Abstract
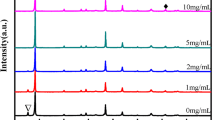
In this paper, we have shown that Sb has been doped into the light-absorbing methylammonium lead iodide (CH3NH3PbI3) perovskite. We had anticipated that the introduction of antimony (Sb3+) as a dopant in perovskite would result in improved light-absorbing properties for use in photovoltaic cells, including longer carrier lifetimes and an ideal band gap. We used a simplified and cost-effective method to fabricate thin films of CH3NH3PbI3 perovskite doped with antimony, which were deposited onto cleaned FTO substrates using a modified two-step spin-coating process. To evaluate the characteristics of these films, we utilized three different techniques: XRD, SEM, and UV-Vis spectroscopy to analyze their structural, optical, and dielectric properties. It was discovered that the optical band gap varied with Sb-doping concentration. The XRD data showed that there were no additional peaks, suggesting that Sb was able to partially replace Pb2+ successfully. However, the crystallinity increased with doping up to 1.0%, but decreased at higher concentrations. This finding aligns with the SEM morphology of the resulting films, which exhibited regular crystallites on a more even, compact, and complete surface. Finally, the IV curve showed improvement in the performance of the fabricated PSCs by increasing the Sb-doping ratio until 2.0% but decreased at the high concentration of 3.0%.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request. All authors are declared that all data and materials as well as software application or custom code support their published claims and comply with field standards.
References
S. Colella, E. Mosconi, P. Fedeli, A. Listorti, F. Gazza, F. Orlandi, P. Ferro, T. Besagni, A. Rizzo, G. Calestani, G. Gigli, F. De Angelis, R. Mosca, MAPbI3−xClx mixed halide perovskite for hybrid solar cells: the role of chloride as dopant on the transport and structural properties. Chem. Mater. 25(22), 4613–4618 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1021/cm402919x
M.A. Green, A. Ho-Baillie, H.J. Snaith, The emergence of perovskite solar cells. Nat. Photonics 8(7), 506–514 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/nphoton.2014.134
Y. Jiang, M.A. Green, R. Sheng, A. Ho-Baillie, Room temperature optical properties of organic–inorganic lead halide perovskites. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 137, 253–257 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solmat.2015.02.017
J.S. Yeo, R. Kang, S. Lee, Y.J. Jeon, N. Myoung, C.L. Lee, D.Y. Kim, J.M. Yun, Y.H. Seo, S.S. Kim, S.I. Na, Highly efficient and stable planar perovskite solar cells with reduced graphene oxide nanosheets as electrode interlayer. Nano Energy 12, 96–104 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2014.12.022
P. Qin, S. Tanaka, S. Ito, N. Tetreault, K. Manabe, H. Nishino, M.K. Nazeeruddin, M. Grätzel, Inorganic hole conductor-based lead halide perovskite solar cells with 12.4% conversion efficiency. Nat. Commun. 5(1), 3834 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms4834
X. Fan, X. Peng, S. Zhang, Y. Xiang, Fabrication of planar heterojunction perovskite solar cells, in 2014 International Symposium on Next-Generation Electronics (ISNE). (IEEE, New York, 2014), pp.1–2
N.G. Park, Perovskite solar cells: an emerging photovoltaic technology. Mater. Today 18(2), 65–72 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mattod.2014.07.007
J. Burschka, N. Pellet, S.J. Moon, R. Humphry-Baker, P. Gao, M.K. Nazeeruddin, M. Grätzel, Sequential deposition as a route to high-performance perovskite-sensitized solar cells. Nature 499(7458), 316–319 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12340
Q. Chen, H. Zhou, Z. Hong, S. Luo, H.S. Duan, H.H. Wang, Y. Liu, G. Li, Y. Yang, Planar heterojunction perovskite solar cells via vapor-assisted solution process. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136(2), 622–625 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1021/ja411509g
M. Liu, M.B. Johnston, H.J. Snaith, Efficient planar heterojunction perovskite solar cells by vapour deposition. Nature 501(7467), 395–398 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12509
T.B. Song, Q. Chen, H. Zhou, C. Jiang, H.H. Wang, Y. Yang, Y. Liu, J. You, Y. Yang, Perovskite solar cells: film formation and properties. J. Mater. Chem. A 3(17), 9032–9050 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/C4TA05246C
