Abstract
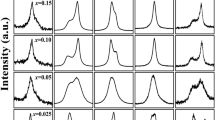
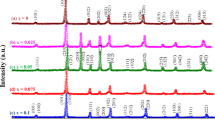
Rietveld analysis on (Na1 − xKx)0.5Bi0.5TiO3 {x = 0, 15%, 20%, 22.5%, 25%, & 30%}, depicts change in structural symmetry from R3c for NBT to R3m and P4mm in NBT-KBT solid solutions. A mixed phase with R3m and P4mm is obtained for doping from 20 to 25%, where 22.5% composition has an equal proportion of both phases. Frequency and temperature-dependent dielectric relaxation studies for (Na1 − xKx)0.5Bi0.5TiO3 shows a transition from a high-temperature paraelectric state to ergodic relaxor state (TC = 300–330˚C) with a crossover in domain-structure & number density at x = 22.5%. The change in the structural symmetry of ceramics greatly influences observed dielectric properties. Havriliak Negami (H-N) parameters substantiate the presence of relaxor-isotherms with change in dipolar interactions and the random field with K-doping concentration. The H-N analysis with relaxation time ‘τ,’ relaxation time distribution function, and asymmetry parameter ‘β’ strongly supports enhanced piezoelectric properties for x = 22.5% specimen. Polarization traced with E-field supports the outcomes of H-N analysis. Enhanced piezoelectric coefficient d33 = 208pC/N is observed for 22.5% K-doped NBT, with an electromechanical coupling factor of ~ 44%.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data supporting this study’s findings are available within the article.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
B.C. Sekhar, B. Dhanalakshmi, B.S. Rao, S. Ramesh, K.V. Prasad, P.S. Rao, B.P. Rao, Multifunctional ferroelectric materials, 71st edn. (Intech open, London, 2021)
P. Sahlot, S. Pandey, A. Pandey, A.M. Awasthi, “Harmonic magneto-dielectric study in doped-, double-, and layered-perovskites”. J. Appl. Phys 127, 154103 (2020)
K. Uchino, S. Nomura, L.E. Cross, R.E. Newnham, S.J. Jang, “Electrostrictive effect in perovskites and its transducer applications”. J. Mater. Sci 16, 569 (1981)
R. Pirc, R. Blinc, V.S. Vikhnin, “Effect of polar nano-regions on giant electrostriction and piezoelectricity in relaxor ferroelectrics”. Phys. Rev. B 69, 212105 (2004)
R. Blinc, J. Dolinšek, A. Gregorovič, B. Zalar, C. Filipič, Z. Kutnjak, A. Levstik, R. Pirc, “Local polarization distribution and Edwards-Anderson order parameter of relaxor ferroelectrics”. Phys. Rev. Lett 83, 424 (1999)
S. Svirskas, M. Ivanov, S. Bagdzevicius, J. Macutkevic, A. Brilingas, J. Banys, J. Dec, S. Miga, M. Dunce, E. Birks, M. Antonova, “Dielectric properties of 0.4Na0.5Bi0. 5TiO3–(0.6-x)SrTiO3–xPbTiO3 solid solutions”. Acta Mater 64, 123 (2014)
I.W. Chen, L. Ping, W. Ying, “Structural origin of relaxor perovskites”. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 57, 1525 (1996)
G. Xu, Z. Zhong, H. Hiraka, G. Shirane, “Three-dimensional mapping of diffuse scattering in pb (Zn1/3Nb2/3)O3 – xPbTiO3. Phys. Rev. B 70, 174109 (2004)
J. Rödel, W. Jo, K.T. Seifert, E.M. Anton, T. Granzow, D. Damjanovic, “Perspective on the development of lead-free piezoceramics”. J. Am. Ceram. Soc 92, 1153 (2009)
E. Ringgaard, T. Wurlitzer, “Lead-free piezoceramics based on alkali niobates”. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc 25, 2701 (2005)
T.S. Ilina, A.M. Kislyuk, D.A. Kiselev, E.D. Politova, G.M. Kaleva, A.V. Mosunov, N.V. Sadovskaya, “Phase transitions, dielectric and piezoelectric properties of (Na0.5Bi0.5)1–xLixTiO3 (x = 0–0.1) ceramics”. Ferroelectrics 574, 144 (2021)
G.O. Jones, P.A. Thomas, “Investigation of the structure and phase transitions in the novel A-site substituted distorted perovskite compound Na0.5Bi0.5TiO3”. Acta Crystallogr., Sect. B: Struct. Sci 58, 168 (2002)
