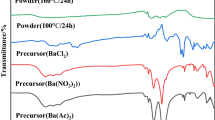
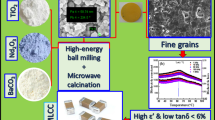
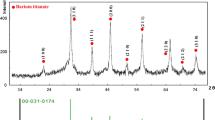
Abstract
The barium titanate ceramics (BaTiO3) are the key components of the multilayer ceramics capacitors (MLCCs). For a long time, huge efforts have been devoted to achieving the fine-grained BaTiO3 ceramics to satisfy the miniaturization and high integration of electronic devices. However, the controllable grain size which is particularly crucial to regulate the BDS, permittivity and dielectric loss has gained little attention. With the target of achieving the micro–nano-BaTiO3 ceramics with different sizes controllably, we prepare them via a self-assembly sintering method. By giving the size of the BaTiO3 powders and the combination way, the binary particle size self-assembly sintering method can controllably synthesize the ceramics with different grain sizes. When the powders combination is 400 nm + 80 nm, the relative density of the ceramics with grain size 450 nm is 92%. As the powders combination is 500 nm + 80 nm, the relative density of the ceramic with grain size 540 nm is 91%. When the ternary and quaternary particle size self-assembly sintering method is used to synthesize the ceramics, the relative density of the ceramics can be increased, but the controllability of the grain size has been reduced. The relative densities of the ceramics obtained by the ternary and quaternary systems were 95% and 96%, respectively, and the grain sizes of the ceramics were 610 nm and 676 nm, respectively. Therefore, the use of binary particle size self-assembly sintering method is beneficial to synthesize the micro–nano-BaTiO3 ceramics controllably.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available on reasonable request.
References
J.L. Li, F. Li, Z. Xu, S.J. Zhang, Multilayer lead-free ceramic capacitors with ultrahigh energy density and efficiency. Adv. Mater. 30(32), 1802155.1-1802155.7 (2018)
X.H. Hao, A review on the dielectric materials for high energy-storage application. J. Adv. Dielect. 3(1), 1330001–1330014 (2013)
M.X. Zhou, R.H. Liang, Z.Y. Zhou, X.L. Dong, Novel BaTiO3-based lead-free ceramic capacitors featuring high energy storage density, high power density, and excellent stability. J. Mater. Chem. C 6(31), 8528–8537 (2018)
L. Sun, Z.C. Shi, H.L. Wang, K. Zhang, D. Dastan, K. Sund, R.H. Fand, Ultrahigh discharge efficiency and improved energy density in rationally designed bilayer polyetherimide-BaTiO3/P(VDF-HFP) composites. J. Mater. Chem. A 8(11), 5750–5757 (2020)
W.Q. Zhang, X.T. Zhu, L. Liang, P. Yin, P.T. Xie, D. Dastan, K. Sun, R.H. Fan, Z.C. Shi, Significantly enhanced dielectric permittivity and low loss in epoxy composites incorporating 3d W-WO3/BaTiO3 foams. J. Mater. Sci. 56(6), 4254–4265 (2021)
M.L. Han, Z.C. Shi, W.Q. Zhang, K. Zhang, H.L. Wang, D. Dastan, R.H. Fan, Significantly enhanced high permittivity and negative permittivity in Ag/Al2O3/3D-BaTiO3/epoxy metacomposites with unique hierarchical heterogeneous microstructures. Compos. A 149, 106559.1-106559.9 (2021)
G. Wang, J.L. Li, X. Zhang, Z.M. Fan, F. Yang, A. Feteira, D. Zhou, D.C. Sinclair, T. Ma, X.L. Tan, D.W. Wang, I.M. Reaney, Ultrahigh energy storage density lead-free multilayers by controlled electrical homogeneity. Energy Environ. Sci. 12(2), 582–588 (2019)
Y.H. Huang, Y.J. Wu, B. Liu, T.N. Yang, J.J. Wang, J. Li, L.Q. Chen, X.M. Chen, From core–shell Ba0.4Sr0.6TiO3@SiO2 particles to dense ceramics with high energy storage performance by spark plasma sintering. J. Mater. Chem. A 6(10), 4477–4484 (2018)
C.J. Xiao, Z.H. Chi, S.M. Feng, F.Y. Li, L.C. Chen, C.Q. Jin, X.H. Wang, L.T. Li, R.Z. Chen, Ferroelectricity of 30 nm BaTiO3 ceramics prepared by high pressure sintering. J. Electroceram. 21(1–4), 39–42 (2008)