H. Chen, Y. Zhan, G. Xu, W. Chen, S. Wang, M. Zhang, Y. Li, Y. Li, Organic N-type molecule: managing the electronic states of bulk perovskite for high-performance photovoltaics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 30(36), 2001788 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202001788
H.S. Kim, C.R. Lee, J.H. Im, K.B. Lee, T. Moehl, A. Marchioro, S.J. Moon, R. Humphry-Baker, J.H. Yum, J.E. Moser, M. Grätzel, N.G. Park, Lead iodide perovskite sensitized all-solid-state submicron thin film mesoscopic solar cell with efficiency exceeding 9%. Sci. Rep. 2(1), 591 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep00591
J.A. Christians, R.C.M. Fung, P.V. Kamat, An inorganic hole conductor for organo-lead halide perovskite solar cells. Improved hole conductivity with copper iodide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136(2), 758–764 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1021/ja411014k
G. Xu, R. Xue, S.J. Stuard, H. Ade, C. Zhang, J. Yao, Y. Li, Y. Li, Reducing energy disorder of hole transport layer by charge transfer complex for high performance p–i–n perovskite solar cells. Adv. Mater. 33(13), 2006753 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202006753
S.Y. Liu, J.W. Jung, C.Z. Li, J. Huang, J. Zhang, H. Chen, A.K.Y. Jen, Three-dimensional molecular donors combined with polymeric acceptors for high performance fullerene-free organic photovoltaic devices. J. Mater. Chem. A 3(44), 22162–22169 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/C5TA06639E
W. Chen, H. Chen, G. Xu, R. Xue, S. Wang, Y. Li, Y. Li, Precise control of crystal growth for highly efficient CsPbI2Br perovskite solar cells. Joule 3(1), 191–204 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joule.2018.10.011
P.P. Boix, S. Agarwala, T.M. Koh, N. Mathews, S.G. Mhaisalkar, Perovskite solar cells: beyond methylammonium lead iodide. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 6(5), 898–907 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1021/jz502547f
J.W. Lee, D.J. Seol, A.N. Cho, N.G. Park, High-efficiency perovskite solar cells based on the black polymorph of HC(NH2)2PbI3. Adv. Mater. 26(29), 4991–4998 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201401137
J.W. Lee, D.H. Kim, H.S. Kim, S.W. Seo, S.M. Cho, N.G. Park, Formamidinium and cesium hybridization for photo- and moisture-stable perovskite solar cell. Adv. Energy Mater. 5(20), 1501310 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1002/aenm.201501310
F.M. Tezel, İA. Kariper, A new approach to prepare polycrystalline PbTe–TeO thin film, and its optical, structural, surface and electrical characterization. Surf. Rev. Lett. 28(04), 2150019 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1142/S0218625X21500190
B.E. Cohen, S. Gamliel, L. Etgar, Parameters influencing the deposition of methylammonium lead halide iodide in hole conductor free perovskite-based solar cells. APL Mater. (2014). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4885548
J. Padchasri, R. Yimnirun, Effects of annealing temperature on stability of methylammonium lead iodide perovskite powders. J. Alloys Compd. 720, 63–69 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.05.170
D. Thakur, J.R. Wu, A. Chandel, K.J. Cheng, S.E. Chiang, K.B. Cai, S.H. Chen, C.C. Yang, Y.L. Zhong, C.T. Yuan, J.L. Shen, S.H. Chang, Structural, optical and excitonic properties of urea grading doped CH3NH3PbI3 thin films and their application in inverted-type perovskite solar cells. J. Alloys Compd. 858, 157660 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.157660
S. Chatterjee, A.J. Pal, Introducing Cu2O thin films as a hole-transport layer in efficient planar perovskite solar cell structures. J. Phys. Chem. C 120(3), 1428–1437 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.5b11540
F. Meydaneri Tezel, F.N. Güven, İA. Kariper, Production and characterization of Cu-doped perovskite thin film electrodes for supercapacitors. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 143, 109766 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inoche.2022.109766
F. Meydaneri Tezel, İA. Kariper, A new process to synthesize CrSe thin films with nanosize by CBD method. Mater. Res. Express 6(3), 036412 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/aaf593
Q. Mohsen, O.H. Abd-Elkader, A.E.A. Farouk, H.M.A. Hassan, N.Y. Mostafa, Influence of tungsten substitution on structure, optical, vibrational and magnetic properties of hydrothermally prepared NiFe2O4. Appl. Phys. A: Mater. Sci. Process. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-04452-6
