Abstract
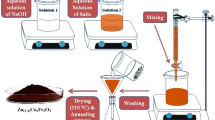
Cerium-doped zinc spinel ferrite (ZnCexFe2−xO4) nanoparticles with x = 0.00–0.20 were synthesized via sol–gel method and annealed at 600 °C for 3 h. The existence of FCC spinel phase with secondary phase of the prepared samples was confirmed by the XRD pattern. The crystallite size was estimated by Williamson–Hall, Scherrer’s formula, modified Scherrer’s formula, and size strain plot found in the range of 12–19 nm. Scanning Electron Microscopy showed nonuniform and nonspherical grains distribution in the samples. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy confirmed the existence of two characteristic absorption bands in the samples. Complex impedance, complex dielectric constant, tangent loss, AC conductivity, and complex electric modulus were determined in the 1 MHz to 3 GHz frequency range. It is found that dielectric constant almost remains constant up to 1.4 GHz and after that relaxation peaks are observed. Vibrating sample magnetometry showed that saturation magnetization decreased by 44.37%. Low dielectric losses at high frequencies made them good contestants for microwave devices.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
M. Amiri, M. Salavati-Niasari, A. Akbari, Magnetic nanocarriers: evolution of spinel ferrites for medical applications. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 265, 29–44 (2019)
J.K. Khan et al., Properties of Al3+ substituted nickel ferrite (NiAlxFe2−xO4) nanoparticles synthesised using wet sol–gel auto-combustion. J. Sol–gel Sci. Technol. 1, 1–12 (2020)
S. Gul et al., Al-substituted zinc spinel ferrite nanoparticles: preparation and evaluation of structural, electrical, magnetic and photocatalytic properties. Ceram. Int. 46(9), 14195–14205 (2020)
G. Mustafa et al., Dielectric, impedance, and modulus spectroscopic studies of lanthanum-doped nickel spinel ferrites NiLaxFe2−xO4 nanoparticles. J. Sol–gel Sci. Technol. 1, 1–10 (2020)
C. Chinnasamy et al., The influence of Fe3+ ions at tetrahedral sites on the magnetic properties of nanocrystalline ZnFe2O4. Mater. Sci. Eng.: A 304, 983–987 (2001)
T. Sato et al., Morphology and magnetic properties of ultrafine ZnFe2O4 particles. Appl. Phys. A 50(1), 13–16 (1990)
L. Raghavan et al., Room temperature ferrimagnetism and low temperature disorder effects in zinc ferrite thin films. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 385, 265–271 (2015)
S. Aslam et al., Structural, optical and magnetic elucidation of co-doping of Nd3+ and Pr3+ on lithium nanoferrite and its technological application. Res. Phys. 12, 1334–1339 (2019)
Y. Yang et al., Synthesis of nonstoichiometric zinc ferrite nanoparticles with extraordinary room temperature magnetism and their diverse applications. J. Mater. Chem. C 1(16), 2875–2885 (2013)
I. Ahmad et al., Fabrication of highly resistive La–Zn co-substituted spinel strontium nanoferrites for high frequency devices applications. Mater. Chem. Phys. 259, 124031 (2021)
S. Mansour, M. Elkestawy, A comparative study of electric properties of nano-structured and bulk Mn–Mg spinel ferrite. Ceram. Int. 37(4), 1175–1180 (2011)
L.Y. Matzui et al., Functional magnetic composites based on hexaferrites: correlation of the composition, magnetic and high-frequency properties. Nanomaterials. 9(12), 1720 (2019)
P.-J. Wang et al., Ultrahigh enhancement rate of the energy density of flexible polymer nanocomposites using core–shell BaTiO3@MgO structures as the filler. J. Mater. Chem. A 8(22), 11124–11132 (2020)
F.A. Sheikh et al., Effects of bismuth on structural and dielectric properties of cobalt–cadmium spinel ferrites fabricated via micro-emulsion route. Chin. Phys. B 28(8), 088701 (2019)
