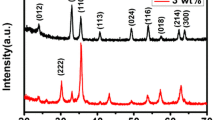
Abstract
Acetone is an important raw material for organic synthesis in modern industrial production. However, working in an environment with large acetone concentrations can cause explosive accidents in addition to irreversible damage to the central nervous system. Here, we fabricated a highly sensitive and fast response sensor based on p–n Co3O4–ZnO heterojunctions assembled by porous nanoflowers towards acetone gas through an environmentally friendly hydrothermal method. The 1% Co3O4–ZnO heterojunction has a band gap of 3.1767 eV and is narrower than ZnO with a band gap of 3.209 eV, which promotes electron transition and thus enhances gas-sensitive performance. In addition, the catalysis of Co3O4 reduces the activation energy of the reaction. According to the above advantages, the 1% Co3O4–ZnO heterojunction sensor displays a response as high as 615.5 toward 100 ppm of acetone and is about 16 times higher than that of the ZnO-based sensor. Moreover, long-term stability and good selectivity for various volatile organic compounds (VOCs) are achieved as well as the optimal operating temperature drops from 373 to 273 °C compared to ZnO. The scientific findings of this work will provide value for fabricating reliable acetone gas sensors.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data available on request from the authors. The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author, upon reasonable request.
References
S.M. Majhi, A. Mirzaei, H.W. Kim, S.S. Kim, T.W. Kim, Recent advances in energy-saving chemiresistive gas sensors: a review. Nano Energy. 79, 105369 (2021)
L. Cheng, S.Y. Ma, X.B. Li, J. Luo, W.Q. Li, F.M. Li, Y.Z. Mao, T.T. Wang, Y.F. Li, Highly sensitive acetone sensors based on Y-doped SnO2 prismatic hollow nanofibers synthesized by electrospinning. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 200, 181–190 (2014)
P.R. Galassetti, B. Novak, D. Nemet, C. Rose-Gottron, D.M. Cooper, S. Meinardi, R. Newcomb, F. Zaldivar, D.R. Blake, Breath ethanol and acetone as indicators of serum glucose levels: an initial report. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 7, 115–123 (2005)
Z. Cai, S. Park, Synthesis of pd nanoparticle-decorated SnO2 nanowires and determination of the optimum quantity of pd nanoparticles for highly sensitive and selective hydrogen gas sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 322, 128651 (2020)
J. Liu, L. Zhang, J. Fan, B. Zhu, J. Yu, Triethylamine gas sensor based on Pt-functionalized hierarchical ZnO microspheres. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 331, 129425 (2021)
M. Punginsang, D. Zappa, E. Comini, A. Wisitsoraat, G. Sberveglieri, A. Ponzoni, C. Liewhiran, Selective H2S gas sensors based on ohmic hetero-interface of Au-functionalized WO3 nanowires. Appl. Surf. Sci. 571, 151262 (2022)
C. Wang, Y. Li, F. Gong, Y. Zhang, S. Fang, H. Zhang, Advances in doped ZnO nanostructures for gas sensor. Chem. Record 20, 1553–1567 (2020)
T. Li, W. Zeng, Z. Wang, Quasi-one-dimensional metal-oxide-based heterostructural gas-sensing materials: a review. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 221, 1570–1585 (2015)
H.-J. Cho, V.T. Chen, S. Qiao, W.-T. Koo, R.M. Penner, I.-D. Kim, Pt-functionalized PdO nanowires for room temperature hydrogen gas sensors. ACS Sens. 3, 2152–2158 (2018)
M. Bai, H. Huang, Z. Liu, T. Zhan, S. Xia, X. Li, N. Sibirev, A. Bouravleuv, V.G. Dubrovskii, G. Cirlin, InAs/InP core/shell nanowire gas sensor: Effects of InP shell on sensitivity and long-term stability. Appl. Surf. Sci. 498, 143756 (2019)
Y. Qiu, Y. Wang, Morphology-controlled synthesis of Co9S8 nanotubes for ethanol gas sensors. Appl. Surf. Sci. 585, 152764 (2022)
J. Deng, B. Yu, Z. Lou, L. Wang, R. Wang, T. Zhang, Facile synthesis and enhanced ethanol sensing properties of the brush-like ZnO-TiO2 heterojunctions nanofibers. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 184, 21–26 (2013)
Z. Zhu, Z. Li, X. Xiong, X. Hu, X. Wang, N. Li, T. Jin, Y. Chen, ZnO/ZnSe heterojunction nanocomposites with oxygen vacancies for acetone sensing. J. Alloys Compd. 906, 164316 (2022)
