Abstract
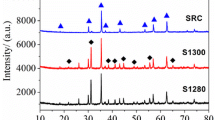
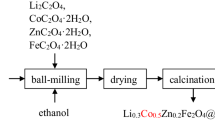
Li0.4Zn0.2Fe2.4O4/Y3Fe5O12-BBSZ (LiZn/YIG-BBSZ) ferrite-glass nanocomposites have been fabricated using a low-temperature liquid phase sintering process. According to the XRD results, a clear signature of phase separation of Li0.4Zn0.2Fe2.4O4 (LiZn) ferrite and Y3Fe5O12 (YIG) ferrite with a small amount of YFeO3 is present. The LiZn/YIG-BBSZ exhibits a dense granular structure with a porosity of 1.11% and a low average grain size of ~ 1.3 µm. Compared to the Li0.4Zn0.2Fe2.4O4-BBSZ (LiZn-BBSZ) or the Y3Fe5O12-BBSZ (YIG-BBSZ) composites, the LiZn/YIG-BBSZ possesses a relatively high saturation magnetization of ~ 46.4 emu/g and a relatively low coercivity of ~ 57.2 Oe mainly due to its optimized porosity and grain size. Owing to the increase in intrinsic and extrinsic damping and the dynamic magnetic inhomogeneity, high ferromagnetic resonance (FMR) linewidth of ~ 1018.4 Oe has been achieved for the LiZn/YIG-BBSZ, which is much larger than that of the LiZn-BBSZ or the YIG-BBSZ. The enlarged FMR linewidth and tunable saturation magnetization of the ferrite-glass nanocomposites may show promise for the electromagnetic shielding or microwave absorbers design.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
H.J. Kwon, J.Y. Shin, J.H. Oh, The microwave absorbing and resonance phenomena of Y-type hexagonal ferrite microwave absorbers. J. Appl. Phys. 75, 6109 (1994)
A. Houbi, Z.A. Aldashevich, Y. Atassi, Z.B. Telmanovna, M. Saule, K. Kubanych, Microwave absorbing properties of ferrites and their composites: A review. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 529, 167839 (2021)
S. Vinayasree, M. Soloman, V. Sunny, P. Mohanan, P. Kurian, M. Anantharaman, A microwave absorber based on strontium ferrite–carbon black–nitrile rubber for S and X-band applications. Compos. Sci. Technol. 82, 69–75 (2013)
K. Praveena, G.V. Jagadeesha Gowda, A. El-Denglawey, V. Jagadeesha Angadi, Manganese ferrite—polyaniline nanocomposites for microwave absorbers in X band. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 33, 5678–5685 (2022)
L. Wang, Y. Guan, X. Qiu, H. Zhu, S. Pan, M. Yu, Q. Zhang, Efficient ferrite/Co/porous carbon microwave absorbing material based on ferrite@metal–organic framework. Chem. Eng. J. 326, 945–955 (2017)
P.D. Baba, G.M. Argentina, W.E. Courtney, G.F. Dionne, D.H. Temme, Fabrication and properties of microwave lithium ferrites. IEEE Trans. Magn. 8, 83–94 (1972)
K.D. Martinson, I.B. Panteleev, K.A. Steshenko, V.I. Popkov, Effect of Bi2O3 contents on magnetic and electromagnetic properties of LiZnMn ferrite ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 42, 3463–3472 (2022)
V.G. Harris, Modern microwave ferrites. IEEE Trans. Magn. 48, 1075–1104 (2012)
R.C. Pullar, Review of the synthesis, properties and applications of hexaferrite ceramics. Prog. Mater. Sci. 57, 1191–1334 (2012)
S. Borah, N.S. Bhattacharyya, Broadband magneto-dielectric response of particulate ferrite polymer composite at microwave frequencies. Composite B 43, 1988–1994 (2012)
T. Wang, Z. Zhou, Zhong, Low-temperature processing of LiZn-based ferrite ceramics by co-doping of V2O5 and Sb2O3: Composition, microstructure and magnetic properties. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 99, 1–8 (2022)
H. Su, H. Zhang, X. Tang, Effects of Bi2O3–WO3 additives on sintering behaviors and magnetic properties of NiCuZn ferrites. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 117, 231–234 (2005)
Q. Yang, H. Zhang, Y. Liu, Q. Wen, Microstructure and magnetic properties of microwave sintered M-type barium ferrite for application in LTCC devices. Mater. Lett. 63, 406–408 (2009)
J.L. Ortiz-Quiñonez, S. Das, U. Pal, Catalytic and pseudocapacitive energy storage performance of metal (Co, Ni, Cu and Mn) ferrite nanostructures and nanocomposites. Prog. Mater. Sci. 130, 100995 (2022)
H. Jalili, B. Aslibeiki, A. Hajalilou, O. Musalu, L.P. Ferreira, M.M. Cruz, Bimagnetic hard/soft and soft/hard ferrite nanocomposites: Structural, magnetic and hyperthermia properties. Ceram. Int. 48, 4886–4896 (2022)
