Abstract
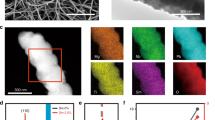
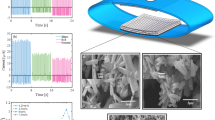
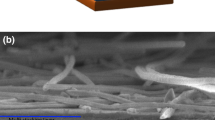
In this work, a simple hydrothermal technique has been used to grow the manganese (Mn)-doped ZnO nanostructure on the flexible indium tin oxide substrate. The Mn doping concentrations (1%, 2.5%, and 5%) have been systematically optimized with respect to piezoelectric output. The output performance of the piezoelectric nanogenerator (PENG) device with 2.5% Mn-doped ZnO achieved 3.3 times higher than the pure PENG device. Peak-to-peak open-circuit voltage and short-circuit current of the Mn-doped PENG device is 5.32 V and 52.33 nA, respectively. The PENG device with a 2.5% Mn doping exhibits a maximum power density of 60.01 nW/cm2 at a 110-MΩ load resistance. The device’s durability has also been tested, and it showed good stability without deterioration. Finally, utilizing a commercial compressor, the system has proven to capture vibrational energy.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available on reasonable request.
References
G. Timilsina, K.U. Shah, in Energy technologies for sustainable development goal 7, ed. by A.A. Adenle, M.R. Chertow, E.H.M. Moors, D.J. Pannell, (Oxford University Press, Oxford, 2020), p. 36
P. Pradhan, L. Costa, D. Rybski, W. Lucht, J.P. Kropp, A systematic study of sustainable development goal (SDG) interactions. Earth’s Future 5(11), 1169–1179 (2017)
N. AlQattan, M. Acheampong, F.M. Jaward, F.C. Ertem, N. Vijayakumar, T. Bello, Reviewing the potential of Waste-to-energy (WTE) technologies for sustainable development goal (SDG) numbers seven and eleven. Renew. Energy Focus 27, 97–110 (2018)
Y. Yang, L. Lin, Y. Zhang, Q. Jing, T.C. Hou, Z.L. Wang, Self-powered magnetic sensor based on a triboelectric nanogenerator. ACS Nano 6(11), 10378–10383 (2012)
J. Zhao, R. Ghannam, K.O. Htet, Y. Liu, M.K. Law, V.A. Roy, B. Michel, M.A. Imran, H. Heidari, Self-powered implantable medical devices: photovoltaic energy harvesting review. Adv. Healthc. Mater 9(17), 2000779 (2020)
A. Nozariasbmarz, H. Collins, K. Dsouza, M.H. Polash, M. Hosseini, M. Hyland, J. Liu, A. Malhotra, F.M. Ortiz, F. Mohaddes, V.P. Ramesh, Review of wearable thermoelectric energy harvesting: from body temperature to electronic systems. Appl. Energy 258, 114069 (2020)
M. Manikandan, P. Rajagopalan, N. Patra, S. Jayachandran, M. Muralidharan, S.M. Prabu, I.A. Palani, V. Singh, Development of Sn-doped ZnO based ecofriendly piezoelectric nanogenerator for energy harvesting application. Nanotechnology 31(18), 185401 (2020)
P. Rajagopalan, S. Huang, L. Shi, H. Kuang, H. Jin, S. Dong, W. Shi, X. Wang, J. Luo, Novel insights from the ultra-thin film, strain-modulated dynamic triboelectric characterizations. Nano Energy 80, 105560 (2021)
F. Mokhtari, G.M. Spinks, C. Fay, Z. Cheng, R. Raad, J. Xi, J. Foroughi, Wearable electronic textiles from nanostructured piezoelectric fibers. Adv. Mater. Technol 5(4), 1900900 (2020)
G. Jiji, A retrospect on the role of piezoelectric nanogenerators in the development of the green world. RSC Adv. 7(53), 33642–33670 (2017)
X. Wang, J. Zhou, J. Song, J. Liu, N. Xu, Z.L. Wang, Piezoelectric field effect transistor and nanoforce sensor based on a single ZnO nanowire. Nano Lett. 6(12), 2768–2772 (2006)
S. Paria, S.K. Karan, R. Bera, A.K. Das, A. Maitra, B.B. Khatua, A facile approach to develop a highly stretchable PVC/ZnSnO3 piezoelectric nanogenerator with high output power generation for powering portable electronic devices. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res 55(40), 10671–10680 (2016)
