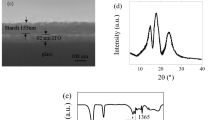
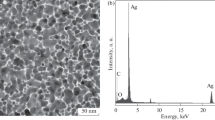
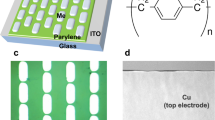
Abstract
A polymer based memristor as an artificial synapse has been one proficient approach to mimic biological synapse. It remembers the last state and modulate the output accordingly with subsequent voltage signals at low voltages and at high processing speeds. A functional layer of poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDOT) polymer is deposited by electro-polymerization using cyclic voltammetry. Here, we studied Pt/PEDOT/Al based memristor, which exhibited excellent artificial synapse like plasticity. We discuss the basic function of remembering and forgetting of the devices through synapticity and plasticity. STDP, which is the most important Hebbian learning rule for learning and memory showed up to 75% change in synaptic weight under wide range of input signals. The devices show excellent plasticity behavior mimicking biosynaptic behavior, which makes them a suitable system for neuromorphic applications.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during the current study are included in the manuscript or available from the corresponding author.
References
C.D. James, J.B. Aimone, N.E. Miner, C.M. Vineyard, F.H. Rothganger, K.D. Carlson, S.A. Mulder, T.J. Draelos, A. Faust, M.J. Marinella et al., A historical survey of algorithms and hardware architectures for neural-inspired and neuromorphic computing applications. Biol. Inspired Cogn. Archit. 19, 49–64 (2017)
P. Sheridan, W. Ma, W. Lu, Pattern recognition with memristor networks. In: 2014 IEEE International Symposium on circuits and systems (ISCAS), pp. 1078–1081 (2014). IEEE
S. Resisi, S.M. Popoff, Y. Bromberg, Image transmission through a dynamically perturbed multimode fiber by deep learning. Laser Photonics Rev. 15(10), 2000553 (2021)
F. Pedregosa, G. Varoquaux, A. Gramfort, V. Michel, B. Thirion, O. Grisel, M. Blondel, P. Prettenhofer, R. Weiss, V. Dubourg et al., Scikit-learn: machine learning in python. J. Mach. Learn Res. 12, 2825–2830 (2011)
S. Thiago, M. Walmir, A review of machine learning approaches to spam filtering. Expert Syst. Appl. 36(7), 10206–10222 (2009)
D. Ielmini, Brain-inspired computing with resistive switching memory (rram): devices, synapses and neural networks. Microelectron. Eng. 190, 44–53 (2018)
B.J. Shastri, A.N. Tait, T.F. de Lima, W.H. Pernice, H. Bhaskaran, C.D. Wright, P.R. Prucnal, Photonics for artificial intelligence and neuromorphic computing. Nat. Photonics 15(2), 102–114 (2021)
D. Kuzum, S. Yu, H.P. Wong, Synaptic electronics: materials, devices and applications. Nanotechnology 24(38), 382001 (2013)
J. von Neumann, The principles of large-scale computing machines. IEEE Ann. Hist. Comput. 10(04), 243–256 (1988)
S. Oh, H. Hwang, I. Yoo, Ferroelectric materials for neuromorphic computing. APL Mater. 7(9), 091109 (2019)
Y. Van De Burgt, A. Melianas, S.T. Keene, G. Malliaras, A. Salleo, Organic electronics for neuromorphic computing. Nat. Electron. 1, 386–397 (2018)
R. Waser, M. Aono, Nanoionics-based resistive switching memories. Nat. Mater. 6, 833840 (2007)
D.B. Strukov, G.S. Snider, D.R. Stewart, R.S. Williams, The missing memristor found. Nature 453(7191), 80–83 (2008)
S.H. Jo, T. Chang, I. Ebong, B.B. Bhadviya, P. Mazumder, W. Lu, Nanoscale memristor device as synapse in neuromorphic systems. Nano Lett. 10(4), 1297–1301 (2010)
H. Han, Z. Xu, K. Guo, Y. Ni, M. Ma, H. Yu, H. Wei, J. Gong, S. Zhang, W. Xu, Tunable synaptic plasticity in crystallized conjugated polymer nanowire artificial synapses. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2(3), 1900176 (2020)
Y.-Y. Zhao, W.-J. Sun, J. Wang, J.-H. He, H. Li, Q.-F. Xu, N.-J. Li, D.-Y. Chen, J.-M. Lu, All-inorganic ionic polymer-based memristor for high-performance and flexible artificial synapse. Adv. Funct. Mater. 30(39), 2004245 (2020)
V. Milo, C. Zambelli, P. Olivo, E. Pérez, K. Mahadevaiah, M.G. Mahadevaiah, O. Ossorio, C. Wenger, D. Ielmini, Multilevel hfo2-based rram devices for low-power neuromorphic networks. APL Mater. 7(8), 081120 (2019)
S. Deswal, A. Kumar, A. Kumar, Nbox based memristor as artificial synapse emulating short term plasticity. AIP Adv. 9(9), 095022 (2019)
K. Qian, G. Cai, V.C. Nguyen, T. Chen, P.S. Lee, Direct observation of conducting filaments in tungsten oxide based transparent resistive switching memory. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8(41), 27885–27891 (2016)
Y. Park, J.-S. Lee, Artificial synapses with short-and long-term memory for spiking neural networks based on renewable materials. ACS Nano 11(9), 8962–8969 (2017)
W. Lan, J. Gu, S. Wu, Y. Peng, M. Zhao, Y. Liao, T. Xu, B. Wei, L. Ding, F. Zhu, Toward improved stability of nonfullerene organic solar cells: impact of interlayer and built-in potential. Eco. Mat. 3(5), 12134 (2021)
