Abstract
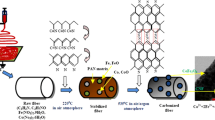
Nickel/carbon (Ni/C) nanofibrous structures with magnetic material nickel in the core and carbon in the shell are fabricated by the co-axial electrospinning method. The crystallinity, morphology, elemental composition, and microstructure of the carbonized nanofibers are characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), field emission scanning electron microscope (FESEM), energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX), and high-resolution transmission electron microscope (HRTEM) respectively. Rietveld refinement method of XRD pattern was carried out to determine the structural parameters of face-centered cubic (FCC) Ni with space group Fm3m. The average crystallite size and the lattice strain have been calculated using the Williamson–Hall (W–H) plot method. It is demonstrated that the compressive lattice strain is attributed due to the presence of polymer-derived carbon material. Raman data confirms the formation of pure C in the Ni/C nanofibers. Furthermore, a vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM) is used for the magnetic measurement of the Ni/C nanofibers. It is observed that the nanofibers show typical ferromagnetic behavior having the optimum value of saturation magnetization of 5.12 emu/g. The temperature-dependent magnetic measurements suggest the ferromagnetic behavior of Ni/C nanofibers within the room temperature (300 K).











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data analyzed during the study are included in this article.
9. References
H. Wu, W. Pan, D. Lin, H. Li, Electrospinning of ceramic nanofibers: fabrication, assembly and applications. J. Adv. Ceram. 1, 2226–4108 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40145-012-0002-4
N.A.M. Barakat, B. Kim, H.Y. Kim, Production of smooth and pure nickel metal nanofibers by the electrospinning technique: nanofibers possess splendid magnetic properties. J. Phys. Chem. C 113, 531–536 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1021/jp805692r
C. Wang, X. Han, P. Xu, J. Wang, Y. Du, X. Wang, W. Qin, T. Zhang, Controlled synthesis of hierarchical nickel and morphology-dependent Electromagnetic Properties. J. Phys. Chem. C 114, 3196–3203 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1021/jp908839r
B. Pant, G.P. Ojha, J. Acharya, M. Park, Eggshell membrane templated synthesis of Ni/MoC decorated carbon fibers with good electrochemical behaviour. Int. J. Hydrog Energy 46, 2774–2782 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020.10.139
M. Adabi, M. Adabi, Electrodeposition of nickel on electrospun carbon nanofiber mat electrode for electrochemical sensing of glucose. J. Dispers Sci. Technol. 42, 262–269 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1080/01932691.2019.1678483
J.P. Cheng, W.D. Wang, X.C. Wang, F. Liu, Recent research of core–shell structured composites with NiCo2O4 as scaffolds for electrochemical capacitors. J. Chem. Eng. 393, 124747 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.124747
J. Lu, H. Wan, T. Ju, Z. Ying, W. Zhang, B. Li, Y. Zhang, Super flexible electrospun carbon/nickel nanofibrous film electrode for supercapacitors. J. Alloys Compd. 774, 593–600 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.09.383
Z. Bai, S. Liu, P. Chen, G. Cheng, G. Wu, H. Li, Y. Liu, Nickel nanoparticles embedded in porous carbon nanofibers and its electrochemical properties. Nanotechnology 31, 30 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6528/ab8594
Y. Shen, Y. Wei, J. Ma, Q. Li, J. Li, W. Shao, P. Yan, G. Huang, X. Du, Tunable microwave absorption properties of nickel-carbon nanofibers prepared by Electrospinning. Ceram. Int 45, 3313–3324 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.10.242
Y. Huang, H. Zhang, G. Zeng, Z. Li, D. Zhang, H. Zhu, R. Xie, L. Zheng, J. Zhu, The microwave absorption properties of carbon-encapsulated nickel nanoparticles/ silicone resin flexible absorbing material. J. Alloys Compd. 682, 138–143 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.04.289
X. Chen, L. Cheng, H. Li, A. Barhoum, Y. Zhang, X. He, W. Yang, M.M. Bubakir, H. Chen, Magnetic nanofibers: unique properties, fabrication techniques, and emerging applications. Chem. Select 3, 9127–9143 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1002/slct.201702480
Y.T. Jeon, G.H. Lee, J. Park, Y. Chang, Comparison of the magnetic Properties of Metastable Hexagonal Close-Packed Ni Nanoparticles with those of the stable face-centered cubic ni nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. B 110, 1187 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1021/jp054608b