D.A. Vinnik, V.E. Zhivulin, D.P. Sherstyuk, AYu. Starikov, P.A. Zezyulina, S.A. Gudkova, D.A. Zherebtsov, K.N. Rozanov, S.V. Trukhanov, K.A. Astapovich, A.S.B. Sombra, D. Zhou, R.B. Jotania, C. Singh, A.V. Trukhanov, Ni substitution effect on the structure, magnetization, resistivity and permeability of zinc ferrites. J. Mater. Chem. C 9, 5425–5436 (2021)
A.V. Trukhanov, M.A. Almessiere, A. Baykal, S.V. Trukhanov, Y. Slimani, D.A. Vinnik, V.E. Zhivulin, A.Y. Starikov, D.S. Klygach, M.G. Vakhitov, T.I. Zubar, D.I. Tishkevich, E.L. Trukhanova, M. Zdorovets, Influence of the charge ordering and quantum effects in heterovalent substituted hexaferritesontheirmicrowavecharacteristics. J. Alloys Compd. 788, 1193–1202 (2019)
B. Hu, Z. Chen, Z. Su, X. Wang, A. Daigle, P. Andalib, J. Wolf, M.E. McHenry, Y. Chen, V.G. Harris, Nanoscale-driven crystal growth of hexaferrite heterostructures for magnetoelectric tuning of microwave semiconductor integrated devices. ACS Nano 8, 11172–11180 (2014)
S. Sutradhar, S. Pati, S. Acharya, S. Das, D. Das, P.K. Chakrabarti, Sol–gel derived nanoparticles of Zn substituted lithium ferrite (Li0.32Zn0.36Fe2.32O4): magnetic and Mössbauer effect measurements and their theoretical analysis. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 324, 1317–1325 (2012)
X.N. Jiang, Z.W. Lan, Z. Yu, P.Y. Liu, D.Z. Chen, C.Y. Liu, Sintering characteristics of LiZn ferrites fabricated by a sol–gel process. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 321, 52–55 (2009)
Y. Gao, Z. Wang, Microwave absorption and electromagnetic interference shielding properties of Li-Zn ferrite-carbon nanotubes composite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 528, 167808 (2021)
P. Liu, L. Li, Z. Yao, J. Zhou, M. Du, T. Yao, Synthesis and excellent microwave absorption property of polyaniline nanorods coated Li0.435Zn0.195Fe2.37O4 nanocomposites. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 27, 7776–7787 (2016)
P.V.B. Reddy, V.R. Reddy, A. Gupta, R. Gopalan, C.G. Reddy, Mössbauer study of nano-crystalline Li–Zn ferrites. Hyperfine Interact. 183, 81–86 (2008)
Y.S. Cho, V.L. Burdick, V.R.W. Amarakoon, Synthesis of nanocrystalline lithium zinc ferrites using polyacrylic acid, and their initial densification. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 82, 1416–1420 (1999)
X.M. Liu, S.Y. Fu, H.M. Xiao, C. Huang, Synthesis of nanocrystalline spinel CoFe2O4 via a polymer-pyrolysis route. Physica B 370, 14–21 (2005)
Y. Lin, X. Liu, T. Ye, H. Yang, F. Wang, C. Liu, Synthesis and characterization of CoFe2O4 /Y3Fe5O12 composites based on polyaniline. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 27, 4833–4838 (2016)
X. Cai, H. Guo, H. Zhu, D. Yin, H. Guo, D. Bi, K. Yu, H. Yang, J. Pan, Effect of cooling medium on the preparation and microwave absorption properties in low frequency for LiZn ferrites hollow microspheres. J. Alloys Compd. 906, 164290 (2022)
R. Yao, S. Liao, X. Chen, G. Tang, G. Wang, F. Zheng, Effects of ZnO and NiO on material properties of microwave absorptive glass-ceramic tile derived from iron ore tailings. Ceram. Int. 42, 8179–8189 (2016)
A.V. Anupama, V. Kumaran, B. Sahoo, Magnetorheological fluids containing rod-shaped lithium–zinc ferrite particles: the steady-state shear response. Soft Matter 14, 5407–5419 (2018)
V. Rathod, A.V. Anupama, V.M. Jali, V.A. Hiremath, B. Sahoo, Combustion synthesis, structure and magnetic properties of Li–Zn ferrite ceramic powders. Ceram. Int. 43, 14431–14440 (2017)
K. Sun, Z. Zhang, R. Fan, M. Chen, C. Cheng, Q. Hou, X. Zhang, Y. Liu, Random copper/yttrium iron garnet composites with tunable negative electromagnetic parameters prepared by in situ synthesis. RSC Adv. 5, 61155–61160 (2015)
C. Cheng, Y. Liu, R. Ma, R. Fan, Nickel/yttrium iron garnet metacomposites with adjustable negative permittivity behavior toward electromagnetic shielding application. Composite A 155, 106842 (2022)
