Abstract
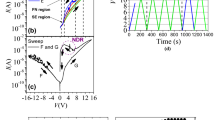
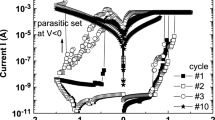
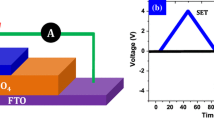
The electrochemical metallization (ECM) memory using polymer materials has attracted much attention for the development of future information devices. Particularly, the study of ionic transportation and current conduction mechanism in the metal–insulator-metal (MIM) structured device is crucial to realize the filament growth behaviour associated with the resistive switching memory characteristics. This work demonstrates the MIM device using the poly (vinylidene fluoride-hexafluoro propylene) (PVdF-HFP) sandwiched between an electrochemically active Ag electrode and an inert electrode (Au). The asymmetric electrode configuration of the Au/Ag/PVdF-HFP/Au device revealed bipolar-resistive switching behaviour for more than 102 continuous sweep cycles with a low SET/RESET voltage of + 1.26 V/ − 0.35 V, respectively. Note that, the device exhibited remarkably higher ON/OFF resistance ratio of ~ 107 with high data retention time for more than 104 s. Analysis of current conduction in the Au/Ag/PVdF-HFP/Au device shows that the electron transport is a combined effect of space charge limited (I ∝ Vα, α ~ 2), trap-filled charge limited (I ∝ Vα, α > 2), and ohmic conduction mechanism (I ∝ Vα, α ~ 1), which majorly altered between one cycle to another. Depth profiling X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy confirms that the conducting filament growth process varies from the initial to the final sweep cycle. It interprets a cycle-to-cycle variation in the resistive switching behaviour and its stability majorly constitutes by the variation of current conduction mechanism in the PVdF-HFP-based memristor.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data are available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
W.P. Lin, S.J. Liu, T. Gong, Q. Zhao, W. Huang, Polymer-based resistive memory materials and devices. Adv. Mater. 26, 570 (2014)
Y. Chen, G. Liu, C. Wang, W. Zhang, R.-W. Li, L. Wang, Polymer memristor for information storage and neuromorphic applications. Mater. Horizons 1, 489 (2014)
O. Bohnke, G. Frand, M. Rezrazi, C. Rousselot, C. Truche, Fast ion transport in new lithium electrolytes gelled with PMMA. 1: influence of polymer concentration. Solid State Ion. 66, 97 (1993)
H.-W. Chen, T.-P. Lin, F.-C. Chang, Ionic conductivity enhancement of the plasticized PMMA/LiClO4 polymer nanocomposite electrolyte containing clay. Polymer 43, 5281 (2002)
R. Waser, R. Dittmann, G. Staikov, K. Szot, Redox-based resistive switching memories—nanoionic mechanisms, prospects, and challenges. Adv. Mater. 21, 2632 (2009)
S. Moller, C. Perlov, W. Jackson, C. Taussig, S.R. Forrest, A polymer/semiconductor write-once read-many-times memory. Nature 426, 166 (2003)
B. Cho, S. Song, Y. Ji, T.W. Kim, T. Lee, Organic resistive memory devices: performance enhancement, integration, and advanced architectures. Adv. Funct. Mater. 21, 2806 (2011)
K. Krishnan, M. Aono, K. Terabe, T. Tsuruoka, Significant roles of the polymer matrix in the resistive switching behavior of polymer-based atomic switches. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 52, 445301 (2019)
Z. Wang, L. Wang, M. Nagai, L. Xie, M. Yi, W. Huang, Nanoionics-enabled memristive devices: strategies and materials for neuromorphic applications. Adv. Electron. Mater. 3, 1600510 (2017)
