Abstract
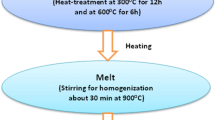
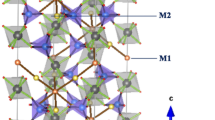
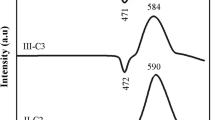
Many technologies have applied sodium ions’ solid electrolytes, ranging from batteries to chemical sensors. This study investigated phosphate glasses featuring electrolyte developed through the 20Na2O–(50 − x)Na2WO4–xTiO2–30P2O5 system (with 0 ≤ x ≤ 25 mol%), with the melt-quenching approach employed. For the estimation of the activation energy, differential scanning calorimetry was utilized, whereby crystallization (Ec) was relied upon. Ec = 144.77 kJ/mol characterized the glass (x = 5). The determination of the crystallization mechanism was possible through the Avrami parameter (n), which was found to be approximately ≈ 2; therefore, the crystallization mechanism was expected to be a periodic landscape that is one-dimensional in nature. The bonds forming the glasses’ framework were shown to be established through the PO4 units, as revealed by Raman spectroscopy. TiO2 insertion into the framework of glass resulted in new bond formation, namely P–O–Ti and/or Ti–O–Ti. Shifting the Na2WO4 mol% to TiO2 mol% resulted in the structural units’ transformation into Q2, Q1, and finally Q0 units. Through the durability analysis, the results confirmed that the explored glasses’ dissolution is reliant upon their composition, which is of a glassy nature. There is an increase in durability when Na2WO4 is replaced by TiO2.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
No data were used for the research described in the article.
References
J.W. Fergus, Ion transport in sodium ion conducting solid electrolytes. Solid State Ionics 227, 102–112 (2012)
Y. Wang, S. Song, C. Xu, N. Hu, J. Molenda, L. Lu, Development of solid-state electrolytes for sodium-ion battery—a short review. Nano Mater. Sci. 1(2), 91–100 (2019)
Z. Yan, Y. Liang, J. Xiao, W. Lai, W. Wang, Q. Xia et al., A high-kinetics sulfur cathode with a highly efficient mechanism for superior room-temperature Na–S batteries. Adv. Mater. 32(8), 1906700 (2020)
H.A. Thabit, N.A. Kabir, N.M. Ahmed, Synthesis and thermoluminescence characteristics and structural and optical studies of ZnO/Ag/ZnO system for dosimetric applications. J. Lumin. 236, 118097 (2021)
P.J. Melling, A.R. Allnatt, Modelling of leaching and corrosion of glass. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 42(1–3), 553–559 (1980)
E. Fernández, F.J. Gil, M.P. Ginebra, F.C.M. Driessens, J.A. Planell, S.M. Best, Calcium phosphate bone cements for clinical applications. Part I: solution chemistry. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 10, 169–176 (1999)
H. Ebendorff-Heidepriem, W. Seeber, D. Ehrt, Dehydration of phosphate glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 163(1), 74–80 (1993)
M.R. Reidmeyer, D.E. Day, Phosphorus oxynitride glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 181(3), 201–214 (1995)
L. Pascual, A. Durán, Nitridation of glasses in the system R2O-MO-P2O5. Mater. Res. Bull. 31(1), 77–95 (1996)
A. Le Sauze, R. Marchand, Chemically durable nitrided phosphate glasses resulting from nitrogen/oxygen substitution within PO4 tetrahedra. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 263, 285–292 (2000)
H.A. Abo-Mosallam, Influences of SrO on the structure, thermo-physical and chemical properties of zinc iron borophosphate glasses as host matrices for radioactive waste. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 571, 121084 (2021)
S.V. Pershina, B.D. Antonov, I.I. Leonidov, Effect of MoO3 on structural, thermal and transport properties of lithium phosphate glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 569, 120944 (2021)
A. Ibrahim, M.S. Sadeq, Influence of cobalt oxide on the structure, optical transitions and ligand field parameters of lithium phosphate glasses. Ceram. Int. 47(20), 28536–28542 (2021)