C. Boehler, Z. Aqrawe, M. Asplund, Applications of pedot in bioelectronic medicine. Bioelectron. Med. 2(2), 89–99 (2019)
S. Choi, H. Lee, R. Ghaffari, T. Hyeon, D.-H. Kim, Recent advances in flexible and stretchable bio-electronic devices integrated with nanomaterials. Adv. Mater. 28(22), 4203–4218 (2016)
T. Feng, D. Xie, Y. Lin, H. Zhao, Y. Chen, H. Tian, T. Ren, X. Li, Z. Li, K. Wang et al., Efficiency enhancement of graphene/silicon-pillar-array solar cells by hno3 and pedot-pss. Nanoscale 4(6), 2130–2133 (2012)
B. Yin, Q. Liu, L. Yang, X. Wu, Z. Liu, Y. Hua, S. Yin, Y. Chen, Buffer layer of pedot: Pss/graphene composite for polymer solar cells. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 10(3), 1934–1938 (2010)
Y. Van De Burgt, E. Lubberman, E.J. Fuller, S.T. Keene, G.C. Faria, S. Agarwal, M.J. Marinella, A. Alec Talin, A. Salleo, A non-volatile organic electrochemical device as a low-voltage artificial synapse for neuromorphic computing. Nat. Mater. 16(4), 414–418 (2017)
H. Ha, O. Kim, Bipolar switching characteristics of nonvolatile memory devices based on poly (3, 4-ethylenedioxythiophene): poly (styrenesulfonate) thin film. Appl. Phys. Lett. 93(3), 265 (2008)
J.Y. Kim, H.Y. Jeong, J.W. Kim, T.H. Yoon, S.-Y. Choi, Critical role of top interface layer on the bipolar resistive switching of al/pedot: Pss/al memory device. Curr. Appl. Phys. 11(2), 35–39 (2011)
Z. Wang, F. Zeng, J. Yang, C. Chen, Y. Yang, F. Pan, Reproducible and controllable organic resistive memory based on al/poly (3, 4-ethylene-dioxythiophene): poly (styrenesulfonate)/al structure. Appl. Phys. Lett. 97(25), 271 (2010)
H. Okuzaki, H. Suzuki, T. Ito, Electromechanical properties of poly (3, 4-ethylenedioxythiophene)/poly (4-styrene sulfonate) films. J. Phys. Chem. B. 113(33), 11378–11383 (2009)
S. Li, F. Zeng, C. Chen, H. Liu, G. Tang, S. Gao, C. Song, Y. Lin, F. Pan, D. Guo, Synaptic plasticity and learning behaviours mimicked through ag interface movement in an ag/conducting polymer/ta memristive system. J. Mater. Chem. C 1(34), 5292–5298 (2013)
P. Yadav, S. Singhal, A. Patra, Electropolymerized poly (3, 4-ethylenedioxyselenophene) on flexible substrate: a comparative study of electronic and electrochromic properties with sulfur analogue and rigid substrate. Synth. Metals 260, 116264 (2020)
S. Möller, C. Perlov, W. Jackson, C. Taussig, S.R. Forrest, A polymer/semiconductor write-once read-many-times memory. Nature 426(6963), 166–169 (2003)
P.-J. Chia, L.-L. Chua, S. Sivaramakrishnan, J.-M. Zhuo, L.-H. Zhao, W.-S. Sim, Y.-C. Yeo, P.K.-H. Ho, Injection-induced de-doping in a conducting polymer during device operation: asymmetry in the hole injection and extraction rates. Adv. Mater. 19(23), 4202–4207 (2007)
G.-q Bi, M.-m Poo, Synaptic modifications in cultured hippocampal neurons: dependence on spike timing, synaptic strength, and postsynaptic cell type. J. Neurosci. 18(24), 10464–10472 (1998)
T. Ohno, T. Hasegawa, T. Tsuruoka, K. Terabe, J.K. Gimzewski, M. Aono, Short-term plasticity and long-term potentiation mimicked in single inorganic synapses. Nat. Mater. 10(8), 591–595 (2011)
T. Chang, S.-H. Jo, W. Lu, Short-term memory to long-term memory transition in a nanoscale memristor. ACS Nano 5(9), 7669–7676 (2011)
S. Song, K.D. Miller, L.F. Abbott, Competitive hebbian learning through spike-timing-dependent synaptic plasticity. Nat. Neurosci. 3(9), 919–926 (2000)
B.L. Jackson, B. Rajendran, G.S. Corrado, M. Breitwisch, G.W. Burr, R. Cheek, K. Gopalakrishnan, S. Raoux, C.T. Rettner, A. Padilla et al., Nanoscale electronic synapses using phase change devices. ACM J. Emerg. Technol. Comput. Syst. 9(2), 1–20 (2013)
E.L. Bienenstock, L.N. Cooper, P.W. Munro, Theory for the development of neuron selectivity: orientation specificity and binocular interaction in visual cortex. J. Neurosci. 2(1), 32–48 (1982)
Funding
N.S. would like to thank Council for Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) grant under senior research fellowship (SRF) for financial support. This research was funded by CSIR-NPL research support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AP prepared the PEDOT thin films. NS and AB did measurements. NS did data analysis and writing manuscript. AK did overall planning, editing, and supervision of work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Saini, N., Bisht, A., Patra, A. et al. Synaptic plasticity in electro-polymerized PEDOT based memristors for neuromorphic application. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 33, 27053–27061 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-09368-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-09368-2