I. Levin, D.S. Keeble, G. Cibin, H.Y. Playford, M. Eremenko, V. Krayzman, W.J. Laws, I.M. Reaney, “Nanoscale polar heterogeneities and branching bi-displacement directions in K0.5Bi0.5TiO3”. Chem. Mater 31, 2450 (2019)
P. Fan, K. Liu, W. Ma, H. Tan, Q. Zhang, L. Zhang, C. Zhou, D. Salamon, S.T. Zhang, Y. Zhang, B. Nan, “Progress and perspective of high strain NBT-based lead-free piezoceramics and multilayer actuators. J. Materiomics ” 7, 508 (2021)
V.A. Isupov, “Properties of Pb (Ti, Zr) O3 piezoelectric ceramics and nature of their orientational dielectric polarization”. Sov Phys. Solid State 10, 989 (1968)
A. Sasaki, T. Chiba, Y. Mamiya, E. Otsuki, “Dielectric and piezoelectric properties of (Bi0.5Na0.5)TiO3–(Bi0.5K0.5)TiO3 systems”. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys 38, 5564 (1999)
A.R. Kulkarni, P. Lunkenheimer, A. Loidl, Scaling behaviour in the frequency dependent conductivity of mixed alkali glasses”. Solid State Ionics 112, 69 (1998)
Z. Tan, S. Xie, L. Jiang, J. Xing, Y. Chen, J. Zhu, D. Xiao, Q. Wang, “Oxygen octahedron tilting, electrical properties and mechanical behaviors in alkali niobate-based lead-free piezoelectric ceramics”. J. Materiomics 5, 372 (2019)
R. Pirc, R. Blinc, “Spherical random-bond–random-field model of relaxor ferroelectrics”. Phys. Rev. B 60, 13470 (1999)
S. Havriliak, S. Negami, “A complex plane representation of dielectric and mechanical relaxation processes in some polymers”. Polymer 8, 161 (1967)
P. Varade, N.S. Sowmya, N. Venkataamani, A.R. Kulkarni, “Microstructural and mechanical behavior of Na0.4K0.1Bi0.5TiO3 ferroelectric ceramics”. Ceram. Int 48, 26546 (2022)
M. Otoničar, S.D. Škapin, M. Spreitzer, D. Suvorov, “Compositional range and electrical properties of the morphotropic phase boundary in the Na0.5Bi0.5TiO3–K0.5Bi0.5TiO3 system”. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc 30, 971 (2010)
D.L. Sidebottom, P.F. Green, R.K. Brow, “Two contributions to the ac conductivity of alkali oxide glasses”. Phys. Rev. Lett 74, 5068 (1995)
J.J. Molina, S. Lectez, S. Tazi, M. Salanne, J.F. Dufrêche, J. Roques, E. Simoni, P.A. Madden, P. Turq, “Ions in solutions: determining their polarizabilities from first-principles”. J. Chem. Phys 134, 014511 (2011)
D. Adamchuk, R. Grigalaitis, S. Svirskas, J. Macutkevic, E. Palaimiene, J. Banys, L. Mitoseriu, G. Canu, M.T. Buscaglia, V. Buscaglia, “Distributions of relaxation times in relaxor ferroelectric ba(Ti0.8Ce0.2)O3”. Ferroelectrics 553, 103 (2019)
M. Algueró, J.M. Gregg,, L. Mitoseriu, Nanoscale ferroelectrics and multiferroics: key processing and characterization issues, and nanoscale effects, 1st edn. (Wiley, NewYork, 2016)
T. Zheng, H. Wu, Y. Yuan, X. Lv, Q. Li, T. Men, C. Zhao, D. Xiao, J. Wu, K. Wang, J.F. Li, “The structural origin of enhanced piezoelectric performance and stability in lead free ceramics”. Energy Environ. Sci 10, 528 (2017)
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the IRCC, Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay, for the XRD, dielectric, and polarization (BDS) facilities. P. Sahlot thanks the institute for financial support through the institute’s post-doctoral fellowship. The authors would like to acknowledge Dr. P.K. Ojha, Naval Materials Research Laboratory, for providing poling and piezoelectric measurement facilities.
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
PV: sample preparation and data acquisition. PS: Software and analysis, writing, and editing. ARK: supervision, review, and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sahlot, P., Varade, P. & Kulkarni, A.R. Phase modified ferroelectricity in Na0.5-xKxBi0.5TiO3. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 34, 547 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-09943-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-09943-1