Abstract
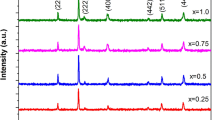
The structural, characteristic, dielectric, and magnetic features of Co0.5Ni0.5CrxFe2 − xO4 (\(0.0 \le x \le 1.0\) with a step of 0.2 x-concentration) nanoparticles are prepared via the hydrothermal method. The investigation of characteristics, structural, and magnetic features of the produced nanoparticles are examined through XRD, FT-IR, SEM–EDS, TEM-SAED, and VSM, respectively. AC conductivity and the dielectric investigations are also reported. According to the XRD measurements, all samples have the M-type hexagonal crystal structure nanocrystallites of between 27 and 97 nm. Refined structural parameters using Rietveld analysis are carried out using the TOPAS refinement program. A good match was observed between the diffraction patterns obtained and calculated by Rietveld analysis. Moreover, the morphological analyses indicate that the relatively small spherical structures of Ni–Co ferrites particles can be seen to change from spherical to relatively oval-shaped with increasing chromium content. The results of the FT-IR study show that the spinel structure has formed as predicted because the expected range of absorption bands is present. According to magnetic measurements, Cr-substituted Ni–Co ferrite nanostructures reveal a relatively soft ferromagnetic property. The coercive field (Hc) variation has a propensity to decrease in relation to the Cr-concentration. The electromagnetic constitutive parameters are calculated from measured S-parameters (S11 and S21) using network analyzer and the return losses of the samples are then obtained to determine microwave absorption properties. According to the dielectric and magnetic tangent losses or dissipation factors, both dielectric and magnetic features can mutually reinforce in terms of microwave absorption properties in the X-band. The Cr2O3 impurity peaks obtained by XRD analysis have an effect on the microwave absorption properties. The results of the microwave absorption based on each concentration reveal that there exist electromagnetic wave absorptions between approximately 11 GHz and 12.4 GHz in the X-band. The absorption trend is also towards the Ku-band.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
R. Jasrotia, G. Kumar, K.M. Batoo, S.F. Adil, M. Khan, R. Sharma, A. Kumar, V.P. Singh, Phys. B Condens. Matter 569, 1 (2019)
A. Teber, R. Bansal, I.S. Unver, Z. Mehmedi, Int. J. High Speed Electron. Syst. 27, 1840011 (2018)
B.I. Kharisov, H.V.R. Dias, O.V. Kharissova, Arab. J. Chem. 12, 1234 (2019)
H. Liang, H. Xing, M. Qin, H. Wu, Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 135, 105959 (2020)
R. Jasrotia, S. Kour, P. Puri, A.D. Jara, B. Singh, C. Bhardwaj, V.P. Singh, R. Kumar, Solid State Sci. 110, 106445 (2020)
H. Liang, L. Zhang, H. Wu, Small 18, 1 (2022)
P. Lathiya, J. W.-J. of the A. C. Society, and undefined 2022, Wiley Online Libr. 105, 2678 (2021).
V. Tukaram, S.S. Shinde, R.B. Borade, A.B. Kadam, Phys. B Condens. Matter. 577, 411783 (2020)
R. Willson, S. Sabale, V. Jadhav, V. Khot, Xiaoli, Z. Meiling Xin, and H. Chen, (n.d.).
K. Raju, G. Venkataiah, D.H. Yoon, Ceram. Int. 40, 9337 (2014)
H. Bi, X. Jiang, S. Li, J. Yang, Jinshu Xuebao/Acta Metall. Sin. 33, 1074 (1997)
J. Li, Y. Li, X. Tian, L. Zou, X. Zhao, S. Wang, S. Wang, Mater. Sci. Appl. 08, 1014 (2017)
C.A. Huang, C.K. Lin, Y.H. Yeh, Surf. Coatings Technol. 205, 139 (2010)
P.A. Shaikh, R.C. Kambale, A.V. Rao, Y.D. Kolekar, J. Alloys Compd. 492, 590 (2010)
K. Maaz, W. Khalid, A. Mumtaz, S.K. Hasanain, J. Liu, J.L. Duan, Phys. E Low-Dimensional Syst. Nanostruct. 41, 593 (2009)
M.B. Mohamed, K. El-Sayed, Compos. Part B Eng. 56, 270 (2014)