T. Zhou, H. Zhang, L. Jia, J. Li, Y. Liao, L. Jin, H. Su, Grain growth, densification, and gyromagnetic properties of LiZnTi ferrites with H3BO3-Bi2O3-SiO2-ZnO glass addition. J. Appl. Phys. 115, 17A511 (2014)
T. Zhou, D. Zhang, L. Jia, F. Bai, J. Jin, Y. Liao, T. Wen, C. Liu, H. Su, N. Jia, Z. Zheng, V.G. Harris, H. Zhang, Z. Zhong, Effect of NiZn ferrite nanoparticles upon the structure and magnetic and gyromagnetic properties of low-temperature processed LiZnTi ferrites. J. Phys. Chem. C 119, 13207–13214 (2015)
Z. Yue, J. Zhou, X. Wang, Z. Gui, L. Li, Preparation and magnetic properties of titanium-substituted LiZn ferrites via a sol-gel auto-combustion process. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 23, 189–193 (2003)
M.N. Akhtar, M.A. Khan, M. Ahmad, G. Murtaza, R. Raza, S.F. Shaukat, M.H. Asif, N. Nasir, G. Abbas, M.S. Nazir, M.R. Raza, Y3Fe5O12 nanoparticulate garnet ferrites: Comprehensive study on the synthesis and characterization fabricated by various routes. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 368, 393–400 (2014)
B. Raneesh, H. Soumya, J. Philip, S. Thomas, K. Nandakumar, Magnetoelectric properties of multiferroic composites (1–x)ErMnO3 –xY3Fe5O12 at room temperature. J. Alloys Compd. 611, 381–385 (2014)
R. Abbas, K.D. Martinson, T.Y. Kiseleva, G.P. Markov, P.Y. Tyapki, V.I. Popkov, Effect of fuel type on the solution combustion synthesis, structure, and magnetic properties of YIG nanocrystals. Mater. Today Commun. 32, 103866 (2022)
P. Vaqueiro, M.A. López-Quintela, Influence of complexing agents and pH on yttrium-iron garnet synthesized by the sol-gel method. Chem. Mater. 9, 2836–2841 (1997)
P. Scherrer, Bestimmung der Grösse und der inneren Struktur von Kolloidteilchen mittels Röntgenstrahlen. Nachr. Ges. Wiss. Göttingen 26, 98 (1918)
M. Kavanloui, B. Hashemi, Effect of B2O3 on the densification and magnetic properties of Li–Zn ferrite. Mater. Des. 32, 4257–4261 (2011)
A. Goldman, Modern Ferrite Technology, 2nd edn. (Springer, Pittsburgh, 2009)
V. Sharma, S. Kumari, B.K. Kuanr, Exchange-coupled hard-soft ferrites; a new microwave material. J. Alloys Compd. 736, 266–275 (2018)
J.B. Youssef, C. Brosseau, Magnetization damping in two-component metal oxide micropowder and nanopowder compacts by broadband ferromagnetic resonance measurements. Phys. Rev. B 74, 214413 (2006)
R.S. Azis, M.M. Syazwan, N.M.M. Shahrani, A.N. Hapishah, R. Nazlan, F.M. Idris, I. Ismail, M.M.M. Zulkimi, I.R. Ibrahim, Z. Abbas, N.M. Saiden, Influence of sintering temperature on the structural, electrical and microwave properties of yttrium iron garnet (YIG). J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 29, 8390–8401 (2018)
D. Zhang, L. Jin, H. Zhang, Q. Yang, Y. Rao, Q. Wen, T. Zhou, C. Liu, Z. Zhong, J.Q. Xiao, Chemical epitaxial growth of nm-thick yttrium iron garnet films with low Gilbert damping. J. Alloys Compd. 695, 2301–2305 (2017)
Acknowledgements
This work was partly supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 62171096) and the Sichuan Science and Technology Support Project (Grant No. 2021YFG0091).
Funding
National Natural Science Foundation of China, 62171096, Lichuan Jin, Sichuan Science and Technology Support Project, 2021YFG0091, Lichuan Jin.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YG: Experiments, investigation, and writing—original draft. LJ: Discussion, resources, review & editing. YL: Discussion, review & editing. TZ: Supervision, analysis, writing—review & editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Consent for publication
The authors declare that this manuscript has not been submitted to, nor is under review at, another journal or other publishing venue.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, Y., Jin, L., Liang, Y. et al. Phase components, microstructures, and magnetic properties of liquid-phase-sintered Li0.4Zn0.2Fe2.4O4/Y3Fe5O12 ferrite nanocomposites. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 34, 1250 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-10656-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-10656-8