Abstract
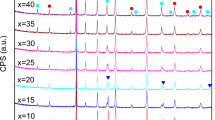
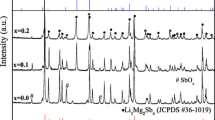
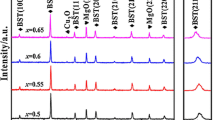
(1−x)Ba0.5Sr0.5TiO3–xLi2MgTiO4 and (1−x)Ba0.5Sr0.5TiO3–xLi2Mg3TiO6 composite ceramics were prepared via the conventional solid-state reaction method. Microstructures and dielectric tunable properties of Ba0.5Sr0.5TiO3–Li2MgTiO4 and Ba0.5Sr0.5TiO3–Li2Mg3TiO6 composite ceramics were investigated. In this composite system, the cubic perovskite BST phase can coexist well with the rock-salt Li2MgTiO4 phase and Li2Mg3TiO6 phase. Only at 1300 °C sintering temperature, due to the decomposition of Li2MgTiO4, a trace of Mg2TiO4 impurity is produced when dielectric content is higher than 55wt% in Ba0.5Sr0.5TiO3–Li2MgTiO4 composite ceramics. At the test frequency of 10 kHz, with the increase of Li2MgTiO4 content from 10wt% to 60wt%, the dielectric constant of Ba0.5Sr0.5TiO3–Li2MgTiO4 composite ceramics sintered at 1300 °C decreases from 962 to 90, the dielectric loss remains below 0.009, and the tunability under an electric field strength of 3 kV/mm gradually decreases from 12.1 to 4.2%. With the gradual increase of Li2Mg3TiO6 content from 10 wt% to 60 wt%, the dielectric constant of Ba0.5Sr0.5TiO3–Li2Mg3TiO6 composite ceramics sintered at 1280 °C decreases from 1042 to 79, the dielectric loss remains below 0.003, and the tunability at 3 kV/mm decreases from 17.2 to 4.9%.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data sharing not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
References
L. Sengupta, W. Drach, Ferroelectr. 153, 359 (1994)
A. Tagantsev, V. Sherman, K. Astafiev, J. Venkatesh, N. Setter, J. Electroceram. 11, 5 (2003)
A. Ahmed, I. Goldthorpe, A. Khandani, Appl. Phys. Rev. 2, 011302 (2015)
L. Sengupta, S. Sengupta, IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Contr 44, 792 (1997)
X. Chou, Z. Zhao, W. Zhang, J. Zhai, Mater. Des. 31, 3703 (2010)
T. Lin, J. Chu, S. Wang, Mater. Lett. 59, 2786 (2005)
P. Liu, J. Ma, L. Meng, J. Li, L. Ding, J. Wang, H. Zhang, Mater. Chem. Phys. 114, 624 (2009)
M. Zhang, J. Zhai, J. Zhang, H. Jiang, X. Yao, Mater. Res. Bull. 46, 1102 (2011)
G. Hu, F. Gao, L. Liu, X. Cao, Z. Liu, Ceram. Int. 37, 1321 (2011)
L. Sengupta, S. Sengupta, Mater. Res. Innovations 2, 278 (1999)
W. Chang, L. Sengupta, J. Appl. Phys. 92, 3971 (2002)
U. Chung, C. Elissalde, M. Maglione, C. Estournes, M. Pate, J. Ganne, Appl. Phys. Lett. 92, 042902 (2008)
H. Zhang, S. Or, H. Chan, J. Phys. Chem. Solids 70, 1218 (2009)
Z. Xu, F. Ling, Z. Hong, Y. Xu, J. Alloys Compd. 907, 164496 (2022)
J. Wu, X. Wang, Y. Fan, Mater. Res. Bull. 46, 2217 (2011)
C. Lou, A. Chen, L. Lu, J. Wu, L. Cheng, R. Liu, S. Chen, Y. Chen, Y. Shi, C. Li, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 39, 4149 (2019)
H. You, S. Koo, J. Ha, J. Koh, J. Park, Curr. Appl. Phys. 9, 875 (2009)
L. Ji, J. Zhang, Y. Gao, Ceram. Int. 40, 11419 (2014)
Z. Fu, P. Liu, J. Ma, X. Zhao, H. Zhang, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 36, 625 (2016)
Z. Fu, P. Liu, J. Ma, X. Chen, H. Zhang, Mater. Lett. 164, 436 (2016)
Y. Zhang, D. Zhou, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 99, 3645 (2016)
Y. Tseng, J. Chen, Y. Kuo, C. Huang, J. Alloys Compd. 509, L308 (2011)
G. Yao, X. Hu, X. Tian, P. Liu, J. Zhou, Ceram. Int. 41, S563 (2015)
M. Satya Kishore, S. Marinel, V. Pralong, V. Caignaert, S. D’Astorg, B. Raveau, Mater. Res. Bull. 41, 1378 (2006)
J. Bian, Y. Dong, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2, 325 (2010)
H. Wu, E. Kim, RSC Adv. 6, 47443 (2016)
O. Levy, D. Stroud, Phys. Rev. B 56, 8035 (1997)
K. Johnson, J. Appl. Phys. 33, 2826 (1962)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant Numbers 61671214 and 61401152. The authors wish to acknowledge the Analytical and Testing Center in Huazhong University of Science and Technology for XRD analysis.
Funding
This study was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China, (Grant Number: 61671214).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by ZF, CL, and ZX. The first draft of the manuscript was written by ZF and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Fu, Z., Xu, Z., Liu, C. et al. Microstructures and dielectric tunable properties of Ba0.5Sr0.5TiO3–Li2MgTiO4 and Ba0.5Sr0.5TiO3–Li2Mg3TiO6 composite ceramics. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 34, 541 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-09970-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-09970-y