Abstract
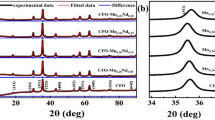
Barium ferrite has wide applications in electronic devices, and its preparation process optimization plays an important role in the improvement of microwave electromagnetic and absorption properties. In this paper, M-type barium ferrite was synthesized by the citrate sol–gel method. During sintering, the precursor gel first experienced free water evaporation and impurity volatilization, and then went through two endothermic reactions, eventually generating M-type barium ferrite. As the sintering temperature increased from 800 to 1400 °C, the products transformed from the particles exhibited a long rod shape without an obvious M-type barium ferrite phase to the hexagonal block particles mainly composed of M-type barium ferrite. Meanwhile, with increasing temperature, the particles and grain size became larger, the size uniformity was first strengthened and then weakened, the magnetic properties were first enhanced and then weakened, and the dielectric loss capacity continued to weaken, which were related to the changes of structure and microstructure, e.g., densification, magnetic domain state, and specific surface area. The products were equipped with the main loss mechanisms of dipole turning polarization, space charge polarization, interfacial polarization, natural resonance, eddy current loss, and multiple reflections/scattering. Besides they possessed great impedance performance and obvious interference cancelation, further improving the absorption ability. After optimization, the barium ferrite sintered at 1200 °C exhibited a maximum microwave absorption bandwidth of 6.16 GHz with a matching thickness of 2.34 mm, and it achieved the minimum reflection loss of − 38.97 dB at 39.93 GHz when the matching thickness is 3.10 mm. It is indicated that the nanoparticles sintered at the appropriate temperature are the potential candidates as wide-band electromagnetic wave absorbers in the Ka-band.


















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
K.S. Sandeep, K. Yaswanth, J. Penke et al., Facile synthesis of Al substituted Cu-ferrite infused reduced graphene oxide (rGO) nanohybrid for improving microwave absorption at gigahertz frequencies. J. Alloys Compd. 901, 163659 (2022)
B. Zpa, W. Dan, G. Xiang et al., High strength and microwave-absorbing polymer-derived SiCN honeycomb ceramic prepared by 3D printing. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 42(4), 1322–1331 (2021)
S. Jan, A. Mashadi, S. Didin et al., Role of neodymium substitution on the structural, magnetic and microwave absorbing properties of nickel ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 563, 170023 (2022)
X.Y. Wang, S.C. Wei, Y. Yuan et al., Effect of copper sulfide nanosphere shell on microstructure and microwave absorption properties of cobalt ferritecarbon nanotube composites. J. Alloy. Compd. 909(15), 164676 (2022)
C. Mahshid, N. Mahmoud, G. Hamidreza, Enhanced microwave absorption performance of graphene/doped Li ferrite nanocomposites. Adv. Powder Technol. 32(12), 4697–4710 (2021)
C.Y. Liu, Y.J. Zhang, Y. Tang et al., The tunable magnetic and microwave absorption properties of the Nb5+–Ni2+ co-doped M-type barium ferrite. J. Mater. Chem. C 5(14), 3461–3472 (2017)
M. Wang, Q. Xu, W. Shan et al., Formation of BaFe12−xNixO19 ceramics with considerably high dielectric and magnetic property coexistence. J. Alloy. Compd. 765, 951–960 (2018)
D. Lisjak, The low-temperature sintering of M-type hexaferrites. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 32(12), 3351–3360 (2012)
J. Liu, H. Huang, P. Qiu et al., Topotactic fluorination induced stable structure and tunable electronic transport in perovskite barium ferrite thin films. Ceram. Int. 46(7), 8761–8765 (2020)
D.H. Chen, Y.Y. Chen, Synthesis of barium ferrite ultrafine particles by coprecipitation in the presence of polyacrylic acid. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 235(1), 9–14 (2001)
S. Veisi, M. Yousefi, M. Amini, Magnetic and microwave absorption properties of Cu/Zr doped M-type Ba/Sr hexaferrites prepared via sol-gel auto-combustion method. J. Alloy. Compd. 773, 1187–1194 (2019)
L.S. Ferreira, T.R. Silva, V.D. Silva et al., Proteic sol–gel synthesis, structure and battery-type behavior of Fe-based spinels (MFe2O4, M = Cu Co, Ni). Adv. Powder Technol. 31(2), 604–613 (2020)
S. Bhaskaran, I.A. Al-Omari, E.V. Gopalan, On the enhanced coercive field and anisotropy observed in cobalt substituted copper ferrite nanoparticles prepared by a modified sol–gel method. J. Alloy. Compd. 884, 161095 (2021)