J. Li, E. Liu, W. Li, X. Meng, S. Tan, Nickel/carbon nanofibers composite electrodes as supercapacitors prepared by electrospinning. J. Alloys Compd. 478, 371–374 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2008.11.024
Y. Liu, M. Hao, Z. Chen, L.L. Liu, Y. Liu, W. Yang, S. Ramakrishna, A review on recent advances in application of Electrospun Nanofiber materials as biosensors. Curr. Opin. Biomed. Eng. 13, 174–189 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cobme.2020.02.001
N.A.M. Barakat, M. Motlak, B.S. Kim, A.G.E. Deen, S.S.A. Deyab, A.M. Hamza, Carbon nanofibers doped by NixCo1–x alloy nanoparticles as effective and stable non precious electrocatalyst for methanol oxidation in alkaline media. J. Mol. Catal. A 394, 177–187 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcata.2014.07.011
A.K. Moghe, B.S. Gupta, Co-axial Electrospinning for Nanofiber Structures: Preparation and Applications. Polym. Rev. 48, 353–377 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1080/15583720802022257
Y. Ji, X. Zhang, Y. Zhu, B. Li, Y. Wang, J. Zhang, Y. Feng, Nickel nanofibers synthesized by the electrospinning method. Mater. Res. Bull. 48, 2426–2429 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2013.02.043
Y. Shen, Y. Wei, J. Li, Y. Zhang, B. Li, X. Lu, B. Ji, P. Yan, X. Du, Fabrication of microwave absorbing Ni/NiO/C nanofibers with robust superhydrophobic properties by electrospinning. J. Mater. Sci. : Mater. Electron. 31, 226–238 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-02462-y
B. Quan, X. Liang, G. Ji, Y. Zhang, G. Xu, Y. Du, Cross-Linking-Derived Synthesis of Porous CoxNiy/C Nanocomposites for excellent electromagnetic behaviours. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 9, 38814–38823 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b13411
L. Sainia, M.K. Patraa, A. Dixit, Large scale re-producible synthesis and magnetic properties of Ni/graphite core-shell nanostructured materials. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 501, 166444 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2020.166444
D. Liu, Y. Du, P. Xu, N. Liu, Y. Wang, H. Zhao, L. Cui, X. Han, Waxberry-like hierarchical Ni@C microspheres with high performance microwave absorption. J. Mater. Chem. C 7, 5037–5046 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1039/C9TC00771G
N. Kaerkitcha, S. Chuangchote, T. Sagawa, Control of physical properties of carbon nanofibers obtained from co-axial electrospinning of PMMA and PAN with adjustable inner/outer nozzle-ends. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 11, 186 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1186/s11671-016-1416-7
G.A. Kaur, M. Shandilya, P. Rana, S. Thakur, P. Uniyal, Modification of structural and magnetic properties of Co0.5Ni0.5Fe2O4 nanoparticles embedded polyvinylidene fluoride nanofiber membrane via electrospinning method. Nano-Struct. Nano-Objects 22, 100428 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoso.2020.100428
P. Xie, B. He, F. Dang, J. Lin, R. Fan, C. Hou, H. Liu, J. Zhang, Y. Ma, Z. Guo, Bio-gel derived nickel/carbon nanocomposites with enhanced microwave absorption. J. Mater. Chem. C 6, 8812–8822 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1039/C8TC02127A
G. Fredi, S. Jeschke, A. Boulaoued, J. Wallenstein, M. Rashidi, F. Liu, R. Harnden, D. Zenkert, J. Hagberg, G. Lindbergh, P. Johansson, L. Stievano, L.E. Asp, Graphitic microstructure and performance of carbon fibre Li-ion structural battery electrodes. Multifunct. Mater. 1, 015003 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1088/2399-7532/aab707
A.C. Ferrari, J. Robertson, Interpretation of Raman spectra of disordered and amorphous carbon. Phys. Rev. B 61, 20 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.61.14095
Q. Lia, Z. Nia, J. Gonga, D. Zhua, Z. Zhua, Carbon nanotubes coated by carbon nanoparticles of turbostratic stacked graphenes. Carbon 46, 434–439 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2007.12.002
A. Manukyan, A. Elsukova, A. Mirzakhanyan, H. Gyulasaryan, A. Kocharian, S. Sulyanov, M. Spasova, F. Römer, M. Farle, E. Sharoyan, Structure and size dependence of the magnetic properties of Ni@C nanocomposites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 467, 150–159 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2018.07.056
