Abstract
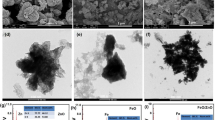
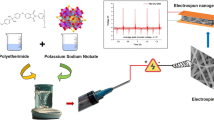
Flexible PVDF-based piezoelectric nanogenerators (PENGs) are promising mechanical energy harvesters for powering wearable devices and portable electronics. In this work, a new hybrid nanocomposite was prepared by coating polyaniline on the surface of halloysite nanotube (HNT@PANI) and PENGs were fabricated by using electrospun nanocomposite fiber mats comprising HNT@PANI and poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF). The rough surface of PANI outer layer and its electronegative properties favors a large interface and a strong interfacial interaction with PVDF matrix, which efficiently improves the β-phase crystal content and the crystallinity of PVDF simultaneously, resulting in an enhanced output performance in the fibrous nanocomposite PENGs. When the nanocomposite fiber mats are composed of 1 wt% HNT@PANI nanoparticles, the open-circuit voltage of the PENG is up to 30 V, which is six times higher than that of pure PVDF, and it can also light up 17 red LEDs. Furthermore, the open-circuit voltage was found unchanged after being subjected to continuous tapping for 5 weeks in the durability test. In addition, the PENG can charge a capacitor to 4.4 V within 60 s. This flexible self-powered PENG with good durability and high outputs has the potential to be used as a self-charging power source and applied in the field of wearable flexible electronic devices.














Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article (and its supplementary information files).
References
M. Abbasipour, R. Khajavi, A.A. Yousefi, M.E. Yazdanshenas, F. Razaghian, A. Akbarzadeh, Improving piezoelectric and pyroelectric properties of electrospun PVDF nanofibers using nanofillers for energy harvesting application. Polym. Adv. Technol. 30(2), 279–291 (2019)
Q. Zhao, L. Yang, K. Chen, Y. Ma, Q. Peng, H. Ji, J. Qiu, Flexible textured MnO2 nanorods/PVDF hybrid films with superior piezoelectric performance for energy harvesting application. Compos. Sci. Technol. 199, 108330 (2020)
H. Li, W. Lian, T. Cheng, W. Zhang, B. Lu, K. Tan, C. Liu, C. Shen, Highly tunable piezoelectricity of flexible nanogenerators based on 3D porously architectured membranes for versatile energy harvesting and self-powered multistimulus sensing. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 9(50), 17128–17141 (2021)
I. Choudhry, H.R. Khalid, H.-K. Lee, Flexible piezoelectric transducers for energy harvesting and sensing from human kinematics. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2(10), 3346–3357 (2020)
J. Li, G. Zhou, Y. Hong, W. He, S. Wang, Y. Chen, C. Wang, Y. Tang, Y. Sun, Y. Zhu, Highly sensitive, flexible and wearable piezoelectric motion sensor based on PT promoted β-phase PVDF. Sens. Actuator A phys. 337, 113415 (2022)
H. Li, H. Song, M. Long, G. Saeed, S. Lim, Mortise-tenon joint structured hydrophobic surface-functionalized barium titanate/polyvinylidene fluoride nanocomposites for printed self-powered wearable sensors. Nanoscale 13(4), 2542–2555 (2021)
N. Ghaedi Dehaghi, M. Kokabi, Polyvinylidene fluoride/barium titanate nanocomposite aligned hollow electrospun fibers as an actuator. Mater. Res. Bull. 158, 112052 (2023)
S. Sharafkhani, M. Kokabi, High performance flexible actuator: PVDF nanofibers incorporated with axially aligned carbon nanotubes. Compos. Part B Eng. 222, 109060 (2021)
L. Wu, Z. Jin, Y. Liu, H. Ning, X. Liu, N. Alamusi, Hu, Recent advances in the preparation of PVDF-based piezoelectric materials. Nanotechnol. Rev. 11(1), 1386–1407 (2022)
P.K. Szewczyk, A. Gradys, S.K. Kim, L. Persano, M. Marzec, A. Kryshtal, T. Busolo, A. Toncelli, D. Pisignano, A. Bernasik, S. Kar-Narayan, P. Sajkiewicz, U. Stachewicz, Enhanced piezoelectricity of electrospun polyvinylidene fluoride fibers for energy harvesting. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 12(11), 13575–13583 (2020)