X. Wu et al., Enhanced infrared radiation properties of CoFe2O4 by single Ce3+-doping with energy-efficient preparation. Ceram. Int. 40(4), 5905–5911 (2014)
M. Kamran, M. Anis-ur-Rehman, Enhanced transport properties in ce doped cobalt ferrites nanoparticles for resistive RAM applications. J. Alloys Compd. 822, 153583 (2020)
M. Mahmoud, M. Abd-Elrahman, Infrared investigations of Cu–Zn ferrite substituted with rare earth ions. Mater. Lett. 73, 226–228 (2012)
M. Khalid et al., Aluminum substitution in Ni–Co based spinel ferrite nanoparticles by sol–gel auto-combustion method. J. Electron. Mater. 50(6), 3302–3311 (2021)
T. Tatarchuk et al., Synthesis, morphology, crystallite size and adsorption properties of nanostructured Mg–Zn ferrites with enhanced porous structure. J. Alloys Compd. 819, 152945 (2020)
A.K. Zak et al., X-ray analysis of ZnO nanoparticles by Williamson–Hall and size–strain plot methods. Solid State Sci. 13(1), 251–256 (2011)
A. Ghasemi, M. Mousavinia, Structural and magnetic evaluation of substituted NiZnFe2O4 particles synthesized by conventional sol–gel method. Ceram. Int. 40(2), 2825–2834 (2014)
Z.A. Gilani et al., Impacts of neodymium on structural, spectral and dielectric properties of LiNi0.5Fe2O4 nanocrystalline ferrites fabricated via micro-emulsion technique. Phys. E: Low-Dimens. Syst. Nanostruct. 73, 169–174 (2015)
K. Shahzadi et al., Impact of aluminum substitution on the structural and dielectric properties of Ni–Cu spinel ferrite nanoparticles synthesized via sol–gel route. Opt. Quant. Electron. 52(4), 1–17 (2020)
A.E. Vladár, V.-D. Hodoroaba, Chap. 2.1.1—characterization of nanoparticles by scanning electron microscopy, characterization of nanoparticles (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2020), pp.7–27
M. Naveed et al., Characterization and evaluation of the antioxidant, antidiabetic, anti-inflammatory, and cytotoxic activities of silver nanoparticles synthesized using Brachychiton populneus leaf extract. Processes 10(8), 1521 (2022)
M.N. Akhtar, M.A. Khan, Effect of rare earth doping on the structural and magnetic features of nanocrystalline spinel ferrites prepared via sol–gel route. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 460, 268–277 (2018)
M.A. Almessiere et al., Structural, magnetic, and Mossbauer parameters’ evaluation of sonochemically synthesized rare earth Er3+ and Y3+ ions-substituted manganese–zinc nanospinel ferrites. ACS Omega 6(34), 22429–22438 (2021)
J. Massoudi et al., Magnetic and spectroscopic properties of Ni–Zn–Al ferrite spinel: from the nanoscale to microscale. RSC Adv. 10(57), 34556–34580 (2020)
J. Ahmad et al., A facile strategy for the preparation of bismuth ferrite nanoparticles: influence of calcination temperature on structural, dielectric, and morphological characteristics. Colloids Surf. A 628, 127328 (2021)
T. Zeeshan et al., Structural, optical, magnetic and (Y–K) angle studies of CdxCo1−xCr0.5Fe1.5O4 ferrite. Ceram. Int. 46(3), 3935–3943 (2020)
G. Nabi et al., Role of cerium-doping in CoFe2O4 electrodes for high performance supercapacitors. J. Energy Storage. 29, 101452 (2020)
Y. Slimani et al., Magneto-optical and microstructural properties of spinel cubic copper ferrites with Li–Al co-substitution. Ceram. Int. 44(12), 14242–14250 (2018)
M. Junaid et al., Structural, spectral, dielectric and magnetic properties of Tb–Dy doped Li–Ni nano-ferrites synthesized via micro-emulsion route. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 419, 338–344 (2016)
C. Koops, On the dispersion of resistivity and dielectric constant of some semiconductors at audiofrequencies. Phys. Rev. 83(1), 121 (1951)
