H. Kim, Solution-method processed Bi-type nanoelectrode materials for supercapacitor applications: a review. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 135, 110084 (2021)
J. vanden Boomgaard, R.A.J. Born, A sintered magnetoelectric composite material BaTiO3-Ni(Co, Mn) Fe2O4. J. Mater. Sci. 13, 1538–1548 (1978)
S.M. Mane, P.M. Tirmali, D.J. Salunkhe, P.B. Joshi, C.B. Kolekar, S.B. Kulkarni, Synthesis, structural and dielectric characterization of lead free x[(Ba0.7Ca0.3)TiO3]–(1–x)[Ba(Zr02Ti08)O3] composite. J. Mater. Sci.-Mater. El. 27, 7204–7210 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-4685-0
P. Jarupoom, P. Jaita, R. Sanjoom, C. Randorn, G. Rujijanagul, High magnetic and ferroelectric properties of BZT-LSM multiferroic composites at room temperature. Ceram. Int. 44, 8768–8776 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.02.006
M.L.V. Mahesh, V.V. Bhanu Prasad, A.R. James, Enhanced dielectric and ferroelectric properties of lead-free Ba(Zr0.15Ti0.85)O3 ceramics compacted by cold isostatic pressing. J. Alloy. Compd. 611, 43–49 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2014.05.098
Z. Yu, C. Ang, R. Guo, A.S. Bhalla, Ferroelectric-relaxor behavior of Ba(Ti0.7Zr0.3)O3 ceramics. J. Appl. Phys. 92, 2655–2657 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1495069
R.S. Devan, B.K. Chougule, Effect of composition on coupled electric, magnetic, and dielectric properties of two phase particulate magnetoelectric composite. J. Appl. Phys. 101, 014109 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2404773
S.M. Mane, A.M. Teli, N.T. Tayade, K.J. Pawar, S.B. Kulkarni, J. Choi, J.W. Yoo, J.C. Shin, Correlative structural refinement-magnetic tunability, and enhanced magnetostriction in low-temperature, microwave-annealed, Ni-substituted CoFe2O4 nanoparticles. J. Alloy. Compd. 895, 162627 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.162627
J. Hao, W. Bai, W. Li, J. Zhai, Correlation between the microstructure and electrical properties in high-performance (Ba0.85 Ca0.15)(Zr0.1Ti0.9) O3 lead-free piezoelectric ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 95, 1998–2006 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1551-2916.2012.05146.x
G. Srinivasan, S. Priya, N.X. Sun, Composite magnetoelctrics (Woodhead publishing, Cambridge, 2015)
M. Oghbaei, O. Mirzaee, Microwave versus conventional sintering: a review of fundamentals, advantages and applications. J. Alloy. Compd. 494, 175–189 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2010.01.068
M.M. Sutar, A.N. Tarale, S.R. Jigajeni, S.B. Kulkarni, V.R. Reddy, P.B. Joshi, Magnetoelectric and magnetodielectric effect in Ba1-xSrxTiO3 and Co09Ni0.1Fe2-xMnxO4 composites. Solid State Sci. 14, 1064–1070 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solidstatesciences.2012.05.016
L. Xu, Y. Xu, Effect of Zr4+ content on crystal structure, micromorphology, ferroelectric and dielectric properties of Ba(ZrxTi1−x)O3 ceramics. J. Mater. Sci.-Mater. El. 31, 5492–5498 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-03114-2
M.P.K. Sahoo, Z. Yajun, J. Wang, R.N.P. Choudhary, Composition control of magnetoelectric relaxor behavior in multiferroic BaZr0.4Ti0.6O3/CoFe2O4 composites. J. Alloy. Compd. 657, 12–20 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.10.040
M. Deluca, C.A. Vasilescu, A.C. Ianculescu et al., Investigation of the composition-dependent properties of BaTi1−xZrxO3 ceramics prepared by the modified Pechini method. J. Euro. Ceram. Soci. 32, 3551–3566 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2012.05.007
Y. Zhang, L. Wu, J. Zhao, W. Yu, A facile precursor-separated method to synthesize nano-crystalline LiFePO4/C cathode materials. J. Elctroanal. Chem. 719, 1–6 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2014.02.003
H.M. Rietveld, A profile refinement method for nuclear and magnetic structures. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2, 65–71 (1969)
N. Doebelin, R. Kleeberg, Profex: a graphical user interface for the Rietveld refinement program BGMN. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 48, 1573–1580 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1107/S1600576715014685
B. Kariuki, International Union of Crystallography extended software/ methods development issue, 20 (1998) n.d, http://www.iucr.org/iucr-top/comm/cpd/Newsletters/.