C.J. Park, S.W. Han, M.W. Shin, Laser-assisted interface engineering for functional interfacial layer of Al/ZnO/Al resistive random access memory (RRAM). ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 12(28), 32131 (2020)
M. Lübben, P. Karakolis, V. Ioannou-Sougleridis, P. Normand, P. Dimitrakis, I. Valov, Graphene-modified interface controls transition from VCM to ECM switching modes in Ta/TaOx based memristive devices. Adv. Mater. 27, 6202 (2015)
Y. Li, Q. Qian, X. Zhu, Y. Li, M. Zhang, Recent advances in organic-based materials for resistive memory applications. InfoMat 2, 995–1033 (2020)
M. Wu, Y. Ting, J. Chen, W. Wu, Low power consumption nanofilamentary ECM and VCM cells in a single sidewall of high-density VRRAM arrays. Adv. Sci. 6, 1902363 (2019)
E. Yalon, I. Karpov, V. Karpov, I. Riess, D. Kalaev, D. Ritter, Detection of the insulating gap and conductive filament growth direction in resistive memories. Nanoscale 7, 15434 (2015)
I. Valov, R. Waser, J.R. Jameson, M.N. Kozicki, Electrochemical metallization memories—fundamentals, applications, prospects. Nanotechnology 22, 254003 (2011)
Y. Yang, P. Gao, S. Gaba, T. Chang, X. Pan, W. Lu, Observation of conducting filament growth in nanoscale resistive memories. Nat. Commun. 3, 732 (2012)
K. Krishnan, T. Tsuruoka, C. Mannequin, M. Aono, Mechanism for conducting filament growth in self-assembled polymer thin films for redox-based atomic switches. Adv. Mater. 28, 640 (2016)
D.H. Kwon, K.M. Kim, J.H. Jang, J.M. Jeon, M.H. Lee, G.H. Kim, X.S. Li, G.S. Park, B. Lee, S. Han, M. Kim, C.S. Hwang, Atomic structure of conducting nanofilaments in TiO2 resistive switching memory. Nat. Nanotechnol. 5, 148 (2010)
I. Valov, E. Linn, S. Tappertzhofen, S. Schmelzer, J. van den Hurk, F. Lentz, R. Waser, Nanobatteries in redox-based resistive switches require extension of memristor theory. Nat. Commun. 4, 1771 (2013)
Y. Yang, R. Huang, Probing memristive switching in nanoionic devices. Nat. Electron. 1, 274 (2018)
K. Krishnan, M. Muruganathan, T. Tsuruoka, H. Mizuta, M. Aono, Highly reproducible and regulated conductance quantization in a polymer-based atomic switch. Adv. Funct. Mater. 27, 1605104 (2017)
Q. Chen, G. Liu, W. Xue, J. Shang, S. Gao, X. Yi, Y. Lu, X. Chen, M. Tang, X. Zheng, R.-W. Li, Controlled construction of atomic point contact with 16 quantized conductance states in oxide resistive switching memory. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 1, 789 (2019)
W. Zhang, C. Wang, G. Liu, X. Zhu, X. Chen, L. Pan, H. Tan, W. Xue, Z. Ji, J. Wang, C. Yu, R.W. Li, Thermally-stable resistive switching with a large ON/OFF ratio achieved in poly(triphenylamine). Chem. Commun. 50, 11856 (2014)
K. Krishnan, A. Gubicza, M. Aono, K. Terabe, I. Valov, T. Tsuruoka, Impact of moisture absorption on the resistive switching characteristics of a polyethylene oxide-based atomic switch. J. Mater. Chem. C 9, 11198 (2021)
Z. Wang, C. Li, P. Lin, M. Rao, Y. Nie, W. Song, Q. Qiu, Y. Li, P. Yan, J.P. Strachan, N. Ge, N. McDonald, Q. Wu, M. Hu, H. Wu, R.S. Williams, Q. Xia, J.J. Yang, In situ training of feed-forward and recurrent convolutional memristor networks. Nat. Mach. Intell. 1, 434 (2019)
L. Zhao, H.Y. Chen, S.C. Wu, Z. Jiang, S. Yu, T.H. Hou, H.S.P. Wong, Y. Nishi, Multi-level control of conductive nano-filament evolution in HfO2 ReRAM by pulse-train operations. Nanoscale 6, 5698 (2014)
