Abstract
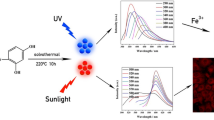
In this paper, novel multifunctional nitrogen and sulfur co-doped fluorescent carbon quantum dots (Y-CDs) were prepared by a solvothermal method using o-phenylenediamine (OPD) as the carbon and nitrogen sources, L-Cysteine (L-Cys) as the sulfur source, and ethanol as the solvent. The prepared Y-CDs had high selectivity for the detection of Zirconium (Zr4+) with a detection limit of 68 nM due to the doping of S elements which formed electrical interactions with Zr4+ and thus caused aggregation fluorescence quenching. In addition, Y-CDs had excellent pH reversible response properties. The fluorescence of Y-CDs was almost completely quenched in the pH range of 1–5, and was restored when the pH returned to neutral or basic. Y-CDs also had good biocompatibility and low toxicity with the application of clear yellow fluorescence imaging in MCF-7 and EC cells. Yellow fluorescence Y-CDs focused mainly on the nucleus in MCF-7 cancer cells, while focused mainly on the cell membrane region in EC normal cells due to the different pH conditions of these two cells. The prepared Y-CDs would have promising applications in the fields of Zr4+ ion detection, pH response and cell imaging and cell identification.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated in this paper will be obtained from corresponding authors according to reasonable requirements.
References
X.T. Tian, X.B. Yin, C. Dots, Unconventional preparation strategies, and applications beyond photoluminescence. Small 15, 1901803 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201901803
Y. Zhang, K.F. Chan, B. Wang, P.W.Y. Chiu, L. Zhang, Spore-derived color-tunable multi-doped carbon nanodots as sensitive nanosensors and intracellular imaging agents. Sens. Actuators B 271, 128–136 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.05.112
X. Chen, Q. Chen, M. Chen, W. Wang, C. Sun, X. Wang, P. Ning, L. Hou, Y. Feng, X. Meng, Evaluating visually a new apoptosis-induced reagent by a ratiometric two-photon fluorescent pH probe. Sens. Actuators B 329, 129104 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2020.129104
M. Kolahdouz, B. Xu, A.F. Nasiri, M. Fathollahzadeh, M. Manian, H. Aghababa, Y. Wu, H.H. Radamson, Carbon-related materials: graphene and carbon nanotubes in semiconductor applications and design. Micromachines (Basel) 13, 081257 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13081257
C. Wang, H. Shi, M. Yang, Z. Yao, B. Zhang, E. Liu, X. Hu, W. Xue, J. Fan, Biocompatible sulfur nitrogen co-doped carbon quantum dots for highly sensitive and selective detection of dopamine. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 205, 111874 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2021.111874
J. Guo, S. Ye, H. Li, Y. Chen, H. Liu, Y. Song, X. Peng, F. Zhou, J. Song, J. Qu, Novel fluorescent probes based on nitrogen–sulfur co-doped carbon dots for chromium ion detection. New J. Chem. 45, 4828–4834 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1039/d0nj06178f
N. Hashemi, M.H. Mousazadeh, Preparation of fluorescent nitrogen-doped carbon dots for highly selective on-off detection of Fe3 + ions in real samples. Opt. Mater. 121, 111515 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2021.111515
Y. Zhou, K.J. Mintz, S.K. Sharma, R.M. Leblanc, Carbon dots: diverse preparation, application, and perspective in surface chemistry. Langmuir 35, 9115–9132 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.9b00595
Y. Jiao, Y. Gao, Y. Meng, W. Lu, Y. Liu, H. Han, S. Shuang, L. Li, C. Dong, One-step synthesis of label-free ratiometric fluorescence Carbon Dots for the detection of silver ions and glutathione and Cellular Imaging Applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 11, 16822–16829 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b01319
M. Zhang, R. Su, J. Zhong, L. Fei, W. Cai, Q. Guan, W. Li, N. Li, Y. Chen, L. Cai, Q. Xu, Red/orange dual-emissive carbon dots for pH sensing and cell imaging. Nano Res. 12, 815–821 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-019-2293-z
T. Li, S.E.J. Wang, X. Chen, Regulating the properties of carbon dots via a solvent-involved molecule fusion strategy for improved sensing selectivity. Anal. Chim. Acta 1088, 107–115 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2019.08.027