D. Meng, D. Liu, G. Wang, Y. Shen, X. San, M. Li, F. Meng, Low-temperature formaldehyde gas sensors based on NiO-SnO2 heterojunction microflowers assembled by thin porous nanosheets. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 273, 418–428 (2018)
U.T. Nakate, Y.T. Yu, S. Park, High performance acetaldehyde gas sensor based on p-n heterojunction interface of NiO nanosheets and WO3 nanorods. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 344, 130264 (2021)
P. Hao, G. Qiu, P. Song, Z. Yang, Q. Wang, Construction of porous LaFeO3 microspheres decorated with NiO nanosheets for high response ethanol gas sensors. Appl. Surf. Sci. 515, 146025 (2020)
L.A. Horsfall, D.C. Pugh, C.S. Blackman, I.P. Parkin, The modification effect of Fe2O3 nanoparticles on ZnO nanorods improves the adsorption and detection capabilities of TEA. J. Mater. Chem. A Mater. 5, 2172–2179 (2017)
J.-H. Lee, J.-H. Kim, S.S. Kim, CuO-TiO2 p-n core-shell nanowires: sensing mechanism and p/n sensing-type transition. Appl. Surf. Sci. 448, 489–497 (2018)
C. Liu, B. Wang, T. Liu, P. Sun, Y. Gao, F. Liu, G. Lu, Facile synthesis and gas sensing properties of the flower-like NiO-decorated ZnO microstructures. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 235, 294–301 (2016)
L. Wang, Z. Lou, R. Zhang, T. Zhou, J. Deng, T. Zhang, Hybrid Co3O4/SnO2 core-shell nanospheres as real-time rapid-response sensors for ammonia gas. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8, 6539–6545 (2016)
S. Wang, Z. Li, P. Wang, C. Xiao, R. Zhao, B. Xiao, T. Yang, M. Zhang, Facile synthesis and enhanced gas sensing properties of In2O3 nanoparticle-decorated ZnO hierarchical architectures. CrystEngComm. 16, 5716 (2014)
X. Liang, J. Zhang, K. Zhang, X. Yang, M. Zhang, The modification effect of Fe2O3 nanoparticles on ZnO nanorods improves the adsorption and detection capabilities of TEA. Inorg. Chem. Front. 9, 259–266 (2022)
C. Qin, B. Wang, Y. Wang, Metal-organic frameworks-derived Mn-doped Co3O4 porous nanosheets and enhanced CO sensing performance. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 351, 130943 (2022)
R. Yoo, A.T. Güntner, Y. Park, H.J. Rim, H.-S. Lee, W. Lee, Sensing of acetone by Al-doped ZnO. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 283, 107–115 (2019)
K. Zhang, S. Qin, P. Tang, Y. Feng, D. Li, Ultra-sensitive ethanol gas sensors based on nanosheet-assembled hierarchical ZnO-In2O3 heterostructures. J. Hazard. Mater. 391, 122191 (2020)
C.D. Spencer, D. Schroeer, Mössbauer study of several cobalt spinels using Co57 and Fe57. Phys. Rev. B 9, 3658–3665 (1974)
T. Zhou, T. Zhang, J. Deng, R. Zhang, Z. Lou, L. Wang, P-type Co3O4 nanomaterials-based gas sensor: Preparation and acetone sensing performance. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 242, 369–377 (2017)
W. Tan, J. Tan, L. Li, M. Dun, X. Huang, Nanosheets-assembled hollowed-out hierarchical Co3O4 microrods for fast response/recovery gas sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 249, 66–75 (2017)
X. Zhang, Y. Xu, H. Liu, W. Zhao, A. Ming, F. Wei, Preparation of porous Co3O4 and its response to ethanol with low energy consumption. RSC Adv. 10, 2191–2197 (2020)
C. Qin, B. Wang, N. Wu, C. Han, C. Wu, X. Zhang, Q. Tian, S. Shen, P. Li, Y. Wang, Metal-organic frameworks derived porous Co3O4 dodecahedeons with abundant active Co3+ for ppb-level CO gas sensing. Appl. Surf. Sci. 506, 144900 (2020)
W. Geng, S. Ge, X. He, S. Zhang, J. Gu, X. Lai, H. Wang, Q. Zhang, Volatile Organic compound gas-sensing Properties of Bimodal Porous α-Fe2O3 with Ultrahigh Sensitivity and fast response. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 10, 13702–13711 (2018)
J. Li, P. Tang, J. Zhang, Y. Feng, R. Luo, A. Chen, D. Li, Facile synthesis and acetone sensing performance of hierarchical SnO2 Hollow Microspheres with controllable size and Shell Thickness. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 55, 3588–3595 (2016)
X. Chang, X. Li, X. Qiao, K. Li, Y. Xiong, X. Li, T. Guo, L. Zhu, Q. Xue, Metal-organic frameworks derived ZnO@MoS nanosheets core/shell heterojunctions for ppb-level acetone detection: ultra-fast response and recovery. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 304, 127430 (2020)