N.Y. Mostafa, A. Badawi, S.I. Ahmed, Influence of Cu and Ag doping on structure and optical properties of In2O3 thin film prepared by spray pyrolysis. Results Phys. 10, 126–131 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2018.05.030
İA. Kariper, T. Özpozan, Optical and electrical properties of nickel xanthate thin films. Bull. Mater. Sci. 37(3), 553–561 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-014-0697-7
A.M. Bolbol, O.H. Abd-Elkader, H. Elshimy, Z.I. Zaki, S.A. Shata, M. Kamel, A.S. Radwan, N.Y. Mostafa, The effect of Zr (IV) doping on TiO2 thin film structure and optical characteristics. Results Phys. 42, 105955 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2022.105955
A. Fakharuddin, F. De Rossi, T.M. Watson, L. Schmidt-Mende, R. Jose, Research update: behind the high efficiency of hybrid perovskite solar cells. APL Mater. 4(9), 091505 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4962143
J.H. Im, C.R. Lee, J.W. Lee, S.W. Park, N.G. Park, 6.5% efficient perovskite quantum-dot-sensitized solar cell. Nanoscale 3(10), 4088–4093 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1039/C1NR10867K
İA. Kariper, Optical and structural properties of PbI2 thin film produced via chemical dipping method. Opt. Rev. 23(3), 401–408 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10043-016-0218-6
I.A. Kariper, Pb-Ag/I thin film by co-precipitation method. Iran. J. Sci. Technol. Trans. A: Sci. 40(2), 137–143 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40995-016-0017-8
A. Badawi, E.M. Ahmed, N.Y. Mostafa, F. Abdel-Wahab, S.E. Alomairy, Enhancement of the optical and mechanical properties of chitosan using Fe2O3 nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 28(15), 10877–10884 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-6866-x
A. Badawi, S.S. Alharthi, N.Y. Mostafa, M.G. Althobaiti, T. Altalhi, Effect of carbon quantum dots on the optical and electrical properties of polyvinylidene fluoride polymer for optoelectronic applications. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-019-3160-1
S. Tolansky, Multiple-Beam Interferometry Surface and Films, vol. 76 (Oxford Univesity Press, London, 1978)
A. Badawi, S.S. Alharthi, N.Y. Mostafa, M.G. Althobaiti, T. Altalhi, Effect of carbon quantum dots on the optical and electrical properties of polyvinylidene fluoride polymer for optoelectronic applications. Appl. Phys. A 125(12), 858 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-019-3160-1
S.M.H. Qaid, M.S. Al Sobaie, M.A. Majeed Khan, I.M. Bedja, F.H. Alharbi, M.K. Nazeeruddin, A.S. Aldwayyan, Band-gap tuning of lead halide perovskite using a single step spin-coating deposition process. Mater. Lett. 164, 498–501 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2015.10.135
H. Tian, L. Hu, C. Zhang, S. Chen, J. Sheng, L. Mo, W. Liu, S. Dai, Enhanced photovoltaic performance of dye-sensitized solar cells using a highly crystallized mesoporous TiO2 electrode modified by boron doping. J. Mater. Chem. 21(3), 863–868 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1039/C0JM02941F
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the Researchers Supporting Project number (RSP2023R468), King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia for supporting this work.
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by AMB, OHA, HE and SAS. All authors reviewed the data and provided suggestions. The first draft of the manuscript was written by AB and critically reviewed and commented on previous versions of the manuscript by [NYM] and [MK]. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Ethical approval
The authors declare that they guarantee the compliance with ethical standards.
Informed consent
We confirm that all authors mentioned in the manuscript have participated in, read, and approved the manuscript, and have given their consent for the submission and subsequent publication of the manuscript.
Consent for publication
We confirm that all the authors mentioned in the manuscript have agreed to publish this paper.
Research involving human participants or animals
This paper contains no research involving human participants and/or animals.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bolbol, A.M., Elshimy, H., Abd-Elkader, O.H. et al. Structure and optical properties of Sb-doped CH3NH3PbI3: effect on perovskite solar cell performance. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 34, 1489 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-10885-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-10885-x