Abstract
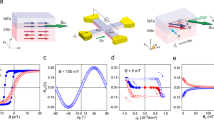
Magnetoelectric coupling is of tremendous importance for the information storage with respect to the pursuit of high density, low power consumption, high speed, and nonvolatile devices. Electric control of the exchange bias is a typical method for realizing the magnetoelectric coupling effect. However, there remains a tremendous challenge to realize a full electric control of exchange bias under the condition of zero magnetic field at room temperature. Here, a resistance device with a large area of the Si/Ta/Pt/Ta/NiFe/NiO/Cu foil exchange bias multilayer was prepared based on the anti-ferromagnetism and resistive switching property of NiO film. The resistance of the system changed into a low resistance state, when applying a certain voltage to the NiFe/NiO multilayers in the vertical direction at room temperature. The exchange bias field of multilayers with a low resistance state decreased. And it was a nonvolatile change. This was primarily related to the effect of the electron capture by the defective oxygen vacancy on the flipping and motion of the magnetic moment at the exchange bias interface. This work provides a potential method for the research of full electric control of magnetization and exploring the exchange bias mechanism.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data that support the findings of this study are included within the article.
References
I. Žutić, J. Fabian, S.D. Sarma, Rev. Mod. Phys. 76, 323 (2004)
S. Parkin, J. Xin, C. Kaiser, A. Panchula, K. Roche, M. Samant, Proc. IEEE. 91, 661 (2003)
N. Sharma, J.P. Bird, C. Binek, P.A. Dowben, D. Nikonov, A. Marshall, Semicond. Sci. Technol. 35, 073001 (2020)
M. Vopsaroiu, J. Blackburn, M.G. Cain, J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 40, 5027 (2007)
J. Nogués, I.K. Schuller, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 192, 203 (1999)
Y. Wang, B. Dai, B. Huang, Y. Ren, J. Xu, Z. Wang, S.J. Tan, J. Ni, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 27, 3778 (2016)
T. Blachowicz, A. Ehrmann, Coatings 11, 122 (2021)
S.M. Wu, S.A. Cybart, D. Yi, J.M. Parker, R. Ramesh, R.C. Dynes, Phys. Rev. Lett. 110, 067202 (2013)
A. Chen, Y.G. Zhao, P. Li, X. Zhang, R.C. Peng, H.L. Huang, L.K. Zou, X.L. Zheng, S. Zhang, P.X. Miao, Y.L. Lu, J.W. Cai, C.W. Nan, Adv. Mater. 28, 363 (2016)
X. Kang, Y.J. Gao, L.F. Liu, W. Chen, X. Zhao, Appl. Phys. Lett. 115, 103501 (2019)
B. Cui, C. Song, G.A. Gehring, F. Li, G.Y. Wang, C. Chen, J.J. Peng, H.J. Mao, F. Zeng, F. Pan, Adv. Funct. Mater. 25, 864 (2015)
N.P. Lu, P.F. Zhang, Q.H. Zhang, R.M. Qiao, Q. He, H.B. Li, Y.J. Wang, J.W. Guo, D. Zhang, Z. Duan, Z.L. Li, M. Wang, S.Z. Yang, M.Z. Yan, E. Arenholz, S.Y. Zhou, W.L. Yang, L. Gu, C.W. Nan, J. Wu, Y. Tokura, P. Yu, Nature 546, 124 (2017)
L.Q. Liu, C.F. Pai, Y. Li, H.W. Tseng, D.C. Ralph, R.A. Buhrman, Science 336, 555 (2012)
K. Garello, C.O. Avci, I.M. Miron, M. Baumgartner, A. Ghosh, S. Auffret, O. Boulle, G. Gaudin, P. Gambardella, Appl. Phys. Lett. 105, 212402 (2014)
C.Y. Guo, C.H. Wan, M.K. Zhao, C. Fang, T.Y. Ma, X. Wang, Z.R. Yan, W.Q. He, Y.W. Xing, J. Feng, X.F. Han, Phys. Rev. B. 104, 094412 (2021)
M.T. Johnson, C.B. Carter, H. Schmalzried, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 83, 1768 (2000)
W. Hu, N. Qin, G.H. Wu, Y.T. Lin, S.W. Li, D.H. Bao, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 134, 14658 (2012)
A. Chen, Y. Wen, B. Fang, Y.L. Zhao, Q. Zhang, Y.S. Chang, P.S. Li, H. Wu, H.L. Huang, Y.L. Lu, Z.M. Zeng, J.W. Cai, X.F. Han, T. Wu, X.X. Zhang, Y.G. Zhao, Nat. Commun. 10, 1 (2019)
S.S. Zhao, L. Wang, Z.Y. Zhou, C.L. Li, G.H. Dong, L. Zhang, B. Peng, T. Min, Z.Q. Hu, J. Ma, W. Ren, Z.G. Ye, W. Chen, P. Yu, C.W. Nan, M. Liu, Adv. Mater. 30, 1801639 (2018)
P.H. Lin, B.Y. Yang, M.H. Tsai, P.C. Chen, K.F. Huang, H.H. Lin, C.H. Lai, Nat. Mater. 18, 335 (2019)
L.J. Wei, Z.Z. Hu, G.X. Du, Y. Yuan, J. Wang, H.Q. Tu, B. You, S.M. Zhou, J.T. Qu, H.W. Liu, R.K. Zheng, Y. Hu, J. Du, Adv. Mater. 30, 1801885 (2018)
J.Y. Son, C.H. Kim, J.H. Cho, Y.H. Shin, H.M. Jang, ACS Nano 4, 3288 (2010)
D.H. Han, J.G. Zhu, J.H. Judy, J. Appl. Phys. 81, 4996 (1997)
J.R. Fermin, Rev. Mex. Fis. 63, 145 (2017)
J.S. Zhao, M. Zhang, S.F. Wan, Z.C. Yang, C.S. Hwang, A.C.S. Appl, Mater. Interfaces. 10, 1828 (2018)
R.D. McMichael, M.D. Stiles, P.J. Chen, W.F. Egelhoff Jr., Phys. Rev. B. 58, 8605 (1998)
Funding
This work was supported by the Unveiling and Leading Project of the 9th Institute of China Electronics Technology Group Corporation (No. 2022SK-007) and the Project of State Key Laboratory of Environment-friendly Energy Materials (No. 20fksy23, No. 21fksy27).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by Jing Ni, Yan Zhang, and Jun Li. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Jing Ni, Yan Zhang, and Bo Dai. All authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ni, J., Zhang, Y., Li, J. et al. Electric control of NiFe/NiO exchange bias through resistive switching under zero magnetic field. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 34, 552 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-09881-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-09881-y