A. Selmi et al., Synthesis, structural and complex impedance spectroscopy studies of Ni0.4Co0.4Mg0.2Fe2O4 spinel ferrite. Phase Trans. 90(10), 942–954 (2017)
S. Mandal et al., Frequency and temperature dependence of dielectric and electrical properties of TFe2O4 (T = ni, zn, Zn0.5Ni0.5) ferrite nanocrystals. J. Alloys Compd. 656, 887–896 (2016)
M.A. Rahman, A.A. Hossain, Electrical transport properties of Mn–Ni–Zn ferrite using complex impedance spectroscopy. Phys. Scr. 89(2), 025803 (2014)
S. Karmakar, H.S. Mohanty, P.D.J.T.E.P.J. Behera, Exploration of alternating current conduction mechanism and dielectric relaxation with Maxwell-Wagner effect in NiO–CdO–Gd 2O3 nanocomposites. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 136, 1–21 (2021)
J. Ghodake et al., Electric properties of Co substituted Ni–Zn ferrites. J. Alloys Compd. 486(1–2), 830–834 (2009)
A. Radoń et al., Electrical conduction mechanism and dielectric properties of spherical shaped Fe3O4 nanoparticles synthesized by co-precipitation method. Materials. 11(5), 735 (2018)
H.S. Aziz et al., Evaluation of electrical, dielectric and magnetic characteristics of Al–La doped nickel spinel ferrites. RSC Adv. 6(8), 6589–6597 (2016)
H.M.T. Farid et al., Structural and dielectric properties of copper-based spinel ferrites. Eur. Phys. J. Plus. 133(2), 1–12 (2018)
R. Tang et al., Dielectric relaxation, resonance and scaling behaviors in Sr3Co2Fe24O41 hexaferrite. Sci. Rep. 5(1), 1–11 (2015)
G. Mustafa et al., Lanthanum doped manganese–zinc spinel ferrite nanoparticles for microwave and soft magnet applications. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 34(4), 249 (2023)
N. Singh, A. Agarwal, S. Sanghi, Dielectric relaxation, conductivity behavior and magnetic properties of mg substituted Zn–Li ferrites. Curr. Appl. Phys. 11(3), 783–789 (2011)
G. Asghar, M. Anis-ur-Rehman, Structural, dielectric and magnetic properties of Cr–Zn doped strontium hexa-ferrites for high frequency applications. J. Alloys Compd. 526, 85–90 (2012)
M. Farid et al., Electric modulus properties of praseodymium substituted copper ferrites. J. Ovon. Res. 12(3), 1 (2016)
V. Harris et al., Cation distribution in NiZn-ferrite films via extended x‐ray absorption fine structure. Appl. Phys. Lett. 68(15), 2082–2084 (1996)
S.A. Morrison et al., Magnetic and structural properties of nickel zinc ferrite nanoparticles synthesized at room temperature. J. Appl. Phys. 95(11), 6392–6395 (2004)
P. Priyadharsini et al., Structural, spectroscopic and magnetic study of nanocrystalline Ni–Zn ferrites. Mater. Chem. Phys. 116(1), 207–213 (2009)
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, Grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZK: Conceptualization, Methodology, Formal analysis, Investigation, Writing—original draft. MK: Conceptualization, Resources, Supervision, Formal analysis, Writing—review & editing. JKK: Investigation, Formal analysis, Writing—review & editing. MGBA: Formal analysis, Writing—review & editing. SJA: Resources, Formal analysis, Writing—review & editing. SN: Formal analysis, Writing—review & editing. KN: Funding acquisition, Writing—review & editing. SZA: Funding acquisition, Writing—review & editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors have no relevant financial or nonfinancial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, Z., Khalid, M., Khan, J.K. et al. Dielectric, impedance, and modulus spectroscopic studies of cerium-doped zinc spinel ferrite ZnCexFe2−xO4 nanoparticle. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 34, 1439 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-10861-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-10861-5