N.E. Horr, Z. Valdez-Nava, C. Tenailleau, S. Guillemet-Fritscha, Microstructure of Ba1−xLaxTiO3−δ ceramics sintered by spark plasma sintering. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 31(6), 1087–1096 (2011)
H. Guo, J. Guo, A. Baker, C.A. Randall, Hydrothermal-assisted cold sintering process: a new guidance for low-temperature ceramic sintering. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8(32), 20909–20915 (2016)
N.J. Lóh, L. Simão, C.A. Faller, A.D. NoniJr, O.R.K. Montedo, A review of two-step sintering for ceramics. Ceram. Int. 42(11), 12556–12572 (2016)
N. Yu, Y. Hidehiro, U. Akinori, T. Tokunaga, K. Sasaki, T. Yamamoto, Electric current-controlled synthesis of BaTiO3. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 100(9), 3843–3850 (2017)
T.K. Hyun, H.H. Young, Sintering of nanocrystalline BaTiO3. Ceram. Int. 30(7), 1719–1723 (2004)
M. Legallais, S. Fourcade, U.C. Chung, D. Michau, M. Maglione, F. Mauvy, C. Elissalde, Fast re-oxidation kinetics and conduction pathway in spark plasma sintered ferroelectric ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 38(2), 543–550 (2018)
M.Q. Xie, Y.X. Che, K. Liu, L.X. Jiang, L.M. Xue, Caking-inspired cold sintering of plastic supramolecular films as multifunctional platforms. Adv. Funct. Mater. 28(36), 1803370.1-1803370.8 (2018)
J. Guo, H.Z. Guo, A.L. Baker, M.T. Lanagan, E.R. Kupp, G.L. Messing, C.A. Randall, Cold sintering: a paradigm shift for processing and integration of ceramics. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 128(38), 11629–11633 (2016)
H. Guo, A. Baker, J. Guo, M.T. Lanagan, E.R. Kupp, G.L. Messing, C.A. Randall, Cold sintering process: a novel technique for low-temperature ceramic processing of ferroelectrics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 99(11), 3489–3507 (2016)
Y. Huan, X.H. Wang, J. Fang, L.T. Li, Grain size effects on piezoelectric properties and domain structure of BaTiO3 ceramics prepared by two step sintering. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 96(11), 3369–3371 (2013)
Y. Huan, X.H. Wang, J. Fang, L.T. Li, Grain size effect on piezoelectric and ferroelectric properties of BaTiO3 ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 34(5), 1445–1448 (2014)
D. Tingaud, P. Jenei, A. Krawczynska, F. Mompiou, J. Gubicza, G. Dirras, Investigation of deformation micro-mechanisms in nickel consolidated from a bimodal powder by spark plasma sintering. Mater. Charact. 99, 118–127 (2015)
Y.C. Shan, Z.H. Zhang, X.N. Sun, J.J. Xu, Q.H. Qin, J.T. Li, Fast densification mechanism of bimodal powder during pressureless sintering of transparent AlON ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 36(3), 671–678 (2016)
Y. Hirata, H. Fujita, T. Shimonosono, Compressive mechanical properties of partially sintered porous alumina of bimodal particle size system. Ceram. Int. 43(2), 1895–1903 (2017)
J.W. Oh, Y.J. Seong, D.S. Shin, S.J. Park, Investigation and two-stage modeling of sintering behavior of nano/micro-bimodal powders. Powder Technol. 352(15), 42–52 (2019)
H.Y. Xu, J. Zou, W.M. Wang, H. Wang, W. Ji, Z.Y. Fu, Densification mechanism and microstructure characteristics of nano- and micro-crystalline alumina by high-pressure and low temperature sintering. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 41(1), 635–645 (2021)
X.Y. Zhai, Y.J. Chen, Y.Q. Ma, S.C. Sun, J.X. Liu, A new strategy of binary-size particles model for fabricating fine grain, high density and low resistivity ITO target. Ceram. Int. 46(9), 13660–13668 (2020)