K. Zhang, J.H. Luo, N. Yu et al., Synthesis and excellent electromagnetic absorption properties of reduced graphene oxide/PANI/BaNd0.2Sm0.2Fe11.6O19 nanocomposites. J. Alloys Compd. 779, 270–279 (2019)
W.J. Feng, J.T. Gang, Y. Cao et al., Microwave absorption property of BaFe12O19/PANI Ti-doped nanocomposites. DEStech Trans. Environ. Energy Earth Sci. 11, 26–35 (2017)
F.Y. Li, Preparation of BaFe12O19 ultrafine particles by polyacrylamide gel method. Funct. Mater. 3, 157–159 (1992)
D. Amutha, D.D. Jayaseelanb, F.D. Gnanamb et al., Densification behaviour and microstructure of gel-derived phase-pure mullite in the presence of sinter additives. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 21(12), 2253–2257 (2001)
Y.M. Jiang, Influence of the sol composition on formation process of barium hexaferrite. J. Yanzhou Univ. Natural Sci. Ed. 2(1), 26–28 (1999)
D.M. Roy, R. Roy, An experimental study of the formation and properties of synthetic serpentines and related layer silicate minerals. Am. Miner. 39(11–12), 957–975 (1954)
M. Wang, Q. Xu, J. Liu et al., Extra up-spin magnetic moments and extraordinary high saturation magnetization of Ni2+ doped barium ferrite in 4f2 site. Mater. Res. Express 6, 086104 (2019)
N. Vinod, M.L. Dhage, M.K. Mane et al., Influence of substitution on structural and magnetic properties of BaFe12O19 powder prepared by sol-gel auto combustion method. J. Alloy. Compd. 509, 4394–4398 (2011)
Y.Y. Meng, M.H. He, Q. Zeng et al., Synthesis of barium ferrite ultrafine powders by a sol–gel combustion method using glycine gels. J. Alloy. Compd. 583, 220–225 (2014)
E. Paimozd, A. Ghasemi, A. Jafari et al., Influence of acid catalysts on the structural and magnetic properties of nanocrystalline barium ferrite prepared by sol–gel method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 320(23), 137–140 (2018)
S.L. Hu, J. Liu, Z.W. Liu et al., Effect of chemical co-precipitation process and calcination temperature on the properties of barium ferrite nano-powders. J. Magn. Mater. Devices 50(6), 12–17 (2019)
Z.X. Zeng, M.S. Lan, Q. Zhang et al., Effect of pH value on multiferroic properties of barium ferrite ceramics prepared by sol–gel method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 563, 169904 (2022)
J.X. Qiu, M.Y. Gu, Magnetic nanocomposite thin films of BaFe12O19 and TiO2 prepared by sol–gel method. Anpl. Surf. Sci. 252(4), 888892 (2005)
J.C. Corral-Huacuz, G. Mendoza-Suárez, Preparation and magnetic properties of Ir–Co and La–Zn substituted barium ferrite powders obtained by sol–gel. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 242, 430–433 (2002)
K. Praveena, K. Sadhana, S. Matteppanavar et al., Effect of sintering temperature on the structural, dielectric and magnetic properties of Ni0.4Zn0.2Mn0.4Fe2O4 potential for radar absorbing. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 423, 343–352 (2017)
N.L. Tang, BET determination of specific surface area of ceramic powder. Silicate Bull. 02, 20–22 (1998)
J. Liu, X. Xue, Morphology and magnetic properties of SrFe12O19 synthesized with oxidized scale. Mater. Lett. 164, 579–582 (2016)
A. Baykal, S. Yoku, S. Güner et al., Magneto-optical properties and Mössbauer investigation of BaxSryPbzFe12O19 hexaferrites. Ceram. Int. 43(4), 3475–3482 (2016)
K.S. Novoselov, S.V. Dubonos, E. Hill et al., Microscopic view on a single domain wall moving through ups and downs of an atomic washboard potential. Physica E 22, 406–409 (2004)
N.V. Matveev, I.V. Levashov, T.V. Volkov et al., Fabrication and use of a nanoscale Hall probe for measurements of the magnetic field induced by MFM tips. Nanotechnology 19(47), 475502 (2008)
S.E. Shafraniuk, Thermoelectricity and Heat Transport in Graphene and Other 2D Nanomaterials (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2018), pp.32–92
J. Jia, C. Liu, N. Ma et al., Exchange coupling controlled ferrite with dual magnetic resonance and broad frequency bandwidth in microwave absorption. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 14(4), 045002 (2013)
J. Li, S. He, K. Shi et al., Coexistence of broad-bandwidth and strong microwave absorption in Co2+–Zr4+ co-doped barium ferrite ceramics. Ceram. Int. 44(6), 6953–6958 (2018)
D.F. Wan, Magnetic Physics (Publishing House of Electronics Industry, Beijing, 1994), pp.112–122
L. Wang, X.F. Yu, X. Li et al., MOF-derived yolk-shell Ni@C@ZnO Schottky contact structure for enhanced microwave absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 383, 123099 (2020)
