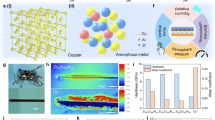
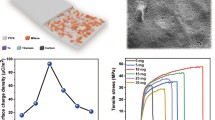
Abstract
Herein, a novel triboelectric nanogenerator (TENG) based on fluorine tin oxide (FTO) as substrate, metallic copper (Cu), and Polydimethyl siloxane (PDMS) as transparent and flexible polymer materials with spray pyrolysis of gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) has been synthesized and characterized having dimensions of 1.5 × 1.5 cm. The spherical shaped synthesized AuNPs have been observed within the morphological images. The x-ray diffraction pattern of the prepared material shows an accurate diffraction peaks at 2theta values indicating the presence of mixed phases of FTO, Cu, AuNPs, and PDMS which are in excellent agreement with the previously mentioned 2theta values in the literature. Further, the energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS) analysis confirms the presence of Cu, gold (Au), oxygen (O), tin (Sn), carbon (C) and silicon (Si) materials within the synthesized TENG. Finally, the synthesized PDMS-based TENG produces maximum AC output voltage and current up to ~ 56 V and ~ 18mA, respectively with very high transmittance of 92.85% along with a transferred electric charge of ~ 18nC, current density of ~ 8 mA/cm2, an output power of ~ 1 W, and a surface power density of ~ 448mW/cm2 with resistance of 3 KΩ. The TENG device is further connected with a bridge-type rectifier circuit to glow LEDs as well as serve as a platform for flexible and wearable electronic devices.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data produced during the experiments are available within the manuscript.
References
T.C. Hou, Y. Yang, H. Zhang, J. Chen, L.J. Chen, Z.L. Wang, Triboelectric nanogenerator built inside shoe insole for harvesting walking energy. Nano Energy. 2(5), 856–862 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2013.03.001
G. Zhu, J. Chen, Y. Liu, P. Bai, Y.S. Zhou, Q. Jing, C. Pan, Z.L. Wang, Linear-grating triboelectric generator based on sliding electrification. Nano Lett. 13(5), 2282–2289 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1021/nl4008985
F. Mugele, Baret electrowetting: from basics to applications. J. Phys. 17(28), R705–R774 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1088/0953-8984/17/28/r01
Y. Chen, J. Au, P. Kazlas, A. Ritenour, H. Gates, M. McCreary, Flexible active-matrix electronic ink display. Nature. 423(6936), 136–136 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/423136a
S. Kim, H.J. Kwon, S. Lee, H. Shim, Y. Chun, W. Choi, J. Kwack, D. Han, M. Song, S. Kim, S. Mohammadi, I. Kee, Low-power flexible organic light-emitting diode display device. Adv. Mater. 23(11), 3511–3516 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201101066
B. Yoon, D.Y. Ham, O. Yarimaga, H. An, C.W. Lee, J.M. Kim, Inkjet printing of conjugated polymer precursors on paper substrates for colorimetric sensing and flexible electrothermochromic display. Adv. Mater. 23(46), 5492–5497 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201103471
H.H. Chou, A. Nguyen, A. Chortos, J.W.F. To, C. Lu, J. Mei, T. Kurosawa, W.G. Bae, J.B.H. Tok, Z. Bao, A chameleon-inspired stretchable electronic skin with interactive colour changing controlled by tactile sensing. Nat. Commun. 6(1), 8011 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms9011
T. Zhou, C. Zhang, C.B. Han, F.R. Fan, W. Tang, Z.L. Wang, Woven structured triboelectric nanogenerator for wearable devices. ACS Appl. Mater. Interface. 6(16), 14695–14701 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1021/am504110u
Y. Yang, H. Zhang, Z.H. Lin, Y.S. Zhou, Q. Jing, Y. Su, J. Yang, J. Chen, C.C. Hu, Z.L. Wang, Human skin based triboelectric nanogenerators for harvesting biomechanical energy and as self-powered active tactile sensor system. ACS Nano 7(10), 9213–9222 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1021/nn403838y
Z.L. Wang, Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016, pp.1–99
S. Pan, Z. Zang, Fundamental theories and basic principles of triboelectric effect. Rev. Frict. 7, 2–17 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40544-018-0217-7
L.S. McCarty, G.M. Whitesides, Electrostatic charging due to separation of ions at interfaces: contact electrification of ionic electrets Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 47(12), 2188–2207 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.200701812
K. Friedrich, Polymer composites for tribological applications. Adv. Ind. Eng. Polym. Res. 1, 3–39 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aiepr.2018.05.001
