Abstract
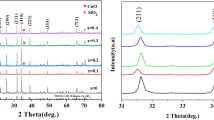
The dielectric ceramics of Ca1−xCuxSiO3 (x = 0 − 0.025) were prepared by solid-phase reaction method. The effects of Cu doping on phase composition, crystal structure, and dielectric properties of CaSiO3 ceramics were investigated. XRD results indicated that appropriate content of Cu doping could suppress impurity phases and obtain pure α-CaSiO3 calcined powders. After sintering, α-CaSiO3 phase was the main phase accompanied with a small quantity of impurity phases in undoped ceramics, which transformed to the single β-CaSiO3 phase after Cu doping. The phase transformation could be attributed to the change of the geometric position of SiO4 tetrahedron. SEM images showed that grain morphology changed from irregular and loose particles to dense lath by Cu doping. The Ca0.985Cu0.015SiO3 ceramics sintered at 1125 °C exhibited excellent dielectric properties: εr = 5.22, Q × f = 18,948 GHz, τf = − 63 ppm/°C, and these make the ceramics promising for use in microwave applications.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article [and its supplementary information files].
References
F. Huang, H. Su, Q. Zhang, X. Wu, X. Tang, Effect of Sr2+ substitution on the Raman spectrum, phase composition and microwave dielectric properties of CaMg1−xSrxSi2O6 ceramics. Ceram. Int. 48, 3904–3911 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.10.177
M. Kono, H. Takagi, T. Tatekawa, H. Tamura, High Q dielectric resonator material with low dielectric constant for millimeter-wave applications. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 26, 1909–1912 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2005.09.019
H. Wang, J. Chen, W. Yang, S. Feng, H. Ma, G. Jia, S. Xu, Effects of Al2O3 addition on the sintering behavior and microwave dielectric properties of CaSiO3 ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 32, 541–545 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2011.09.014
A. Belous, O. Ovchar, D. Durilin, M.M. Krzmanc, M. Valant, D. Suvorov, High-Q microwave dielectric materials based on the spinel Mg2TiO4. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 89, 3441–3445 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1551-2916.2006.01271.x
N. Mori, Y. Sugimoto, J. Harada, Y. Higuchi, Dielectric properties of new glass-ceramics for LTCC applied to microwave or millimeter-wave frequencies. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 26, 1925–1928 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2005.09.023
C. Su, L. Fang, Z. Wei, X. Kuang, H. Zhang, LiCa3ZnV3O12: a novel low-firing, high Q microwave dielectric ceramic. Ceram. Int. 40, 5015–5018 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2013.08.081
M. Terada, K. Kawamura, I. Kagomiya, K.-I. Kakimoto, H. Ohsato, Effect of Ni substitution on the microwave dielectric properties of cordierite. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 27, 3045–3048 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2006.11.050
T. Kolodiazhnyi, G. Annino, M. Spreitzer, T. Taniguchi, R. Freer, F. Azough, A. Panariello, W. Fitzpatrick, Development of Al2O3–TiO2 composite ceramics for high-power millimeter-wave applications. Acta Mater. 57, 3402–3409 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2009.03.050
S.W. Lim, J. Bang, Microwave dielectric properties of Mg4Nb2O9 ceramics produced by hydrothermal synthesis. J. Electroceram. 23, 116–120 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10832-007-9322-0
K.X. Song, X.M. Chen, X.C. Fan, Effects of Mg/Si ratio on microwave dielectric characteristics of forsterite ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 90, 1808–1811 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1551-2916.2007.01656.x
T. Sugiyama, T. Tsunooka, K.I. Kakimoto, H. Ohsato, Microwave dielectric properties of forsterite-based solid solutions. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 26, 2097–2100 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2005.09.102
K.X. Song, X.M. Chen, C.W. Zheng, Microwave dielectric characteristics of ceramics in Mg2SiO4–Zn2SiO4 system. Ceram. Int. 34, 917–920 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2007.09.057
P.N. De Aza, Z.B. Luklinsk, M.R. Anseau, M. Hector, F. Guitian, S. De Aza, Reactivity of a wollastonite-tricalcium phosphate bioeutectic ceramic in human parotid saliva. Biomaterials 21, 1735–1741 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1016/s0142-9612(00)00058-2
W. Hu, H. Liu, H. Hao, Z. Yao, M. Cao, Z. Wang, Z. Song, Influence of TiO2 additive on the microwave dielectric properties of α-CaSiO3–Al2O3 ceramics. Ceram. Int. 41, S510–S514 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2015.03.138
N. Tangboriboon, T. Khongnakhon, S. Kittikul, R. Kunanuruksapong, A. Sirivat, An innovative CaSiO3 dielectric material from eggshells by sol–gel process. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 58, 33–41 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-010-2351-1
W. Cai, T. Jiang, X.Q. Tan, Q. Wei, Y. Li, Development of low dielectric constant calcium silicate fired at low temperature. Electron. Comp. Mater. 21, 16–18 (2002)