E.K. Al-Shakarchi, N.B. Mahmood, Three techniques used to produce BaTiO3 fine powder. J. Mod. Phys. 02, 1420–1428 (2011). https://doi.org/10.4236/jmp.2011.211175
G. H. Kwei, A. C. Lawson, S. J. L. Billinge, S.-W. Cheong, Structures of the ferroelectric phases of barium titanate, J. Phys. Chem.-US., 97, 2368–2377 (1993). https://pubs.acs.org/sharingguidelines.
C.J. Xiao, C.Q. Jin, X.H. Wang, Crystal structure of dense nanocrystalline BaTiO3 ceramics. Mater. Chem. Phys. 111, 209–212 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2008.01.020
A. Boultif, D. Louër, Powder pattern indexing with the dichotomy method. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 37, 724–731 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1107/S0021889804014876
D. Louër, A. Boultif, Powder pattern indexing and the dichotomy algorithm. Z. Kristallogr. Suppl. 26, 191–196 (2007)
L.S. Cavalcante, M. Anicete-Santos, J.C. Sczancoski, L.G.P. Simões, M.R.M.C. Santos, J.A. Varela, P.S. Pizani, E. Longo, Intense and broad photoluminescence at room temperature in structurally disordered Ba[Zr0.25Ti0.75]O3 powders: an experimental/theoretical correlation. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 69, 1782–1789 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2007.12.022
O.A. Maslova, Y.I. Yuzyuk, N. Ortega, A. Kumar, S.A. Barannikova, R. Katiyar, Phase transition peculiarities in BaTiO3-based perovskite superlattices. AIP Conf. Proc. 2051, 020190-1–020190-4 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5083433
O.A. Maslova, Y.I. Yuzyuk, S.A. Barannikova, A Comparative Analysis of asymmetric (BaTiO3) (1–x)Λ/(BaZrO3)xΛ superlattices via x-ray diffraction and Raman spectroscopy. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/6345691
V. Buscaglia, S. Tripathi, V. Petkov, M. Dapiaggi, M. Deluca, A. Gajovic, Y. Ren, Average and local atomic-scale structure in BaZrxTi1-xO3 (x = 0.10, 0.20, 0.40) ceramics by high-energy x-ray diffraction and Raman spectroscopy. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 26, 065901 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1088/0953-8984/26/6/065901
L.H. Robins, D.L. Kaiser, L.D. Rotter, P.K. Schenck, Investigation of the structure of barium titanate thin films by Raman spectroscopy. J. Appl. Phys. 76, 7487 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.357978
J. Kreisel, P. Bouvier, M. Maglione, B. Dkhil, A. Simon, High-pressure Raman investigation of the Pb-free relaxor BaTi0.65Zr0.35O3. Phys. Rev. B 69, 092104 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.69.092104
A. Kumar, M.A. Dar, P. Sharma, D. Varshney, Structural and Raman scattering study of Ni-doped CoFe2O4. AIP Conf. Proc. 1591, 1148–1150 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4872884
R. Pandey, L.K. Pradhan, S. Kumar, M. Kar, Crystal structure, magnetic and dielectric properties of (1–x) BiFe0.80Ti0.20O3–(x)Co0.5Ni0.5Fe2O4 multiferroic composites. J. Alloy. Compd. 762, 668–677 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.05.198
R. Sharma, P. Pahuja, R.P. Tandon, Structural, dielectric, ferromagnetic, ferroelectric and ac conductivity studies of the BaTiO3-CoFe1.8Zn02O4 multiferroic particulate composites. Ceram. Int. 40, 9027–9036 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2014.01.115
S.A. Lokare, D.R. Patil, R.S. Devan, S.S. Chougule, Y.D. Kolekar, B.K. Chougule, Electrical conduction, dielectric behavior and magnetoelectric effect in (x)BaTiO3+ (1–x) Ni0.94Co0.01Mn0.05Fe2O4 ME composites. Mater. Res. Bull. 43, 326–332 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2007.03.004
D.R. Patil, A.D. Sheikh, C.A. Watve, B.K. Chougule, Magnetoelectric properties of ME particulate composites. J. Mater. Sci. 43, 2708–2712 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-008-2456-x