H. Gao, P.T. Minh, H. Wang, S. Minko, J. Locklin, T. Nguyen, S. Sharma, High-performance flexible yarn for wearable piezoelectric nanogenerators. Smart Mater. Struct. 27(9), 095018 (2018)
P. Saxena, P. Shukla, A comprehensive review on fundamental properties and applications of poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF). Adv. Compos. Hybrid. Mater. 4(1), 8–26 (2021)
D.M. Nivedhitha, S. Jeyanthi, Polyvinylidene fluoride, an advanced futuristic smart polymer material: a comprehensive review. Polym. Adv. Technol. 34(2), 474–505 (2022)
X. Zhang, W. Xia, J. Liu, M. Zhao, M. Li, J. Xing, PVDF-based and its copolymer-based piezoelectric composites: preparation methods and applications. J. Electron. Mater. 51(10), 5528–5549 (2022)
P.K. Mahato, A. Seal, S. Garain, S. Sen, Effect of fabrication technique on the crystalline phase and electrical properties of PVDF films. Mater. Sci. 33(1), 157–162 (2015)
S. Debili, A. Gasmi, M. Bououdina, Synergistic effects of stretching/polarization temperature and electric field on phase transformation and piezoelectric properties of polyvinylidene fluoride nanofilms. Appl. Phys. A 126(4), 309 (2020)
A. Gebrekrstos, M. Sharma, G. Madras, S. Bose, New physical insights into shear history dependent polymorphism in poly(vinylidene fluoride). Cryst. Growth Des. 16(5), 2937–2944 (2016)
Y. Wu, S.L. Hsu, C. Honeker, D.J. Bravet, D.S. Williams, The role of surface charge of nucleation agents on the crystallization behavior of poly(vinylidene fluoride). J. Phys. Chem. B 116(24), 7379–7388 (2012)
B.S. Athira, A. George, K. Vaishna Priya, U.S. Hareesh, E.B. Gowd, K.P. Surendran, A. Chandran, High-performance flexible piezoelectric nanogenerator based on electrospun PVDF-BaTiO3 nanofibers for self-powered vibration sensing applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 14(39), 44239–44250 (2022)
B. Zhao, Z. Chen, Z. Cheng, S. Wang, T. Yu, W. Yang, Y. Li, Piezoelectric nanogenerators based on electrospun PVDF-coated mats composed of multilayer polymer-coated BaTiO3 nanowires. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 5(6), 8417–8428 (2022)
N. Jia, Q. Xing, G. Xia, J. Sun, R. Song, W. Huang, Enhanced β-crystalline phase in poly(vinylidene fluoride) films by polydopamine-coated BaTiO3 nanoparticles. Mater. Lett. 139, 212–215 (2015)
R. Mitra, B. Sheetal Priyadarshini, A. Ramadoss, U. Manju, Stretchable polymer-modulated PVDF-HFP/TiO2 nanoparticles-based piezoelectric nanogenerators for energy harvesting and sensing applications. Mat. Sci. Eng. B 286, 116029 (2022)
L. Liu, W. Fu, L. Wang, H. Tian, X. Shan, Piezoelectricity of PVDF composite film doped with dopamine coated nano-TiO2. J. Alloys Compd. 885, 160829 (2021)
K. Yoon, A. Kelarakis, Nanoclay-directed structure and morphology in PVDF electrospun membranes. J. Nanomater. 2014, 1–7 (2014)
S. Tiwari, A. Gaur, C. Kumar, P. Maiti, Enhanced piezoelectric response in nanoclay induced electrospun PVDF nanofibers for energy harvesting. Energy 171, 485–492 (2019)
G. Chen, G. Chen, L. Pan, D. Chen, Electrospun flexible PVDF/GO piezoelectric pressure sensor for human joint monitoring. Diam. Relat. Mater. 129, 109358 (2022)
M.M. Abolhasani, K. Shirvanimoghaddam, M. Naebe, PVDF/graphene composite nanofibers with enhanced piezoelectric performance for development of robust nanogenerators. Compos. Sci. Technol. 138, 49–56 (2017)
R.T. Selvan, C.Y. Jia, W.A.D.M. Jayathilaka, A. Chinappan, H. Alam, S. Ramakrishna, Enhanced piezoelectric performance of electrospun PVDF-MWCNT-Cu nanocomposites for energy harvesting application. NANO 15(04), 2050049 (2020)
S. Bairagi, S.W. Ali, Investigating the role of carbon nanotubes (CNTs) in the piezoelectric performance of a PVDF/KNN-based electrospun nanogenerator. Soft Matter 16(20), 4876–4886 (2020)