C. Pan, L. Dong, G. Zhu, S. Niu, R. Yu, Q. Yang, Y. Liu, Z.L. Wang, High-resolution electroluminescent imaging of pressure distribution using a piezoelectric nanowire LED array. Nat. Photonics 7(9), 752–758 (2013)
R. Sun, S.C. Carreira, Y. Chen, C. Xiang, L. Xu, B. Zhang, M. Chen, I. Farrow, F. Scarpa, J. Rossiter, Stretchable piezoelectric sensing systems for self-powered and wireless health monitoring. Adv. Mater. Technol 4(5), 1900100 (2019)
H. Mei, M.F. Haider, R. Joseph, A. Migot, V. Giurgiutiu, Recent advances in piezoelectric wafer active sensors for structural health monitoring applications. Sensors 19(2), 383 (2019)
E.J. Ko, E.J. Lee, M.H. Choi, T.H. Sung, D.K. Moon, PVDF based flexible piezoelectric nanogenerators using conjugated polymer: PCBM blend systems. Sens. Actuators A: Phys 259, 112–120 (2017)
L. Yang, Q. Zhao, K. Chen, Y. Ma, Y. Wu, H. Ji, J. Qiu, PVDF-based composition-gradient multilayered nanocomposites for flexible high-performance piezoelectric nanogenerators. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 12(9), 11045–11054 (2020)
C. Yoon, B. Jeon, G. Yoon, Enhanced output performance of sandwich-type ZnO piezoelectric nanogenerator with adhesive carbon tape. Sens. Actuators A: Phys 318, 112499 (2021)
B. Saravanakumar, S.J. Kim, Growth of 2D ZnO nanowall for energy harvesting application. J. Phys. Chem. C 118(17), 8831–8836 (2014)
P. Rajagopalan, V. Singh, I.A. Palani, Enhancement of ZnO-based flexible nano generators via a sol–gel technique for sensing and energy harvesting applications. Nanotechnology 29(10), 105406 (2018)
W. Zhang, H. Yang, L. Li, S. Lin, P. Ji, C. Hu, D. Zhang, Y. Xi, Flexible piezoelectric nanogenerators based on a CdS nanowall for self-powered sensors. Nanotechnology 31(38), 385401 (2020)
R. Yu, X. Wang, W. Wu, C. Pan, Y. Bando, N. Fukata, Y. Hu, W. Peng, Y. Ding, Z.L. Wang, Temperature dependence of the piezophototronic effect in CdS nanowires. Adv. Funct. Mater 25(33), 5277–5284 (2015)
J.H. Kang, D.K. Jeong, S.W. Ryu, Transparent, flexible piezoelectric nanogenerator based on GaN membrane using electrochemical lift-off. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 9(12), 10637–10642 (2017)
W. Wu, L. Wang, Y. Li, F. Zhang, L. Lin, S. Niu, D. Chenet, X. Zhang, Y. Hao, T.F. Heinz, J. Hone, Piezoelectricity of single-atomic-layer MoS 2 for energy conversion and piezotronics. Nature 514(7523), 470–474 (2014)
X. Niu, W. Jia, S. Qian, J. Zhu, J. Zhang, X. Hou, J. Mu, W. Geng, J. Cho, J. He, X. Chou, High-performance PZT-based stretchable piezoelectric nanogenerator. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 7(1), 979–985 (2018)
K.I. Park, S. Xu, Y. Liu, G.T. Hwang, S.J.L. Kang, Z.L. Wang, K.J. Lee, Piezoelectric BaTiO3 thin film nanogenerator on plastic substrates. Nano Lett. 10(12), 4939–4943 (2010)
A.B. Djurišić, X. Chen, Y.H. Leung, A.M.C. Ng, ZnO nanostructures: growth, properties and applications. J. Mater. Chem 22(14), 6526–6535 (2012)
Ü Özgür, Y.I. Alivov, C. Liu, A. Teke, M. Reshchikov, S. Doğan, V.C.S.J. Avrutin, S.J. Cho, A.H. Morkoç, A comprehensive review of ZnO materials and devices. J. Appl. Phys 98(4), 11 (2005)
L. Zhang, S. Bai, C. Su, Y. Zheng, Y. Qin, C. Xu, Z.L. Wang, A high-reliability kevlar fiber‐ZnO nanowires hybrid nanogenerator and its application on self‐powered UV detection. Adv. Funct. Mater 25(36), 5794–5798 (2015)
