Abstract
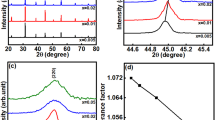
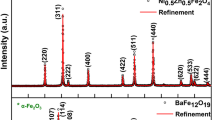
The compositions (Ba0.85Ca0.15TiO3)1-x-(CoFe2O4)x (BCT)1-x-(CFO)x (where x = 0.10, 0.20, 0.30 and 0.40) were synthesized to study the effect of simultaneous growth of ferroelectric and ferromagnetic phase for switching applications. X-ray diffraction confirms the double-phase formation in all composites possessing tetragonal and cubic symmetry. SEM micrograph strongly suggests the homogenous and uniform dispersion of the grains and grain size in the ceramic. The dielectric and electrical characteristics of ceramics have been thoroughly investigated in temperature range − 50 to 410 °C, and frequency (102–106 Hz). The grain and grain boundary also significantly contribute to relaxation process, shown by fitting of Nyquist plots. The frequency dependence of impedance plots has been used to characterize the electrical conduction of the sample at various observed temperatures, which demonstrate the Negative Temperature Coefficient of Resistance (NTCR) behavior. The composite with x = 0.40 of pure CFO in (BCT)1-x-(CFO)x composite showed maximum value of saturated magnetization, remnant magnetization and coercive field of Ms≈38 emu/g, Mr≈15 emg/g and Hc≈ 0.66 T, respectively.















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
W. Eerenstein, N. Mathur, J.F. Scott, Multiferroic and magnetoelectric materials. Nature 442(7104), 759–765 (2006)
Y. Yamasaki et al., Magnetic reversal of the ferroelectric polarization in a multiferroic spinel oxide. Phys. Rev. Lett. 96(20), 207204 (2006)
L. Chapon et al., Structural anomalies and multiferroic behavior in magnetically frustrated T b Mn2O5. Phys. Rev. Lett. 93(17), 177402 (2004)
K. Sadhana et al., Magnetic field induced polarization and magnetoelectric effect of Ba0.8Ca0.2TiO3-Ni0.2Cu0.3Zn0.5Fe2O4 nanomultiferroic. J. Appl. Phys. 113(17), 17C731 (2013)
G.A. Kaur et al., Structural and ferroelectric growth of Ba0.85Mg0.15TiO3–Ga2O3 ceramic through hydrothermal method. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 32(18), 23631–23644 (2021)
C. Lu et al., Multiferroic oxide thin films and heterostructures. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2(2), 021304 (2015)
B. Cui et al., Manipulation of electric field effect by orbital switch. Adv. Func. Mater. 26(5), 753–759 (2016)
D. Zhang et al., Magnetic-field-induced dielectric behaviors and magneto-electrical coupling of multiferroic compounds containing cobalt ferrite/barium calcium titanate composite fibers. J. Alloy. Compd. 740, 1067–1076 (2018)
N. Zhang et al., Investigation of the magnetoelectric effect driven by a single magnetic field in Tb1−xDyxFe2−y–Pb (Zr, Ti) O3 bilayers. J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 18(48), 10965 (2006)
I. Aazem et al., Electrode materials for stretchable triboelectric nanogenerator in wearable electronics. RSC Adv. 12(17), 10545–10572 (2022)
M. Lal et al., Study of structural and magnetoelectric properties of 1–x(Ba0.96Ca0.04TiO3)–x(ZnFe2O4) ceramic composites. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 29(1), 80–85 (2018)
Kumar, S. et al.: Influence of Ga2O3 on structural and morphological properties of lead-free BCT at low temperature. In AIP Conference Proceedings. AIP Publishing LLC (2022).
P. Zhu, Q. Zheng, R. Sun, Magnetic and dielectric properties of Ni0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4/barium titanate (BaTiO3) ceramic composites prepared by an in situ sol–gel method. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 26(11), 9074–9080 (2015)
N.M. Aimon et al., Multiferroic behavior of templated BiFeO3–CoFe2O4 self-assembled nanocomposites. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 7(4), 2263–2268 (2015)
D.H. Kim et al., Magnetic phase formation in self-assembled epitaxial BiFeO3–MgO and BiFeO3–MgAl2O4 nanocomposite films grown by combinatorial pulsed laser deposition. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 8(4), 2673–2679 (2016)
Kumar, S. et al.: A very low temperature growth of BaTiO3 nanoparticles by sol‐hydrothermal method. Physica Status Solidi (A), 2022.
J.B. Silva, W. De Brito, N.D. Mohallem, Influence of heat treatment on cobalt ferrite ceramic powders. Mater. Sci. Eng., B 112(2–3), 182–187 (2004)
L. Leonel et al., Structural characterization of barium titanate–cobalt ferrite composite powders. Ceram. Int. 37(4), 1259–1264 (2011)
Kaur, G.A., et al.: Effect of addition of Ga2O3 on structural and morphological properties of Ba0. 85Ca0. 15Zr0. 10Ti0. 90O3 by sol-hydrothermal method. In AIP Conference Proceedings. AIP Publishing LLC (2022).