Q. Jin, B. Cui, X.T. Zhang, J. Wang, A binary particle self-assembly sintering method to realize controllable synthesis of fine-grained barium titanate ceramics. J. Electron. Mater. 50(1), 325–335 (2021)
Y. Yang, L. Gao, G.P. Lopez, B.B. Yellen, Tunable assembly of colloidal crystal alloys using magnetic nanoparticle fluids. ACS Nano 7(3), 2705–2716 (2013)
A.A. Shah, M. Ganesan, J. Jocz, M.J. Solomon, Direct current electric field assembly of colloidal crystals displaying reversible structural color. ACS Nano 8(8), 8095–8103 (2014)
H. Cong, B. Yu, J. Tang, Z.J. Li, X.S. Liu, Current status and future developments in preparation and application of colloidal crystals. Chem. Soc. Rev. 42(19), 7774–7800 (2013)
H.P. Ding, Z.K. Zhao, J.S. Jin, L. Deng, P. Gong, X.Y. Wang, Densification mechanism of Zr-based bulk metallic glass prepared by two-step spark plasma sintering. J. Alloys Compd. 850, 156724–156736 (2021)
A. Ndayishimiye, M.Y. Sengul, S.H. Bang, K. Tsuji, K. Takashima, T.H. Beauvoir, D. Denux, J.M. Thibaud, A.C.T. Duin, C. Elissalde, G. Goglio, C.A. Randall, Comparing hydrothermal sintering and cold sintering process: mechanisms, microstructure, kinetics and chemistry. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 40(4), 1312–1324 (2020)
J.M. Liu, H. Rongxia, R.B. Zhang, G.H. Liu, X.L. Wang, Z.D. Jia, L.M. Wang, Mechanism of flash sintering with high electric field: in the view of electric discharge and breakdown. Scr. Mater. 187, 93–96 (2020)
L. Sun, Z.C. Shi, B.L. He, H.L. Wang, S. Liu, M.H. Huang, J. Shi, D. Dastan, H. Wang, Asymmetric trilayer all-polymer dielectric composites with simultaneous high efficiency and high energy density: a novel design targeting for advanced energy storage capacitors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 31(35), 2100280.1-2100280.10 (2021)
S.B. Sun, Z.C. Shi, L. Sun, L. Liang, D. Dastan, B.L. He, H.L. Wang, M.H. Huang, R.H. Fan, Achieving concurrent high energy density and efficiency in all-polymer layered paraelectric/ferroelectric composites via introducing a moderate layer. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 13(23), 27522–27532 (2021)
P. Yin, Z.C. Shi, L. Sun, P.T. Xie, D. Dastan, K. Sun, R.H. Fan, Improved breakdown strengths and energy storage properties of polyimide composites: the effect of internal interfaces of C/SiO2 hybrid nanoparticles. Polym. Compos. 42(6), 3000–3010 (2021)
L. Liang, Z.C. Shi, X.L. Tan, S.B. Sun, M. Chen, D. Dastan, B.H. Dong, L.X. Cao, Largely improved breakdown strength and discharge efficiency of layer-structured nanocomposites by filling with a small loading fraction of 2D zirconium phosphate nanosheets. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 9(3), 2101646.1-2101646.13 (2022)
S.M. Xia, Z.C. Shi, L. Sun, S.B. Sun, D. Dastan, R.H. Fan, Suppressing the loss and enhancing the breakdown strengths of high-k materials via constructing layered structure. Mater. Lett. 312, 131654.1-131654.4 (2022)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 21071115), the Key Science and Technology Innovation Team of Shaanxi Province (2019TD-007).
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 21071115), the Key Science and Technology Innovation Team of Shaanxi Province (2019TD-007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. QJ designed research, performed research, analyzed data, and wrote the paper. ES and KC analyzed data and revised the English grammar. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, Q., Song, E. & Cai, K. Simple synthesis of barium titanate ceramics with controllable grain size. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 33, 26801–26812 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-09345-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-09345-9