H. Es-Soufi, L. Bih, Effect of TiO2 on the chemical durability and optical properties of Mo-based phosphate glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 558, 120655 (2021)
H.A. Thabit, N.A. Kabir, N.M. Ahmed, Synthesis & thermoluminescence characteristics & structural and optical studies of ZnO/Ag/ZnO system for dosimetric applications. J. Lumin. 236, 118097 (2021)
H. Segawa, N. Akagi, T. Yano, S. Shibata, Properties and structures of TiO2–ZnO–P2O5 glasses. J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn. 118(1376), 278–282 (2010)
H. Es-soufi, L. Ouachouo, M.I. Sayyed, S. Hashim, H. Bih, L. Bih, Synthesis and investigation of the physical, structural, and radiation shielding properties of the titano-bismuth phosphate glasses. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 34(12), 1040 (2023)
I. Mimouni, A. Bouziani, Y. Naciri, M. Boujnah, M.A. El Belghiti, M. El Azzouzi, Effect of heat treatment on the photocatalytic activity of α-Fe2O3 nanoparticles: towards diclofenac elimination. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 29, 7984–7996 (2021)
D.S. Brauer, Bioactive glasses—structure and properties. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 54(14), 4160–4181 (2015)
A. Kiani, N.J. Lakhkar, V. Salih, M.E. Smith, J.V. Hanna, R.J. Newport et al., Titanium-containing bioactive phosphate glasses. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 370(1963), 1352–1375 (2012)
E.A. Abou Neel, W. Chrzanowski, J.C. Knowles, Effect of increasing titanium dioxide content on bulk and surface properties of phosphate-based glasses. Acta Biomater. 4(3), 523–534 (2008)
T. Kasuga, Y. Abe, Calcium phosphate invert glasses with soda and titania. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 243(1), 70–74 (1999)
M. Kaur, A. Singh, V. Thakur, L. Singh, Effect of TiO2 substitution on optical and structural aspects of phosphate glasses. J. Mol. Struct. 1089, 95–101 (2015)
M. Ataalla, A.S. Afify, M. Hassan, M. Abdallah, M. Milanova, H.Y. Aboul-Enein, A. Mohamed, Tungsten-based glasses for photochromic, electrochromic, gas sensors, and related applications: a review. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 491, 43–54 (2018)
H. Es-Soufi, L. Bih, A.R. Lima, A. El Bouari, B. Manoun, S. Hussain, Investigation DSC and XRD on the crystallization kinetics in the phosphate Li2O–Li2WO4–TiO2–P2O5 glassy ionic system. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. (2021). https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-190511/v1
M. Nalin, G. Poirier, S.J.L. Ribeiro, Y. Messaddeq, L. Cescato, Glasses in the SbPO4–WO3 system. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 353(16–17), 1592–1597 (2007)
D. Boudlich, L. Bih, M.E.H. Archidi, M. Haddad, A. Yacoubi, A. Nadiri, B. Elouadi, Infrared, Raman, and electron spin resonance studies of vitreous alkaline tungsten phosphates and related glasses. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 85(3), 623–630 (2002)
K.C. Sekhar, A. Hameed, N. Narsimlu, J.S. Alzahrani, M.A. Alothman, I.O. Olarinoye et al., Synthesis, optical, structural, and radiation transmission properties of PbO/Bi2O3/B2O3/Fe2O3 glasses: an experimental and in silico study. Opt. Mater. 117, 111173 (2021)
H. Es-soufi, L. Bih, Synthesis, characterization, and optical properties of titano-molybdenum phosphate glasses. J. Electron. Mater. 51(5), 2528–2544 (2022)
A. Rezikyan, G.G. Moore, Fluctuation electron microscopy study of crystal nucleation in TiO2–SiO2 glass with heat treatment. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 32(48), 485402 (2020)
H.A. Thabit, A.K. Ismail, M.I. Sayyed, H. Es-soufi, Preparation, characterization, and mechanical-optical properties of telluro-borate glasses containing tungsten. Ceram. Int. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2023.05.185