K. Ke, P. Pötschke, D. Jehnichen, D. Fischer, B. Voit, Achieving β-phase poly(vinylidene fluoride) from melt cooling: effect of surface functionalized carbon nanotubes. Polymer 55(2), 611–619 (2014)
A. Issa, M. Al-Maadeed, A. Luyt, D. Ponnamma, M. Hassan, Physico-mechanical, dielectric, and piezoelectric properties of PVDF electrospun mats containing silver nanoparticles. C J. Carbon Res. 3(4), 30 (2017)
S. Manna, S.K. Batabyal, A.K. Nandi, Preparation and characterization of silver—poly(vinylidene fluoride) nanocomposites: formation of piezoelectric polymorph of poly(vinylidene fluoride). J. Phys. Chem. B 110(25), 12318–12326 (2006)
J. Yan, Y.G. Jeong, High performance flexible piezoelectric nanogenerators based on BaTiO3 nanofibers in different alignment modes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8(24), 15700–15709 (2016)
M. Abbasipour, R. Khajavi, A.A. Yousefi, M.E. Yazdanshenas, F. Razaghian, The piezoelectric response of electrospun PVDF nanofibers with graphene oxide, graphene, and halloysite nanofillers: a comparative study. J. Mater. Sci. 28(21), 15942–15952 (2017)
X. Cai, T. Lei, D. Sun, L. Lin, A critical analysis of the α, β and γ phases in poly(vinylidene fluoride) using FTIR. RSC Adv. 7(25), 15382–15389 (2017)
T. Zhu, C. Qian, W. Zheng, R. Bei, S. Liu, Z. Chi, X. Chen, Y. Zhang, J. Xu, Modified halloysite nanotube filled polyimide composites for film capacitors: high dielectric constant, low dielectric loss and excellent heat resistance. RSC Adv. 8(19), 10522–10531 (2018)
H. Kang, X. Liu, S. Zhang, J. Li, Functionalization of halloysite nanotubes (HNTs) via mussel-inspired surface modification and silane grafting for HNTs/soy protein isolate nanocomposite film preparation. RSC Adv. 7(39), 24140–24148 (2017)
S.B. Shivanna, M.Q.A. Al-Gunaid, F.H. Al-Ostoot, N. Al-Zaqri, A. Boshaala, S.J. Siddaramaiah, Anasuya, Probing optical efficiency and electrochemical behaviors of polycarbonate incorporating conducting PANI and halloysite nanotubes (HNTs) as core–shell nanofillers. Polym. Bull. 79(11), 10333–10355 (2022)
G. Cao, S. Cai, H. Zhang, Y. Chen, Y. Tian, High-performance conductive polymer composites by incorporation of polyaniline-wrapped halloysite nanotubes and silver microflakes. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 4(5), 3352–3360 (2022)
Y. Zhang, X. He, J. Ouyang, H. Yang, Palladium nanoparticles deposited on silanized halloysite nanotubes: synthesis, characterization and enhanced catalytic property. Sci. Rep. 3, 2948 (2013)
W.L. Zhang, H.J. Choi, Fabrication of semiconducting polyaniline-wrapped halloysite nanotube composite and its electrorheology. Colloid Polym. Sci. 290(17), 1743–1748 (2012)
M. Khalifa, S. Anandhan, PVDF nanofibers with embedded polyaniline–graphitic carbon nitride nanosheet composites for piezoelectric energy conversion. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2(11), 7328–7339 (2019)
M. Khalifa, A. Mahendran, S. Anandhan, Durable, efficient, and flexible piezoelectric nanogenerator from electrospun PANi/HNT/PVDF blend nanocomposite. Polym. Compos. 40(4), 1663–1675 (2018)
A. Mostafaei, A. Zolriasatein, Synthesis and characterization of conducting polyaniline nanocomposites containing ZnO nanorods. Prog. Nat. Sci. 22(4), 273–280 (2012)
J. Han, W. Xing, J. Yan, J. Wen, Y. Liu, Y. Wang, Z. Wu, L. Tang, J. Gao, Stretchable and superhydrophilic polyaniline/halloysite decorated nanofiber composite evaporator for high efficiency seawater desalination. Adv. Fiber Mater. 4(5), 1233–1245 (2022)
C.M. Goodwin, Z.E. Voras, X. Tong, T.P. Beebe, Soft Ion sputtering of pani studied by XPS, AFM, TOF-SIMS, and STS. Coatings 10(10), 967 (2020)
X. Wang, P. Fan, S. Wang, H. Liu, L. Liao, Nanotubular polyaniline/reduced graphene oxide composite synthesized from a natural halloysite template for application as a high performance supercapacitor electrode. ChemistrySelect 7(5), e202104402 (2022)