L. Long, E.Q. Yang, X.S. Qi et al., Positive and reverse core/shell structure CoxFe3-xO4/MoS2 and MoS2/CoxFe3-xO4 nanocomposites: selective production and outstanding electromagnetic absorption comprehensive performance. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 8(1), 613–623 (2020)
T.Y. Hwang, Y.M. Choi, Y.S. Song et al., A noble gas sensor platform: linear dense assemblies of single-walled carbon nanotubes (LACNTs) in a multi-layered ceramic/metal electrode system (MLES). J. Mater. Chem. C 6(5), 972–979 (2018)
C. Li, X. Qi, X. Gong et al., Magnetic-dielectric synergy and interfacial engineering to design yolk-shell structured CoNi@void@C and CoNi@void@C@MoS2 nanocomposites with tunable and strong wideband microwave absorption. Nano Res. 15, 6761–6771 (2022)
J.J. Zhang, X.S. Qi, X. Gong et al., Microstructure optimization of core@shell structured MSe2/FeSe2@MoSe2 (M=Co, Ni) flower-like multicomponent nanocomposites towards high-efficiency microwave absorption. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 128, 59–70 (2022)
X. Wang, W. Cao, M. Cao et al., Assembling nano-microarchitecture for electromagnetic absorbers and smart devices. Adv. Mater. 32, 2002112 (2020)
J.H. Luo, M.N. Feng, Z.Y. Dai et al., MoS2 wrapped MOF-derived N-doped carbon nanocomposite with wideband electromagnetic wave absorption. Nano Res. 15, 5781–5789 (2022)
R. Wang, E. Yang, X. Qi et al., Constructing and optimizing core@shell structure CNTs@MoS2 nanocomposites as outstanding microwave absorbers. Appl. Surf. Sci. 516, 146159 (2020)
C. Li, Z. Li, X. Qi et al., A generalizable strategy for constructing ultralight three-dimensional hierarchical network heterostructure as high-efficient microwave absorber. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 605, 13–22 (2021)
S. Wang, K.F. Chen, M. Wang et al., Controllable synthesis of nickel nanowires and the application in high sensitivity, stretchable strain sensor for body motion sensing. J. Mater. Chem. C 6(17), 4737–4745 (2018)
Z.J. Shen, C.B. Liu, H.L. Yang et al., Fabrication of hollow cube dual-semiconductor Ln2O3/MnO/C nanocomposites with excellent microwave absorption performance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 13(24), 28689–28702 (2021)
E.Q. Yang, X.S. Qi, R. Xie et al., Novel “203” type of heterostructured MoS2-Fe3O4-C ternary nanohybrid: synthesis, and enhanced microwave absorption properties. Appl. Surf. Sci. 442, 622–629 (2018)
B. Wen, H.B. Yang, Y. Lin et al., Novel bimetallic MOF derived hierarchical Co@C composites modified with carbon nanotubes and its excellent electromagnetic wave absorption properties. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 605, 657–666 (2022)
W. Huang, S. Wei, Y. Wang et al., A new broadband and strong absorption performance FeCO3/RGO microwave absorption nanocomposites. Materials 12(13), 2206 (2019)
Z.C. Mo, R.L. Yang, D.W. Lu et al., Lightweight, three-dimensional carbon Nanotube@TiO2 sponge with enhanced microwave absorption performance. Carbon 144, 433–439 (2019)
X. Sun, Y.H. Pu, F. Wu et al., 0D–1D–2D multidimensionally assembled Co9S8/CNTs/MoS2 composites for ultralight and broadband electromagnetic wave absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 423, 130132 (2021)
J.L. Liu, P. Zhang, X.K. Zhang et al., Synthesis and microwave absorbing properties of La-doped Sr-hexaferrite nanopowders via sol–gel auto-combustion method. Rare Met. 36(9), 704–710 (2017)
X.Y. Wang, S.C. Wei, B. Wang et al., Doping sites, magnetic, and microwave absorption properties of barium ferrites with multiple magnetic resonances. J. Mater. Sci. 34(4), 310 (2023)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the project team assistance with funding. Many thanks to the tutor for his thoughtful and thorough guidance.
Funding
The work was supported by the financial supports from National Natural Science Foundation of China (Project 51905543), National Defense Science and Technology Excellence Young Scientists Foundation (Project 2017-JCJQ-ZQ-001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XW: methodology, formal analysis, writing—original draft, and writing—review and editing. BW: formal analysis and writing—review and editing. SW: conceptualization, methodology, and resources. YW: software and resources. YL: methodology, resources, and writing—review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Wang, B., Wei, S. et al. Effect of sintering temperature on the microstructure, magnetic, and microwave absorption properties of M-type barium ferrite nanoparticles prepared by sol–gel method. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 34, 1045 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-10400-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-10400-2