M. Lanza, R. Waser, D. Ielmini, J.J. Yang, L. Goux, J. Sun, A.J. Kenyon, A. Mehonic, S. Spiga, V. Rana, S. Wiefels, S. Menzel, I. Valov, M.A. Villena, E. Miranda, X. Jing, F. Campabadal, M.B. Gonzalez, F. Aguirre, F. Palumbo, K. Zhu, J.B. Roldan, F.M. Puglisi, L. Larcher, T. Hou, T. Prodromakis, Y. Yang, P. Huang, T. Wan, Y. Chai, K.L. Pey, N. Raghavan, S. Duen, T. Wang, Q. Xia, S. Pazos, Standards for the characterization of endurance in resistive switching devices. ACS Nano 15(11), 17214 (2021)
A.M. Rana, T. Akbar, M. Ismail, E. Ahmad, F. Hussain, I. Talib, M. Imran, K. Mehmood, K. Iqbal, M.Y. Nadeem, Endurance and cycle-to-cycle uniformity improvement in tri-layered CeO2/Ti/CeO2 resistive switching devices by changing top electrode material. Sci. Rep. 7, 39539 (2017)
J. Jang, Y. Song, D. Yoo, K. Cho, Y. Kim, J. Pak, M. Min, T. Lee, Energy consumption estimation of organic nonvolatile memory devices on a flexible plastic substrate. Adv. Electr. Mater. 1, 1500186 (2015)
K. Krishnan, M. Aono, T. Tsuruoka, Kinetic factors determining conducting filament formation in solid polymer electrolyte based planar devices. Nanoscale 8, 13976 (2016)
S.H. Lee, H.L. Park, M.H. Kim, S. Kang, S.D. Lee, Interfacial triggering of conductive filament growth in organic flexible memristor for high reliability and uniformity. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 11, 30108 (2019)
M.G. Nair, S.R. Mohapatra, M.-R. Garda, B. Patanair, A.S. Fourcin, S. Thomas, Role of protic ionic liquid concentration in proton conducting polymer electrolytes for improved electrical and thermal properties. Mater. Res. Express 7, 064005 (2020)
G.-Y. Li, J. Li, Z.-J. Li, Y.-P. Zhang, X. Zhang, Z.-J. Wang, W.-P. Han, B. Sun, Y.-Z. Long, H.-D. Zhang, Hierarchical PVDF-HFP/ZnO composite nanofiber–based highly sensitive piezoelectric sensor for wireless workout monitoring. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 5, 766–775 (2021)
J. Pitawala, M.A. Navarra, B. Scrosati, P. Jacobsson, A. Matic, Structure and properties of Li-ion conducting polymer gel electrolytes based on ionic liquids of the pyrrolidinium cation and the bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide anion. J. Power Sources 245, 830 (2014)
S. Das, A. Ghosh, Structure, ion transport, and relaxation dynamics of polyethylene oxide/poly (vinylidene fluoride co-hexafluoropropylene)—lithium bis(trifluoromethane sulfonyl) imide blend polymer electrolyte embedded with ionic liquid. J. Appl. Phys. 119, 095101 (2016)
L.M. McGrath, J. Jones, E. Carey, J.F. Rohan, Ionic liquid based polymer gel electrolytes for use with germanium thin film anodes in lithium ion batteries. Chem. Open 8, 1429 (2019)
K. Polat, Energy harvesting from a thin polymeric film based on PVDF-HFP and PMMA blend. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 126, 497 (2020)
S. Wu, T. Tsuruoka, K. Terabe, T. Hasegawa, J.P. Hill, K. Ariga, M. Aono, A polymer-electrolyte-based atomic switch. Adv. Funct. Mater. 21, 93 (2011)
S. Ge, Y. Wang, Z. Xiang, Y. Cui, Reset voltage-dependent multilevel resistive switching behavior in CsPb1–xBixI3 perovskite-based memory device. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 10, 24620 (2018)
G. Ding, K. Zeng, K. Zhou, Z. Li, Y. Zhou, Y. Zhai, L. Zhou, X. Chen, S.T. Han, Configurable multi-state non-volatile memory behaviors in Ti3C2 nanosheets. Nanoscale 11, 7102 (2019)