T. Zhou, C. Li, H. Jin, Y. Lian, W. Han, Effective adsorption/reduction of cr(VI) oxyanion by halloysite@polyaniline hybrid nanotubes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 9(7), 6030–6043 (2017)
H. Liu, B. Xu, M. Jia, M. Zhang, B. Cao, X. Zhao, Y. Wang, Polyaniline nanofiber/large mesoporous carbon composites as electrode materials for supercapacitors. Appl. Surf. Sci. 332, 40–46 (2015)
Z.-H. Sheng, L. Shao, J.-J. Chen, W.-J. Bao, F.-B. Wang, X.-H. Xia, Catalyst-free synthesis of nitrogen-doped graphene via thermal annealing graphite oxide with melamine and its excellent electrocatalysis. ACS Nano 5(6), 4350–4358 (2011)
C. Merlini, A. Pegoretti, T.M. Araujo, S.D.A.S. Ramoa, W.H. Schreiner, O. de Barra, Electrospinning of doped and undoped-polyaniline/poly(vinylidene fluoride) blends. Synth. Met. 213, 34–41 (2016)
H. Yu, T. Huang, M. Lu, M. Mao, Q. Zhang, H. Wang, Enhanced power output of an electrospun PVDF/MWCNTs-based nanogenerator by tuning its conductivity. Nanotechnology 24(40), 405401 (2013)
S. Shetty, A. Mahendran, S. Anandhan, Development of a new flexible nanogenerator from electrospun nanofabric based on PVDF/talc nanosheet composites. Soft Matter 16(24), 5679–5688 (2020)
V. Jacobs, R.D. Anandjiwala, M. Maaza, The influence of electrospinning parameters on the structural morphology and diameter of electrospun nanofibers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 115(5), 3130–3136 (2010)
J.G. Shin, C.S. Park, E.Y. Jung, B.J. Shin, H.S. Tae, Synthesis of a polyaniline nanoparticle using a solution plasma process with an ar gas bubble channel. Polymers 11(1), 105 (2019)
S.A. Haddadi, A. Ramazani, S.A.S. Talebi, S. Fattahpour, M. Hasany, Investigation of the effect of nanosilica on rheological, thermal, mechanical, structural, and piezoelectric properties of poly(vinylidene fluoride) nanofibers fabricated using an electrospinning technique. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 56(44), 12596–12607 (2017)
C. Chen, Z. Bai, Y. Cao, M. Dong, K. Jiang, Y. Zhou, Y. Tao, S. Gu, J. Xu, X. Yin, W. Xu, Enhanced piezoelectric performance of BiCl3/PVDF nanofibers-based nanogenerators. Compos. Sci. Technol. 192, 108100 (2020)
M. Khalifa, B. Deeksha, A. Mahendran, S. Anandhan, Synergism of electrospinning and nano-alumina trihydrate on the polymorphism, crystallinity and piezoelectric performance of PVDF nanofibers. Jom 70(7), 1313–1318 (2018)
S. Bodkhe, P.S.M. Rajesh, S. Kamle, V. Verma, Beta-phase enhancement in polyvinylidene fluoride through filler addition: comparing cellulose with carbon nanotubes and clay. J. Polym. Res. 21(5), 434 (2014)
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by the Joint Funds of the National Science Foundation of China (Grant No. U20A20172).
Funding
Joint Funds of the National Science Foundation of China, Grant No. U20A20172.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
PF, and JY supervised this project. ZQ, SZ, and PF proposed and designed the research. ZQ, SZ, JJ, and JH performed the characterizations. ZQ, SZ, JHJL, and PF analyzed the data and discussed the results. ZQ and PF wrote the manuscript draft, while all authors gave the comments.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing financial interests or personal relationships.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed content was obtained from all individual participants involved in the study.
Research involving human and/or animal participants
This article does not contain any studies involving animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Qi, Z., Zhang, S., Huang, J. et al. Effect of HNT@PANI hybrid nanoparticles on performance enhancement of electrospun PVDF nanofiber mat for flexible piezoelectric nanogenerators. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 34, 1352 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-10699-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-10699-x