S.J. Peng, F.Y. Cheng, J. Liang, Z.L. Tao, J. Chen, Facile solution-controlled growth of CuInS2 thin films on FTO and TiO2/FTO glass substrates for photovoltaic application. J. Alloys Compd. Alloys Comp. 481(1–2), 786–791 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2009.03.084
B.G. Lewis, D.C. Paine, M.R.S. Bull, Applications and processing of transparent conducting oxides. MRS Bull. 25(08), 22–27 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1557/mrs2000.147
N.F. Ren, L.J. Huang, M. Zhou, B.J. Li, Introduction of Ag nanoparticles and AZO layer to prepare AZO/Ag/FTO trilayer films with high overall photoelectric properties. Ceram. Int. 40(6), 8693–8699 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2014.01.087
F.R. Fan, J.J. Luo, W. Tang, C.Y. Li, C.P. Zhang, Z.Q. Tian, Z.L. Wang, Highly transparent and flexible triboelectricnanogenerator: performance improvements and fundamental mechanisms. J. Mater. Chem. A 2, 13219–13225 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1021/nn507221f
W. Seung, M.K. Gupta, K.Y. Lee, K.S. Shin, J.H. Lee, T.Y. Kim, S. Kim, J.J. Lin, J.H. Kim, S.W. Kim, Nano patterned textile-based wearable triboelectric nanogenerator. ACS Nano. 9, 3501–3509 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1021/nn507221f
S.H. Lee, Y.H. Ko, J.S. Yu, Facile fabrication and characterization of arch-shaped triboelectric nanogenerator with a graphite top electrode. Phys. Status Solidi. A 212, 401–405 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1002/pssa.201431480
L. Zhao, J. Duan, L. Liu, J. Wang, Y. Duan, L. Vaillant-Roca, X. Yang, Q. Tang, Boosting power conversion efficiency by hybrid triboelectric nanogenerator/silicon tandem solar cell toward rain energy harvesting. Nano Energy. 82, 105773 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2021.105773
Y. Liu, N. Sun, J. Liu, Z. Wen, X. Sun, S.-T. Lee, B. Sun, Integrating a silicon solar cell with a triboelectric nanogenerator via a mutual electrode for harvesting energy from sunlight and raindrops. ACS Nano 12(3), 2893–2899 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.8b00416
G. Presnova, D. Presnov, V. Krupenin, Biosensors based on a silicon nanowire field–effect transistor functionalized by gold nanoparticles for the highly sensitive determination of prostate specified antigen. Biosens. Bioelectron. 88, 283–289 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2016.08.054
H. Xiaopei, Y. Zhang, T. Ding, J. Liu, H. Zhao, Multifunctional gold nanoparticles: a novel nanomaterial for various medical applications and biological activities Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. (2020). https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2020.00990
G. Alberti, C. Zanoni, L.R. Magnaghi, R. Biesuz, Gold and silver nanoparticles-based calorimetric sensors new trends and applications. Chemosensors. 9(11), 305 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9110305
A. Sahai, N. Goswami, S.D. Kaushik, S. Tripathi, Cu2O/CuO nanoparticles: novel synthesis by exploding wire technique and extensive characterization. Appl. Surf. Sci. 390, 974–983 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.09.005
A. Aravinthan, S.K. Kannan, M. Govarthanan, J.H. Kim, Accumulation of biosynthesized gold nanoparticles and its impact on various organs of sprague dawley rats: a systematic study. Toxicol. Res. 5(6), 1530–1538 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/c6tx00202a
J. Zhu, P. Zhu, Q. Yang, T. Chen, J. Wang, J. Li, A fully stretchable textile-based triboelectric nanogenerator for human motion monitoring. Mater. Lett. 280, 128568 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2020.128568
Funding
The financial assistance received under RUSA 2.0 grant by the University of Jammu is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ASS—Material preparation, data collection, formal analysis, and the writing of the first draft of the manuscript. DA—contributed to the experimentation, data collection, and formal analysis. RV—Conceptualization, Writing—Review and Editing, Project administration, Funding acquisition, Supervision. NBC—Conceptualization, Writing—Review and Editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that there exists no conflict of financial or non-financial interests related to the work submitted for publication.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sambyal, A.S., Anand, D., Vaid, R. et al. Synthesis and characterization of power efficient triboelectric nanogenerator based on contact-separation mode using spray pyrolysis. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 34, 1458 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-10891-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-10891-z