Y. Sui, B. Zhu, H. Zhang, H. Shu, Z. Chen, Y. Zhang, Y. Zhang, B. Wang, C. Tang, X. Xie, G. Yu, Z. Jin, X. Liu, Temperature-dependent nitrogen configuration of N-doped graphene by chemical vapor deposition. Carbon 81, 814–820 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2014.10.030
J. Xiang, J. Li, X. Zhang, Q. Ye, J. Xua, X. Shenb, Magnetic carbon nanofibers containing uniformly dispersed Fe/Co/Ni nanoparticles as stable and high-performance electromagnetic wave absorbers. J. Mater. Chem. A 2, 16905–16914 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/C4TA03732D
A. Khalil, R. Hashaikeh, Electrospinning of nickel oxide nanofibers: process parameters and morphology control. Mater. Charact. 95, 65–71 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar
B. Kartick, S.K. Srivastava, A. Chandra, Graphene/Nickel Nanofiber Hybrids for Catalytic and Microbial Fuel Cell Applications. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol 16, 303–311 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2016.10667
N. Wu, C. Liu, D. Xu, J. Liu, W. Liu, Q. Shao, Z. Guo, Enhanced Electromagnetic Wave absorption of three-dimensional porous Fe3O4/C composite flowers. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng 6, 12471–12480 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b03097
Y. Soumare, A. Dakhlaoui-Omrani, F. Schoenstein, S. Mercone, G. Viau, N. Jouini, Nickel nanofibers and nanowires: elaboration by reduction in polyol medium assisted by external magnetic field. Solid State Commun 151, 284–288 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssc.2010.12.004
A.H. Morrish, Surface properties of small particles, Magnetic Properties of fine particles, (Science Direct, North-Holland Delta Series, 1992) pp. 181–190, https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-444-89552-3.50026-8
A. Karaphun, S. Hunpratub, S. Phokha, T. Putjuso, E. Swatsitang, Characterization and magnetic properties of SrTi1 – xNixO3 nanoparticles prepared by hydrothermal method. Phys. B 504, 31–38 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2016.10.012
N.A.M. Barakat, B. Kim, C. Yi, Y. Jo, M.H. Jung, K.H. Chu, H.Y. Kim, Influence of Cobalt Nanoparticles’ incorporation on the magnetic Properties of the Nickel Nanofibers: Cobalt-Doped Nickel Nanofibers prepared by Electrospinning. J. Phys. Chem. C 113, 19452–19457 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1021/jp905667s
I.V. Beketov, A.P. Safronov, A.V. Bagazeev, A. Larrañaga, G.V. Kurlyandskaya, A.I. Medvedev, In situ modification of Fe and Ni magnetic nanopowders produced by the electrical explosion of wire. J. Alloys Compd. 586, 483–488 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.01.152
A.D. Omrani, M.A. Bousnina, L.S. Smiri, M. Taibi, P. Leone, F. Schoensteinb, N. Jouini, Elaboration of nickel nanoparticles by modified polyol process and their spark plasma sintering, characterization and magnetic properties of the nanoparticles and the dense nanostructured material. Mater. Chem. Phys. 123, 821–828 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2010.05.068
S. Kumari, L.K. Pradhan, L. Kumar, M.K. Manglam, M. Kar, Effect of annealing temperature on morphology and magnetic properties of cobalt ferrite nanofibers. Mater. Res. Express (2019). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab5fa1
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the Biju Pattnaik Research Fellowship (BPRF)—DST, Govt. of Odisha. The authors acknowledge Dr. Patitapaban Mishra, Department of Geology, of Ravenshaw University, Cuttack, for providing XRD facilities and Dr. Gopal K. Pradhan, Department of Physics, School of Applied Science, KIIT University, Bhubaneswar, for carrying out Raman measurements. The authors are grateful to Dr. Subasa Chandra Sahoo of the Department of Physics, Central University of Kerala, for providing the VSM facility.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
PPS: conceptualization, investigation of material preparation and characterization, writing the draft and editing, visualization. TKP: analysis of results, visualization. SR: investigation, resources for characterization. BS: supervision, conceptualization, editing, and reviewing the draft.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sethy, P.P., Pani, T.K., Rout, S. et al. Structural and magnetic properties of Ni/C core–shell nanofibers prepared by one step co-axial electrospinning method. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 34, 807 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-10194-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-10194-3