J. Zhao, F. Li, S. Zhang, Y. An, S. Sun, Preparation of N-doped yellow carbon dots and N, P co-doped red carbon dots for bioimaging and photodynamic therapy of tumors. New J. Chem. 43, 6332–6342 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1039/C8NJ06351F
H. Kalantaria, S. Yaghmaei, R. Roostaazad, H. Mohammad-Beigi, Removal of zirconium from aqueous solution by Aspergillus niger. Trans. C: Chem. Chem. Eng. 21, 772–780 (2014)
H. Atalay, K.A. Celi, F. Ayaz, Investigation of genotoxic and apoptotic effects of zirconium oxide nanoparticles (20 nm) on L929 mouse fibroblast cell line. Chem. Biol. Interact. 296, 98–104 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2018.09.017
R.V.S. Misra, M.K. Santra, D. Ottoor, One pot green synthesis of C-dots from groundnuts and its application as cr(VI) sensor and in vitro bioimaging agent. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 373, 28–36 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2018.12.028
J.T. Hou, W.X. Ren, K. Li, J. Seo, A. Sharma, X.Q. Yu, J.S. Kim, Fluorescent bioimaging of pH: from design to applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 46, 2076–2090 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1039/c6cs00719h
J. Huang, Y. He, Z. Zhang, B. Lei, W. Wu, Synthesis of high-efficient red carbon dots for pH detection. J. Lumin. 215, 116640 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2019.116640
S. Durrani, Z. Yang, J. Zhang, Z. Wang, H. Wang, F. Durrani, F.G. Wu, F. Lin, Nucleus-targeting pH-Responsive carbon dots for fast nucleus pH detection. Talanta 252, 123855 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2022.123855
C. Dan, Z. Zhao, J. Feng, Y. Xin, Y. Yang, L. Shi, Lysosome-targeted red-fluorescent carbon dots for turn-on detection of permanganate and pH in vivo and in vitro. Sens. Actuators B 349, 130774 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2021.130774
H. Ding, Y. Ji, J.S. Wei, Q.Y. Gao, Z.Y. Zhou, H.M. Xiong, Facile synthesis of red-emitting carbon dots from pulp-free lemon juice for bioimaging. J. Mater. Chem. B 5, 5272–5277 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1039/c7tb01130j
H. Wang, C. Sun, X. Chen, Y. Zhang, V.L. Colvin, Q. Rice, J. Seo, S. Feng, S. Wang, W.W. Yu, Excitation wavelength independent visible color emission of carbon dots. Nanoscale 9, 1909–1915 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1039/c6nr09200d
Z. Bahadır, A. Mermer, Simple emulsification microextraction for the preconcentration of palladium in water samples by flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Anal. Lett. 54, 558–571 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1080/00032719.2020.1785484
J. Zhang, L. Yang, Y. Yuan, J. Jiang, S.-H. Yu, One-pot gram-scale synthesis of nitrogen and sulfur embedded organic dots with distinctive fluorescence behaviors in free and aggregated states. Chem. Mater. 28, 4367–4374 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemmater.6b01360
C. Tan, X. Su, C. Zhou, B. Wang, Q. Zhan, S. He, Acid-assisted hydrothermal synthesis of red fluorescent carbon dots for sensitive detection of Fe(iii). RSC Adv. 7, 40952–40956 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1039/c7ra06223k
H. Ding, J.S. Wei, H.M. Xiong, Nitrogen and sulfur co-doped carbon dots with strong blue luminescence. Nanoscale 6, 13817–13823 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/c4nr04267k
H. Li, S. Han, B. Lyu, T. Hong, S. Zhi, L. Xu, F. Xue, L. Sai, J. Yang, X. Wang, B. He, Tunable light emission from carbon dots by controlling surface defects. Chin. Chem. Lett. 32, 2887–2892 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cclet.2021.03.051
J. Wei, B. Liu, X. Zhang, C. Song, One-pot synthesis of N, S co-doped photoluminescent carbon quantum dots for Hg2 + ion detection. New Carbon Mater. 33, 333–340 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1872-5805(18)60343-9
M. Pirveysian, M. Ghiaci, Synthesis and characterization of sulfur functionalized graphene oxide nanosheets as efficient sorbent for removal of Pb2+, Cd2+, Ni2 + and Zn2 + ions from aqueous solution: a combined thermodynamic and kinetic studies. Appl. Surf. Sci. 428, 98–109 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.09.105