R. Pagoti, S. Panda, V. Patchapureddy, R.K. Padhi, B. Subramanian, H. Jena, B.S. Panigrahi, Structural and spectroscopic investigations of neodymium-doped strontium borophosphate glass. Luminescence 36(7), 1706–1715 (2021)
M. Nagarjuna, T. Satyanarayana, Y. Gandhi, N. Veeraiah, Influence of Ag2O on some physical properties of LiF–TiO2–P2O5 glass system. J. Alloys Compd. 479(1–2), 549–556 (2009)
R.K. Brow, D.R. Tallant, S.T. Myers, C.C. Phifer, The short-range structure of zinc polyphosphate glass. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 191(1–2), 45–55 (1995)
Z. Černošek, M. Chládková, J. Holubová, The influence of TiO2 on the structure and properties of sodium-zinc phosphate glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 531, 119866 (2020)
F. Delahaye-Carrière, Doctoral dissertation Compiègne (1997)
L. Ma, R.K. Brow, M.E. Schlesinger, Dissolution behavior of Na2O–FeO–Fe2O3–P2O5 glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 463, 90–101 (2017)
M.N. Rahaman, Ceramic Processing and Sintering, 2nd edn. (Marcel Dekker, New York, 2003)
Y. Gu, W. Xiao, L. Lu, W. Huang, M.N. Rahaman, D. Wang, Kinetics and mechanisms of converting bioactive borate glasses to hydroxyapatite in aqueous phosphate solution. J. Mater. Sci. 46, 47–54 (2011)
H. Es-soufi, H. Bih, M. Azrour, B. Manoun, P. Lazor, Structure and some physical properties of the sodium ion conducting glasses inside the Na2O–Na2WO4–TiO2–P2O5 system. J. Appl. Surf. Interfaces (2018). https://doi.org/10.48442/IMIST.PRSM/jasi-v4i1-3.11273
R.N. Oosterbeek, K.I. Margaronis, X.C. Zhang, S.M. Best, R.E. Cameron, Non-linear dissolution mechanisms of sodium calcium phosphate glasses as a function of pH in various aqueous media. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 41(1), 901–911 (2021)
C. Solenn, thèse de doctorat Université Rennes 1 (2016)
N. Mascaraque, A. Durán, F. Muñoz, Effect of fluorine and nitrogen on the chemical durability of lithium phosphate glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 417, 60–65 (2015)
H.E. Kissinger, Differential thermal analysis. J. Res. Natl. Bur. Stand. 57(4), 217 (1956)
J.A. Augis, J.E. Bennett, Calculation of the Avrami parameters for heterogeneous solid state reactions using a modification of the Kissinger method. J. Therm. Anal. 13, 283–292 (1978)
D.R. Lide (ed.), CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (CRC Press, Boca Raton, 2001)
M. Avrami, Kinetics of phase change 1. J. Chem. Phys. 7, 1103 (1939)
M. Avrami, J. Chem. Phys. 8, 212 (1940)
M. Avrami, J. Chem. Phys. 9, 177 (1941)
N. Elkhoshkhany, E. Syala, Kinetic characterization of TeO2–Bi2O3–V2O5–Na2O–TiO2 glass system. Ceram. Int. 43(8), 6156–6162 (2017)
Acknowledgements
M.I. Sayyed and S. Hashim gratefully acknowledge Universiti Teknologi Malaysia for providing Prominent Visiting Researcher Scheme (RJ3000.7113.3F000) initiatives under the Department Deputy of Vice-Chancellor (Research and Innovation).
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by HE, MIS, and LB. The first draft of the manuscript was written by HE and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose. The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article. All authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest or non-financial interest in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript. The authors have no financial or proprietary interests in any material discussed in this article.
Research involving human participants and/or animals
This article does not contain any studies involving human participants performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Es-soufi, H., Sayyed, M.I. & Bih, L. Sodium–tungsten–titanium phosphate glasses: an investigation of the structure, chemical endurance, and kinetic characteristics. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 34, 1355 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-10741-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-10741-y