X. Zhu, W. Su, Y. Liu, B. Hu, L. Pan, W. Lu, J. Zhang, R.W. Li, Observation of conductance quantization in oxide-based resistive switching memory. Adv. Mater. 24, 3941 (2012)
Y. Park, M.-K. Kim, J.-S. Lee, Emerging memory devices for artificial synapses. J. Mater. Chem. C 8, 9163 (2020)
E.W. Lim, R. Ismail, Conduction mechanism of valence change resistive switching memory: a survey. Electronics 4, 586 (2015)
A.S. Sokolov, Y.-R. Jeon, S. Kim, B. Ku, D. Lim, H. Han, M.G. Chae, J. Lee, B.G. Ha, C. Choi, Influence of oxygen vacancies in ALD HfO2-x thin films on non-volatile resistive switching phenomena with a Ti/HfO2-x/Pt structure. Appl. Surf. Sci. 434, 822 (2017)
W. Zhu, T.P. Chen, Y. Liu, S. Fung, Conduction mechanisms at low- and high-resistance states in aluminum/anodic aluminum oxide/aluminum thin film structure. J. Appl. Phys. 112, 063706 (2012)
Y.Q. Li, R.C. Fang, A.M. Zheng, Y.Y. Chu, X. Tao, H.H. Xu, S.J. Ding, Y.Z. Shen, Nonvolatile memory devices based on polyimides bearing noncoplanar twisted biphenyl units containing carbazole and triphenylamine side-chain groups. J. Mater. Chem. 21, 15643 (2011)
R. Ge, X. Wu, M. Kim, J. Shi, S. Sonde, L. Tao, Y. Zhang, J.C. Lee, D. Akinwande, Atomristor: nonvolatile resistance switching in atomic sheets of transition metal dichalcogenides. Nano Lett. 18, 434 (2018)
Y.C. Lai, D.Y. Wang, I.S. Huang, Y.T. Chen, Y.H. Hsu, T.Y. Lin, H.F. Meng, T.C. Chang, Y.J. Yang, C.C. Chen, F.C. Hsu, Y.F. Chen, Low operation voltage macromolecular composite memory assisted by graphene nanoflakes. J. Mater. Chem. C 1, 552 (2013)
W. Han, T. Kim, B. Yoo, H.-H. Park, Tunable dielectric properties of poly(vinylidenefluoride-co-hexafluoropropylene) films with embedded fluorinated barium strontium titanate nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 8, 4086 (2018)
X. Guo, J. Liu, L. Cao, Q. Liang, S. Lei, Nonvolatile memory device based on copper polyphthalocyanine thin films. ACS Omega 4, 10419 (2019)
D.I. Son, D.H. Park, W.K. Choi, S.-H. Cho, W.-T. Kim, T.W. Kim, Carrier transport in flexible organic bistable devices of ZnO nanoparticles embedded in an insulating poly(methyl methacrylate) polymer layer. Nanotechnology 20, 195203 (2009)
Y. Zhou, S.-T. Han, Y. Yan, L. Zhou, L.-B. Huang, J. Zhuang, P. Sonar, V.A.L. Roy, Ultra-flexible nonvolatile memory based on donor-acceptor diketopyrrolopyrrole polymer blends. Sci. Rep. 5, 10683 (2015)
C. Oliveira, C.R. Chaves, P. Bargiela, M.D.G.C. da Rocha, A.F. da Silva, J.F.D. Chubaci, M. Boström, C. Persson, M. Malta, Surface studies of the chemical environment in gold nanorods supported by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and ab initio calculations. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 15, 768–776 (2021)
L. Kong, B. Dasgupta, Y. Ren, P.K. Mohseni, M. Hong, X. Li, W.K. Chim, S.Y. Chiam, Evidences for redox reaction driven charge transfer and mass transport in metal-assisted chemical etching of silicon. Sci. Rep. 6, 36582 (2016)
C.Y. Dong, D.S. Shang, L. Shi, J.R. Sun, B.G. Shen, F. Zhuge, R.W. Li, W. Chen, Roles of silver oxide in the bipolar resistance switching devices with silver electrode. Appl. Phys. Lett. 98, 072107 (2011)
I. Roppolo, M. Castellino, K. Bejtka, G. Rizza, D. Perrone, P. Coulon, A. Chiappone, K. Rajan, S. Bocchini, C. Ricciardi, C.F. Pirri, A. Chiolerio, Resistive switching in polymer nanocomposites by matrix-controlled in situ nanoparticles generation. J. Phys. Chem. C 121, 14285 (2017)