H. Wang, Q. Zhang, H. Yang, H. Sun, Synthesis and microwave dielectric properties of CaSiO3 nanopowder by the sol–gel process. Ceram. Int. 34, 1405–1408 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2007.05.001
Q. Ma, S. Wu, C. Jiang, J. Li, Microwave dielectric properties of SnO2-doped CaSiO3 ceramics. Ceram. Int. 39, 2223–2229 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2012.08.066
H. Sun, Q. Zhang, H. Yang, J. Zou, (Ca1−xMgx)SiO3: a low-permittivity microwave dielectric ceramic system. Mater. Sci. Eng B. 138, 46–50 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mseb.2007.01.012
R.P. Sreekanth Chakradhar, B.M. Nagabhushana, G.T. Chandrappa, K.P. Ramesh, J.L. Rao, Solution combustion derived nanocrystalline macroporous wollastonite ceramics. Mater. Chem. Phys. 95, 169–175 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2005.06.002
Y. Cui, X. Liu, M. Jiang, Y. Hu, Q. Su, H. Wang, Lead-free (Ba0.7Ca0.3)TiO3-Ba(Zr0.2Ti0.8)O3-xwt% CuO ceramics with high piezoelectric coefficient by low-temperature sintering. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 23, 1342–1345 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-011-0596-2
C.L. Huang, J.Y. Chen, C.Y. Jiang, Low-temperature sintering microwave dielectrics using CuO-doped Zn(Nb0.95Ta0.05)2O6 ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 93, 2755–2759 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1551-2916.2010.03786.x
Y. Lai, X. Tang, X. Huang, H. Zhang, X. Liang, J. Li, H. Su, Phase composition, crystal structure and microwave dielectric properties of Mg2−xCuxSiO4 ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 38, 1508–1516 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2017.10.035
Q. Zhang, H. Su, X. Tang, Y. Li, R. Peng, X. Jing, Y. Jing, Effects of Cu2+ substitution on bond characteristics, Raman spectra, and microwave dielectric properties of Li2Mg0.6Zn0.4SiO4 ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 41, 3432–3437 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2021.01.038
B.H. Toby, EXPGUI, a graphical user interface for GSAS. J. Appl. Cryst. 34, 210–213 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1107/S0021889801002242
B.H. Toby, R.B. Von Dreele, GSAS-II: the genesis of a modern open-source all purpose crystallography software package. J. Appl. Cryst. 46, 544–549 (2013)
B.W. Hakki, P.D. Coleman, A dielectric resonator method of measuring inductive capacitors in the millimeter range. IEEE Trans. Microwave Theor. Technol. 8, 402–410 (1960). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMTT.1960.1124749
W.E. Courtey, Analysis and evaluation of a method of measuring the complex permittivity and permeability microwave insulators. IEEE Trans. Microwave Theor. Technol. 18, 475–485 (1970). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMTT.1970.1127271
T. Yamanaka, H. Mori, The structure and polytypes of α-CaSiO3 (pseudo-wollastonite). Acta Crystallogr. Sect. B. 37, 1010–1017 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1107/S0567740881004962
S. Kulkarni, B.M. Nagabhushana, N. Suriyamurthy, C. Shivakumara, R.P.S. Chakradhar, R. Damle, Synthesis, luminescence and EPR studies on CaSiO3: Pb, Mn-nano phosphors synthesized by the solution combustion method. Ceram. Int. 39, 1917–1922 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2012.08.041
X. Xing, D. Ling, L. Tan, Microwave synthesis of CaSiO3:(Eu2+, Dy3+) nanorods and verification on luminescence properties. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 25, 4774–4778 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-014-2232-4
J. Wang, J.B. Neaton, H. Zheng, V. Nagarajan, S.B. Ogale, B. Liu, D. Viehland, V. Vaithyanathan, D.G. Schlom, U.V. Waghmare, Epitaxial BiFeO3 multiferroic thin film heterostructures. Science 34, 1719–1722 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1080615
Z.Q. Yu, A.L. Liang, Characteristics of wollastonite as low temperature ceramic raw material. Foshan Ceram. 67, 17–20 (2002)
Funding
This study was supported by the fund of the Applied Basic Research Foundation of Yunnan Province (Grant Nos. 202002AB080001-1), Major Science and Technology Programs of Yunnan Province (Grant Nos. 202102AB080008), and the Science and Technology Program of Yunnan Precious Metal Laboratory (Grant Nos. YPML-2022050205).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by GW, ZL, ML, JH, ML, YL and HX. The first draft of the manuscript was written by GW. YZ, JH and YL commented on previous versions of the manuscript. JL participated in the revision of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declares that they have no competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, G., Lin, Z., Li, M. et al. Effects of Cu doping on phase composition, crystal structure, and dielectric properties of CaSiO3 ceramics. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 34, 815 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-10204-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-10204-4