Z.L. Wang, ZnO nanowire and nanobelt platform for nanotechnology. Mater. Sci. Eng.: R: Rep 64(3–4), 33–71 (2009)
R. Yu, C. Pan, J. Chen, G. Zhu, Z.L. Wang, Enhanced performance of a ZnO nanowire-based self‐powered glucose sensor by piezotronic effect. Adv. Funct. Mater 23(47), 5868–5874 (2013)
Q. Zheng, B. Shi, Z. Li, Z.L. Wang, Recent progress on piezoelectric and triboelectric energy harvesters in biomedical systems. Adv. Sci 4(7), 1700029 (2017)
X. Wang, C.J. Summers, Z.L. Wang, Large-scale hexagonal-patterned growth of aligned ZnO nanorods for nano-optoelectronics and nanosensor arrays. Nano Lett 4(3), 423–426 (2004)
J. Han, F. Fan, C. Xu, S. Lin, M. Wei, X. Duan, Z.L. Wang, ZnO nanotube-based dye-sensitized solar cell and its application in self-powered devices. Nanotechnology 21(40), 405203 (2010)
X. Wang, J. Shi, in Piezoelectric nanogenerators for self-powered nanodevices, ed. by Gianni Ciofani, Arianna Menciassi, (Springer, New York, 2012), pp. 135–172
X. Zhang, W. Wang, D. Zhang, Q. Mi, S. Yu, Self-powered ethanol gas sensor based on the piezoelectric Ag/ZnO nanowire arrays at room temperature. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron 32(6), 7739–7750 (2021)
M.K. Gupta, J.H. Lee, K.Y. Lee, S.W. Kim, Two-dimensional vanadium-doped ZnO nanosheet-based flexible direct current nanogenerator. ACS Nano 7(10), 8932–8939 (2013)
S.H. Shin, Y.H. Kim, M.H. Lee, J.Y. Jung, J.H. Seol, J. Nah, Lithium-doped zinc oxide nanowires–polymer composite for high performance flexible piezoelectric nanogenerator. ACS Nano 8(10), 10844–10850 (2014)
W.Y. Chang, T.H. Fang, J.H. Tsai, Electromechanical and photoluminescence properties of Al-doped ZnO nanorods applied in piezoelectric nanogenerators. J. Low Temp. Phys 178(3), 174–187 (2015)
N. Sinha, G. Ray, S. Godara, M.K. Gupta, B. Kumar, Enhanced piezoelectric output voltage and ohmic behavior in Cr-doped ZnO nanorods. Mater. Res. Bull 59, 267–271 (2014)
T. Zhao, Y. Fu, Y. Zhao, L. Xing, X. Xue, Ga-doped ZnO nanowire nanogenerator as self-powered/active humidity sensor with high sensitivity and fast response. J. Alloys Compd. 648, 571–576 (2015)
K. Batra, N. Sinha, S. Goel, H. Yadav, A.J. Joseph, B. Kumar, Enhanced dielectric, ferroelectric and piezoelectric performance of Nd–ZnO nanorods and their application in flexible piezoelectric nanogenerator. J. Alloys Compd. 767, 1003–1011 (2018)
P. Rajagopalan, P. Jakhar, I.A. Palani, V. Singh, S.J. Kim, Elucidations on the effect of lanthanum doping in ZnO towards enhanced performance nanogenerators. Int. J. Precision Eng. Manufacturing-Green Technol 7(1), 77–87 (2020)
D. Zhu, T. Hu, Y. Zhao, W. Zang, L. Xing, X. Xue, High-performance self-powered/active humidity sensing of Fe-doped ZnO nanoarray nanogenerator. Sens. Actuators B 213, 382–389 (2015)
Y.L. Chu, S.J. Young, L.W. Ji, T.T. Chu, P.H. Chen, Synthesis of Ni-doped ZnO nanorod arrays by chemical bath deposition and their application to nanogenerators. Energies 13(11), 2731 (2020)
N.A. Putri, V. Fauzia, S. Iwan, L. Roza, A.A. Umar, S. Budi, Mn-doping-induced photocatalytic activity enhancement of ZnO nanorods prepared on glass substrates. Appl. Surf. Sci 439, 285–297 (2018)
M. Bououdina, K. Omri, M. El-Hilo, A. El Amiri, O.M. Lemine, A. Alyamani, E.K. Hlil, H. Lassri, E. Mir, Structural and magnetic properties of Mn-doped ZnO nanocrystals. Phys. E: Low-dimensional Syst. Nanostruct 56, 107–112 (2014)
R. Vinod, M.J. Bushiri, S.R. Achary, V. Muñoz-Sanjosé, Quenching and blue shift of UV emission intensity of hydrothermally grown ZnO:Mn nanorods. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 191, 1–6 (2015)