A. Sharma, R.K. Kotnala, N.S. Negi, Observation of multiferroic properties and magnetoelectric effect in (x)CoFe2O4-(1–x)Pb0.7Ca0.3TiO3 composites. J. Alloy. Compd. 582, 628–634 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.08.087
X.G. Tang, K.H. Chew, H.L.W. Chan, Diffuse phase transition and dielectric tunability of Ba(Zry, Ti1-y)O3 relaxor ferroelectric ceramics. Acta Mater. 52, 5177–5183 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2004.07.028
R. Gao, Q. Zhang, Z. Xu, Z. Wang, G. Chen, X. Deng, C. Fu, W. Cai, A comparative study on the structural, dielectric and multiferroic properties of Co0.6Cu0.3Zn0.1Fe2O4/Ba0.9Sr0.1Zr0.1Ti09O3 composite ceramics. Compos. Part B-Eng. 166, 204–212 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2018.12.010
D.D. Dung, N.H. Tuan, N.D. Quan, N.Q. Huy, C.T.T. Trang, N.H. Linh, N.H. Thoan, N.N. Trung, N.T. Trang, L.H. Bac, Biferroic properties in Co-doped 0.2BaZrO3–0.8BaTiO3 materials. Res. Phys. 19, 103535 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2020.103535
B.G. Ghule, N.M. Shinde, S.D. Raut, S.K. Gore, S.F. Shaikh, S.U. Ekar, M. Ubaidullah, J.J. Pak, R.S. Mane, Self-assembled α-Fe2O3-GO nanocomposites: studies on physical, magnetic and ammonia sensing properties. Mater. Chem. Phys. 278, 125617 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2021.125617
J. Rani, K.L. Yadav, S. Prakash, Dielectric and magnetic properties of xCoFe2O4-(1 - X)[0.5Ba(Zr0.2Ti0.8)O3–05(Ba0.7Ca0.3)TiO3] composites. Mater. Res. Bull. 60, 367–375 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2014.09.013
G. Catalan, Magnetocapacitance without magnetoelectric coupling. Appl. Phys. Lett. (2006). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2177543
S.M. Salunkhe, S.R. Jigajeni, M.M. Sutar, A.N. Tarale, P.B. Joshi, Magnetoelectric and magnetodielectric effect in CFMO-PBT nanocomposites. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 74, 388–394 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2012.10.003
P. Pan, J. Tao, F. Ma, N. Zhang, Magnetodielectric effect in (1–x) (Ba0.88Ca0.12)(Ti0.88Zr0.12)O3− xCoFe2O4. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 453, 91–95 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2017.12.107
R. Rakhikrishna, J. Isaac, J. Philip, Magneto-electric coupling in multiferroic nanocomposites of the type x (Na0.5K0.5)094Li0.06NbO3- (1–x)CoFe2O4: role of ferrite phase. Ceram. Int. 43, 664–671 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.09.212
Funding
This work was supported by the Korea Institute for Advancement of Technology (KIAT) grant funded by the Korea Government (Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy-MOTIE) (P0012770) and (N000OOOO). This study was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF-2020R1A2C1015206).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SMM: Conceptualization, experimental, data creation, and analysis, Investigation, Writing—original draft, revision, and editing, AMT: Data curation, Formal analysis, Resources. SAB: Formal analysis, Resources. NTT: Data curation, Resources, Analysis, Software, Writing—original draft, revision. ANT: Formal analysis, Resources, Visualization. PMT: Data curation, Formal analysis, Visualization. SBK: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Resources, Writing—original draft, Validation. JCS: Investigation, Project administration, supervision, Writing—original draft. JL: Formal analysis, Supervision, Writing—original draft, Validation, Visualization, Project administration.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mane, S.M., Teli, A.M., Beknalkar, S.A. et al. Room-temperature multiferroic (magnetoelectric–magnetodielectric) coupling properties of hybrid microwave-sintered (1 − x)BaZr0.25Ti0.75O3 − xCo0.9Ni0.1Fe2O4 lead-free electromagnetic composites. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 34, 1863 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-11236-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-11236-6