R. Atchudan, T.N.J.I. Edison, S. Perumal, N. Clament Sagaya Selvam, Y.R. Lee, Green synthesized multiple fluorescent nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots as an efficient label-free optical nanoprobe for in vivo live-cell imaging. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 372, 99–107 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2018.12.011
Y. Chen, J. Lin, R. Zhang, S. He, Z. Ding, L. Ding, Electrochemiluminescence of water-dispersed nitrogen and sulfur doped carbon dots synthesized from amino acids. Analyst 146, 5287–5293 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1039/d1an00991e
Y. Ru, L. Sui, H. Song, X. Liu, Z. Tang, S.Q. Zang, B. Yang, S. Lu, Rational design of multicolor-emitting chiral carbonized polymer dots for full‐color and white circularly polarized luminescence. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 60, 14091–14099 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202103336
H. Ding, S.B. Yu, J.S. Wei, H.M. Xiong, Full-color light-emitting carbon dots with a surface-state-controlled luminescence mechanism. ACS Nano 10, 484–491 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.5b05406
A. Kirandeep, A. Kumar, S.C. Sharma, E. Sahoo, V. Zangrando, R. Saini, S. Kataria, Kumar, Mehta, Metal organic framework as “turn-on” fluorescent sensor for zr(IV) ions and selective adsorbent for organic dyes. Microchem. J. 171, 106824 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2021.106824
L. Sun, Z. Mo, Q. Li, D. Zheng, X. Qiu, X. Pan, Facile synthesis and performance of pH/temperature dual-response hydrogel containing lignin-based carbon dots. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 175, 516–525 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.02.049
J. Xia, S. Chen, G.Y. Zou, Y.L. Yu, J.H. Wang, Synthesis of highly stable red-emissive carbon polymer dots by modulated polymerization: from the mechanism to application in intracellular pH imaging. Nanoscale 10, 22484–22492 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1039/c8nr08208a
C. He, K. Lu, W. Lin, Nanoscale metal-organic frameworks for real-time intracellular pH sensing in live cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136, 12253–12256 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1021/ja507333c
S. Sailaja Prasannakumaran Nair, N. Kottam, Green synthesized luminescent carbon nanodots for the sensing application of Fe(3+) ions. J. Fluoresc. 30, 357–363 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-020-02505-2
S. Xu, X. He, Y. Huang, X. Liu, L. Zhao, X. Wang, Y. Sun, P. Ma, D. Song, Lysosome-targeted ratiometric fluorescent sensor for monitoring pH in living cells based on one-pot-synthesized carbon dots. Mikrochim Acta 187, 478 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04462-w
J.T. Tao, B. Liu, J. Pan, C. Li, F. Li, Y. Zheng, Construction of green fluorescent carbon dots with high quantum yield for cancer cell recognition and Fe3 + detection. Opt. Mater. 113, 110892 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2021.110892
Funding
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51603187) and the cooperative project funding of Zhejiang Sci-Tech University with Hangzhou Mingshi Culture Dissemination co., LTD (“Application of strong fluorescence graphene quantum dots in heavy metal ion detection and cell imaging”, No. 2022330001004838, Internal No.22060862-J).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YZ: directed the whole experiment and led the manuscript revision. XL: completed most of the experiments, data analysis, and manuscript writing. LZ, XL and HZ participated in some experiments. JC, JP and CL: provided partial experimental comments. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest
Ethical approval
This paper follows all research ethics standards and procedures.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liao, X., Zhou, L., Lu, X. et al. Multifunctional fluorescent carbon quantum dots for Zr4+ ion detection, pH response and cell imaging. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 34, 1205 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-10567-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-10567-8