H. W. and H. F. M Bakr Mohamed, J. Phys. D. Appl. Phys. 43, 455409 (2010).
S. Singhal, R. Sharma, T. Namgyal, S. Jauhar, S. Bhukal, J. Kaur, Ceram. Int. 38, 2773 (2012)
M.B. Mohamed, K. El-Sayed, Mater. Res. Bull. 48, 1778 (2013)
B.G. Toksha, S.E. Shirsath, M.L. Mane, S.M. Patange, S.S. Jadhav, J. Phys. Chem. C 115, 20905 (2011)
M.J. Iqbal, M.R. Siddiquah, J. Alloys Compd. 453, 513 (2008)
S.S. More, R.H. Kadam, A.B. Kadam, A.R. Shite, D.R. Mane, K.M. Jadhav, J. Alloys Compd. 502, 477 (2010)
P.N. Vasambekar, C.B. Kolekar, A.S. Vaingankar, Mater. Chem. Phys. 60, 282 (1999)
S.C. Goh, C.H. Chia, S. Zakaria, M. Yusoff, C.Y. Haw, S. Ahmadi, N.M. Huang, H.N. Lim, Mater. Chem. Phys. 120, 31 (2010)
R.S. Melo, F.C. Silva, K.R.M. Moura, A.S. De Menezes, F.S.M. Sinfrônio, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 381, 109 (2015)
R. Kumar Kotnala, J. Shah, Int. J. Energy Res. 40, 1652 (2016)
R. Topkaya, O. Akman, S. Kazan, B. Aktaş, Z. Durmus, A. Baykal, J. Nanoparticle Res. 14, 1 (2012)
M.F. Sarac, J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 33, 397 (2020)
B. Alim, I. Han, L. Demir, Appl. Radiat. Isot. 112, 5 (2016)
M. Uğurlu, B. Alım, İ Han, L. Demir, J. Alloys Compd. 695, 2619 (2017)
M.N. Ashiq, F. Naz, M.A. Malana, R.S. Gohar, Z. Ahmad, Mater. Res. Bull. 47, 683 (2012)
L. Gama, E.P. Hernandez, D.R. Cornejo, A.A. Costa, S.M. Rezende, R.H.G.A. Kiminami, A.C.F.M. Costa, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 317, 29 (2007)
K. Vijaya Kumar, R. Sridhar, D. Ravinder, Process. Appl. Ceram. 12, 1 (2018)
P.N. Vasambekar, C.B. Kolekar, A.S. Vaingankar, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 186, 333 (1998)
U. Kurtan, R. Topkaya, A. Baykal, M.S. Toprak, Ceram. Int. 39, 6551 (2013)
T. Hou, B. Wang, M. Ma, A. Feng, Z. Huang, Y. Zhang, Z. Jia, G. Tan, H. Cao, G. Wu, Compos. Part B Eng. 180, 107577 (2020)
A. Teber, K. Cil, T. Yilmaz, B. Eraslan, D. Uysal, G. Surucu, A.H. Baykal, R. Bansal, Aerospace 4, 2 (2017)
J. Chen, J. Wu, H. Ge, D. Zhao, C. Liu, X. Hong, Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 82, 141 (2016)
C. Stergiou, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 426, 629 (2017)
A. Teber, I. Unver, H. Kavas, B. Aktas, R. Bansal, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 406, 228 (2016)
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by AT and MFS. The first draft of the manuscript was written by all authors. All authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Teber, A., Sarac, M.F. Cr-substituted nanocrystalline Ni–Co ferrites: tuning dielectric, magnetic, structural, X-band microwave absorption, and characteristic properties. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 34, 290 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-09793-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-09793-3