N. Feng, Q. Wang, A. Zheng, Z. Zhang, J. Fan, S.-B. Liu, J.-P. Amoureux, F. Deng, Understanding the high photocatalytic activity of (B, Ag)-Codoped TiO2 under solar-light irradiation with XPS, solid-state NMR, and DFT calculations. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 135, 1607 (2013)
K. Rajan, A. Chiappone, D. Perrone, S. Bocchini, I. Roppolo, K. Bejtka, M. Castellino, C.F. Pirri, C. Ricciardi, A. Chiolerio, Ionic liquid-enhanced soft resistive switching devices. RSC Adv. 6, 94128–94138 (2016)
K. Rajan, S. Bocchini, A. Chiappone, I. Roppolo, D. Perrone, M. Castellino, K. Bejtka, M. Lorusso, C. Ricciardi, C.F. Pirri, A. Chiolerio, WORM and bipolar inkjet printed resistive switching devices based on silver nanocomposites. Flex. Print. Electron. 2, 024002 (2017)
M.G. Nair, M. Malakar, S.R. Mohapatra, A. Chowdhury, Synthesis of ZnO nanorods and observation of resistive switching memory in ZnO based polymer nanocomposites. AIP Conf. Proc. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5032506
K. Rajan, I. Roppolo, K. Bejtka, A. Chiappone, S. Bocchini, D. Perrone, C.F. Pirri, C. Ricciardi, A. Chiolerio, Performance comparison of hybrid resistive switching devices based on solution-processable nanocomposites. Appl. Surf. Sci. 443, 475–483 (2018)
A. Chiappone, M. Gillono, M. Castellino, K. Bejtka, K. Rajan, I. Roppolo, D. Perrone, S. Bocchini, C. Ricciardi, C.F. Pirri, A. Chiolerio, In situ generation of silver nanoparticles in PVDF for the development of resistive switching devices. Appl. Surf. Sci. 455, 418–424 (2018)
R. Deepak, M.G. Deb, S. Nair, A.L. Halder, S.R. Sharma, Mohapatra, Liquid phase exfoliation of MoS2 nano-sheets and observation of resistive switching memory in MoS2 Nano-sheets-PVDF-HFP composite films. Mater. Today Proc. 18, 5447–5453 (2019)
K. Rajan, S. Bocchini, A. Chiappone, I. Roppolo, D. Perrone, K. Bejtka, C. Ricciardi, C.F. Pirri, A. Chiolerio, Spin-coated silver nanocomposite resistive switching devices. Microelectron. Eng. 168, 27–31 (2017)
Acknowledgements
Dr. KK would like to thank Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB) and Department of Science & Technology (DST), India to carry out this work under early career research (ECR/2017/002615) and DST inspire faculty scheme (DST/INSPIRE/04/2016/000246).
Funding
This work was supported by Department of Science & Technology (DST), India through the DST inspire faculty scheme (DST/INSPIRE/04/ 2016/000246), and Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB) through the Early Career Research award (ECR/2017/002615).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The authors KK and SV have contributed for preparing the manuscript. The materials preparation, device fabrication, data collection, interpretation, and the manuscript construction was performed by KK. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript for publication.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Krishnan, K., Vijayaraghavan, S. Study of current conduction mechanism and resistive switching stability in the PVdF-HFP-based memristor. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 34, 211 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-09697-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-09697-2