M. Yuan, W. Fu, H. Yang, Q. Yu, S. Liu, Q. Zhao, Y. Sui, D. Ma, P. Sun, Y. Zhang, B. Luo, Structural and magnetic properties of Mn-doped ZnO nanorod arrays grown via a simple hydrothermal reaction. Mater. Lett. 63(18–19), 1574–1576 (2009)
D. Mukherjee, T. Dhakal, H. Srikanth, P. Mukherjee, S. Witanachchi, Evidence for carrier-mediated magnetism in Mn-doped ZnO thin films. Phys. Rev. B 81(20), 205202 (2010)
H.K. Yadav, K. Sreenivas, R.S. Katiyar, V. Gupta, Defect induced activation of Raman silent modes in rf co-sputtered Mn doped ZnO thin films. J. Phys. D 40(19), 6005 (2007)
N. Kicir, T. Tüken, M. Akyol, A. Ekicibil, Y. Ufuktepe, Structural, electronic and magnetic properties of Mn doped ZnO nanoplates synthesized by electrodeposition method. J. Electron Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom 237, 146892 (2019)
J. Wang, W. Chen, M. Wang, Properties analysis of Mn-doped ZnO piezoelectric films. J. Alloys Compd. 449(1–2), 44–47 (2008)
T. Yoshimura, H. Sakiyama, T. Oshio, A. Ashida, N. Fujimura, Direct piezoelectric properties of Mn-doped ZnO epitaxial films. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 49(2R), 021501 (2010)
X.M. Cheng, C.L. Chien, Magnetic properties of epitaxial Mn-doped ZnO thin films. J. Appl. Phys 93(10), 7876–7878 (2003)
M. Sima, M. Baibarac, E. Vasile, M. Sima, L. Mihut, Fabrication and Raman scattering of a core–shell structure based on Mn doped ZnO and barium titanate. Appl. Surf. Sci 355, 1057–1062 (2015)
V.V. Strelchuk, A.S. Nikolenko, O.F. Kolomys, S.V. Rarata, K.A. Avramenko, РМ Lytvyn, P. Tronc, C.O. Chey, O. Nur, M. Willander, Optical and structural properties of Mn-doped ZnO nanorods grown by aqueous chemical growth for spintronic applications. Thin Solid Films 601, 22–27 (2016)
R.S. Ganesh, E. Durgadevi, M. Navaneethan, V.L. Patil, S. Ponnusamy, C. Muthamizhchelvan, S. Kawasaki, P.S. Patil, Y. Hayakawa, Low temperature ammonia gas sensor based on Mn-doped ZnO nanoparticle decorated microspheres. J. Alloys Compd. 721, 182–190 (2017)
F. Ahmed, N. Arshi, M.S. Anwar, R. Danish, B.H. Koo, Mn-doped ZnO nanorod gas sensor for oxygen detection. Curr. Appl. Phys 13, 64–68 (2013)
Acknowledgements
Indumathi S would like to express her gratitude to the Indian Institute of Technology Indore for providing facilities and mechatronics instrumentation lab members for their valuable discussion.
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SI contributed to conceptualization, data curation, writing, reviewing, & editing of the manuscript, writing of the original draft, investigation, formal analysis, methodology, software, validation, and visualization. SV contributed to formal analysis, validation, reviewing & editing of the manuscript, project administration, supervision, validation, and funding acquisition. MM contributed to investigation, formal analysis, methodology, and writing, reviewing, & editing of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts of interest to declare.
Ethical approval
None of the authors of this paper conducted any research on humans and animals.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Indumathi, S., Venkatesan, S. & Manikandan, M. Influence of manganese addition in ZnO-based piezoelectric nanogenerator for mechanical energy harvesting. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 34, 563 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-09939-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-09939-x