Abstract
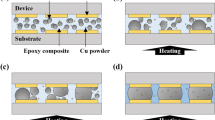
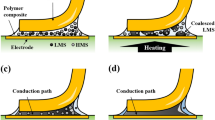
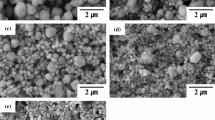
This study developed Cu particle-filled solderable isotropic polymer composites (Cu-SIPCs) to improve the bonding properties of SIPCs with low-melting-point solder (LMPS) fillers. To examine the influence of Cu particle concentration on the bonding properties of Cu-SIPC joints, Cu-SIPCs comprising different Cu particle concentrations in the conductive fillers were formulated, and a bonding test using a quad flat package was conducted. The bonding properties of these joints were measured and compared. The Cu-SIPCs with a Cu particle content of below 10 vol% formed a wide and reliable metallurgical conduction path, with uniformly dispersed Cu particles, due to the proper internal flow and wetting behavior exhibited by molten LMPS fillers. The mechanical bonding strength of the Cu-SIPC joints increased linearly with an increase in the Cu particle content due to the mechanical enhancement effect offered by the Cu particles within the conduction path. However, Cu-SIPCs with excessively high Cu particle concentrations formed weakly shaped conduction paths because of the partly raised viscosity of molten LMPSs and the local agglomeration of Cu particles, which diminished the fluidity of molten LMPSs.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used or analyzed in this study are available with the corresponding author. They can be produced upon reasonable request.
References
H.K. Kim, F.G. Shi, Microelectron. J. 32, 315–321 (2001)
D. Wojciechowski, J. Vanfleteren, E. Reese, H.W. Hagedorn, Microelectron. Reliab. 40, 1215–1226 (2000)
Q. Wang, S. Zhang, G. Liu, T. Lin, P. He, J. Alloys Compd. 820, 153184 (2020)
R. Aradhana, S. Mohanty, S.K. Nayak, Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 99, 102596 (2020)
S. Xu, D.A. Dillard, J.G. Dillard, Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 23, 235–250 (2003)
Y. Li, C.P. Wong, Mat. Sci. Eng. R 51, 1–35 (2006)
B.S. Yim, S.H. Oh, J.S. Jeong, J.M. Kim, J. Compos. Mater. 47, 1141–1152 (2013)
B.S. Yim, J.I. Lee, Y. Heo, J. Kim, S.H. Lee, Y.E. Shin, J.M. Kim, Mater. Trans. 53, 2104–2110 (2012)
B.S. Yim, J.I. Lee, B.H. Lee, Y.E. Shin, J.M. Kim, Microelectron. Reliab. 54, 2944–2950 (2014)
J.W. Baek, K.S. Jang, Y.S. Eom, J.T. Moon, J.M. Kim, J.D. Nam, Microelectron. Eng. 87, 1968–1972 (2010)
F. Wang, Y. Huang, Z. Zhang, C. Yan, Materials 10, 920 (2017)
F.Q. Hu, Q.K. Zhang, J.J. Jiang, Z.L. Song, Mater. Lett. 214, 142–145 (2018)
D. Ma, P. Wu, Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 25, 1225–1233 (2015)
A.K. Gain, L. Zhang, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 27, 781–794 (2016)
O. Mokhtari, H. Nishikawa, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 27, 4232–4244 (2016)
M. McCormack, H.S. Chen, G.W. Kammlott, S. Jin, J. Electron. Mater. 26, 954–958 (1997)
T. Satoh, T. Ishizaki, M. Usui, Mater. Design 124, 203–210 (2017)
Y. Liu, H. Zhang, F. Sun, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 27, 2235–2241 (2016)
F. Guo, J. Mater. Sci: Mater. Electron. 18, 129–145 (2007)
G.F. Ban, F.L. Sun, J.J. Fan, Y. Liu, S.N. Cong, J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 26, 1069–1075 (2017)
H.T. Lee, Y.H. Lee, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 419, 172–180 (2006)
H. Rhee, F. Guo, J.G. Lee, K.C. Chen, K.N. Subramanian, J. Electron. Mater. 32, 1257–1264 (2003)
H. Zhang, Y. Liu, F. Sun, G. Ban, Microelectron. Int. 34, 40–44 (2017)
F. Guo, S. Choi, J.P. Lucas, K.N. Subramanian, J. Electron. Mater. 29, 1241–1248 (2000)
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIT) (No. 2022R1A2C1012409 and No. 2022R1A2C1010405).
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HJY contributed to conceptualization, methodology, investigation, and writing the original draft; JIL contributed to visualization and investigation; MJH contributed to visualization and investigation; JMK contributed to supervision and validation; BSY contributed to supervision and validation.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that can influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Youn, H.J., Lee, J.I., Ha, M.J. et al. An investigation of the bonding properties of Cu particle-filled solderable isotropic polymer composites (Cu-SIPCs). J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 34, 886 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-10276-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-10276-2