X.-T. Xue, L.-Y. Zhu, K.-P. Yuan, C. Zeng, X.-X. Li, H.-P. Ma, H.-L. Lu, D.W. Zhang, ZnO branched p-CuxO @n-ZnO heterojunction nanowires for improving acetone gas sensing performance. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 324, 128729 (2020)
J. Zhang, X. Jia, T. Liu, J. Yang, S. Wang, Y. Li, D. Shao, L. Feng, H. Song, Facile strategy to synthesize porous GO/ZnO heterostructure for enhanced acetone gas sensing properties. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 359, 131601 (2022)
H. Du, X. Li, P. Yao, J. Wang, Y. Sun, L. Dong, Zinc oxide coated tin oxide nanofibers for improved selective acetone sensing. Nanomaterials. 8, 509 (2018)
N. Zhang, H. Li, Z. Xu, R. Yuan, Y. Xu, Y. Cui, Enhanced acetone sensing property of a sacrificial template based on cubic-like MOF-5 doped by ni nanoparticles. Nanomaterials. 10, 386 (2020)
L. Guo, F. Chen, N. Xie, X. Kou, C. Wang, Y. Sun, F. Liu, X. Liang, Y. Gao, X. Yan, T. Zhang, G. Lu, Ultra-sensitive sensing platform based on Pt-ZnO-In2O3 nanofibers for detection of acetone. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 272, 185–194 (2018)
K.T. Alali, J. Liu, Q. Liu, R. Li, H. Zhang, K. Aljebawi, P. Liu, J. Wang, Enhanced acetone gas sensing response of ZnO/ZnCo2O4 nanotubes synthesized by single capillary electrospinning technology. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 252, 511–522 (2017)
Q. Ni, L. Sun, E. Cao, W. Hao, Y. Zhang, L. Ju, Enhanced acetone sensing performance of the ZnFe2O4/SnO2 nanocomposite. Appl. Phys. A 125, 796 (2019)
W. Li, X. Wu, N. Han, J. Chen, W. Tang, Y. Chen, Core-shell Au@ZnO nanoparticles derived from Au@MOF and their sub-ppm level acetone gas-sensing performance. Powder Technol. 304, 241–247 (2016)
M.Z. Ahmad, A.Z. Sadek, K. Latham, J. Kita, R. Moos, W. Wlodarski, Chemically synthesized one-dimensional zinc oxide nanorods for ethanol sensing. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 187, 295–300 (2013)
L. Cai, X. Dong, G. Wu, J. Sun, N. Chen, H. Wei, S. Zhu, Q. Tian, X. Wang, Q. Jing, P. Li, B. Liu, Ultrasensitive acetone gas sensor can distinguish the diabetic state of people and its high performance analysis by first-principles calculation. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 351, 130863 (2022)
X. Gao, F. Li, R. Wang, T. Zhang, A formaldehyde sensor: significant role of p-n heterojunction in gas-sensitive core-shell nanofibers. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 258, 1230–1241 (2018)
D.R. Miller, S.A. Akbar, P.A. Morris, Nanoscale metal oxide-based heterojunctions for gas sensing: a review. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 204, 250–272 (2014)
T. Wang, L. Cheng, Hollow hierarchical TiO2-SnO2-TiO2 composite nanofibers with increased active-sites and charge transfer for enhanced acetone sensing performance. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 334, 129644 (2021)
S. Wicker, K. Großmann, N. Bârsan, U. Weimar, Co3O4-A systematic investigation of catalytic and gas sensing performance under variation of temperature, humidity, test gas and test gas concentration. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 185, 644–650 (2013)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Numbers 61974057 and 50272026), the Applied Research and Development Project of Gansu Academy of Sciences (Grant Number 2018JK-02), and the Technological Project of Chengguan District of Lanzhou (Grant Number 2019RCCX0007).
Funding
This Study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Numbers 61974057 and 50272026), the Applied Research and Development Project of Gansu Academy of Sciences (Grant Number 2018JK-02), and the Technological Project of Chengguan District of Lanzhou (Grant Number 2019RCCX0007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
QC: Conceptualization, Methodology, Investigation, Writing - original draft. XW and HL: Methodology, Investigation, Writing - original draft. DH, YW, XT, YC, WW and MY: Writing - review & editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, Q., Wang, X., Huang, D. et al. Highly sensitive and fast response acetone gas sensor based on Co3O4–ZnO heterojunction assembled by porous nanoflowers. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 34, 128 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-09566-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-09566-y