D. Damjanovic et al., What can be expected from lead-free piezoelectric materials? Funct. Mater. Lett. 3(01), 5–13 (2010)
J. Ma et al., Recent progress in multiferroic magnetoelectric composites: from bulk to thin films. Adv. Mater. 23(9), 1062–1087 (2011)
W. Liu, X. Ren, Large piezoelectric effect in Pb-free ceramics. Phys. Rev. Lett. 103(25), 257602 (2009)
Z. Feng et al., Enhanced piezoelectric properties of solution-modified Ba (Zr0.2Ti0.8) O3–(Ba0.7Ca0.3) TiO3 thick films. J. Alloys Compounds 632, 651–654 (2015)
M. Zakhozheva et al., In situ electric field induced domain evolution in Ba (Zr0.2Ti0.8) O3–03 (Ba0.7Ca0.3) TiO3 ferroelectrics. Appl. Phys. Lett. 105(11), 112904 (2014)
P.W. Rehrig et al., Piezoelectric properties of zirconium-doped barium titanate single crystals grown by templated grain growth. J. Appl. Phys. 86(3), 1657–1661 (1999)
O. Thakur, C. Prakash, A. James, Enhanced dielectric properties in modified barium titanate ceramics through improved processing. J. Alloy. Compd. 470(1–2), 548–551 (2009)
M. Naveed-Ul-Haq et al., A new (Ba, Ca)(Ti, Zr) O 3 based multiferroic composite with large magnetoelectric effect. Sci. Rep. 6, 32164 (2016)
R. Sharma, P. Pahuja, R. Tandon, Structural, dielectric, ferromagnetic, ferroelectric and ac conductivity studies of the BaTiO3–CoFe1.8Zn0.2O4 multiferroic particulate composites. Ceram. Int. 40(7), 9027–9036 (2014)
S. Kashif, K. Shekhar, S. Seema, Role of ferrite phase on the structural, ferroelectric and magnetic properties of (1–x) BCT-x CZFO composites. Mater. Chem. Phys. 255, 123284 (2020)
M. Shandilya et al., Effect of addition of zinc ferrite on dielectric and magnetic properties of (Ba, Ca) TiO3 ceramics. Integr. Ferroelectr. 185(1), 147–154 (2017)
M.R. Raju, R. Choudhary, Effect of Zr+ 4 ion substitution on the structural, dielectric and electrical properties of Sr 5 LaTi 3 Nb 7 O 30 ceramics. J. Mater. Sci. 39(5), 1765–1771 (2004)
R. Ranjan et al., Structural and impedance spectroscopic studies of samarium modified lead zirconate titanate ceramics. Phys. B 404(20), 3709–3716 (2009)
Hasan, S.R. et al.: Investigation of impedance and electric modulus properties of bismuth layer-structured compound barium bismuth niobate (IV): p. 51–54 (2015).
T. Badapanda et al., Structural and impedance spectroscopy study of samarium modified barium zirconium titanate ceramic prepared by mechanochemical route. Curr. Appl. Phys. 14(9), 1192–1200 (2014)
A. Mahmood, Y. Iqbal, A. Ullah, Phase, microstructure and electrical characterization of Ba1−xLax(Zr0.6Ti0.4)1–x/4O3 ceramics. J Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 26(1), 113–121 (2015)
S. Li et al., Effect of composition fluctuation on structural and electrical properties of BZT-xBCT ceramics prepared by plasma activated sintering. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 37(5), 2067–2072 (2017)
A. Shukla, R. Choudhary, A. Thakur, Effect of Mn4+ substitution on thermal, structural, dielectric and impedance properties of lead titanate. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 20(8), 745–755 (2009)
R. Vivekanandan, T. Kutty, Grain boundary layer ceramic capacitors based on donor-doped Ba(Ti1− xSnx)O3. Mater. Sci. Eng., B 6(4), 221–231 (1990)
R. Ranjan et al., Structural, dielectric and transport properties of (PbSm)(ZrTi) O3 Ceramics. Mod. Phys. Lett. B 23(15), 1947–1957 (2009)
A. Singh et al., Ac conductivity and relaxation mechanism in Ba0.9Sr0.1TiO3. J Alloys Compounds 479(1), 39–42 (2009)
D. Carta et al., A structural and magnetic investigation of the inversion degree in ferrite nanocrystals MFe2O4 (M= Mn Co, Ni). J Phys. Chem. C 113(20), 8606–8615 (2009)
Funding
HP council of Science, Technology and Environment (HIMCOSTE), SPG/2021/004175 supported this work for providing the facilities and financial support to undertake the investigations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Monika Mishra: Investigation, Validation, Writing—original draft and Visualization. Shweta Thakur: Writing—original draft, Writing—review & editing, and Supervision. Sapna Thakur: Validation, and Writing—structural & morphology. Mamta Shandilya: Investigation, Validation, and Writing—magnetic behavior & editing. Radheshyam Rai: Conceptualization, Writing—review &editing, Supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mishra, M., Thakur, S., Thakur, S. et al. Comparative studies of structural, impedance and magnetic behavior of cobalt ferrite modified barium calcium titanate particulate composites. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 34, 141 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-09550-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-09550-6