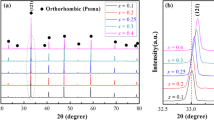
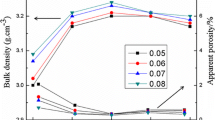
Abstract
Ca1.15Sm0.85Al0.85Ti0.15O4 ceramics with different ball milling temperatures were prepared by the solid-phase method. The X-ray diffraction results showed that the high ball milling temperature (45 ± 5 °C) led to the hydration of the material phase, resulting in the formation of a large amount of (CaO)3Al2O3(H2O)6 phase. The results of the scanning electronic microscope and the energy dispersive spectroscopy confirmed that the hydrated powders resulted in heterogeneous microstructure characteristics with a wide grain size distribution of ceramics sintered, which degraded dielectric characteristics, especially reducing the quality factor (around 30,000). However, controlling the ball mill temperature in the range of 20 ± 5 °C, there was no hydration occurring in the slurry. Thus, the sintered ceramics at optimum temperature exhibited excellent microwave dielectric properties, a dielectric constant of around 19.6, a high-quality factor of 70,000 GHz, and a near zero temperature coefficient (< ± 4 ppm/°C) of resonant frequency in a wide temperature range from − 40 to 125 °C.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
No data was used for the research described in the article.
References
M.T. Sebastian, H. Jantunen, R. Ubic, Other important materials. Microwave Mater. Appl. 2, 267–344 (2015)
H.C. Yang, S.R. Zhang, H.Y. Yang, Q.Y. Wen, Q. Yang, L. Gui et al., The latest process and challenges of microwave dielectric ceramics based on pseudo phase diagrams. J. Adv. Ceram. 10(5), 885–932 (2021)
W.P. Aleksandra, B. Izabela, W. Angelika, O. Agnieszka, M. Waldemar, W. Piotr et al., Synthesis and characterization of low loss dielectric ceramics prepared from composite of titanate nanosheets with barium ions. J. Nanomater. 2017, 1–9 (2017)
X.C. Fan, X.M. Chen, Effects of Ca/Ti cosubstitution upon microwave dielectric characteristics of CaSmAlO4 ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 92(2), 433–438 (2009)
W.S. Kim, E.S. Kim, K.H. Yoon, Effects of Sm3+ substitution on dielectric properties of Ca1−xSm2x/3TiO3 ceramics at microwave frequencies. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 82(8), 2111–2115 (1999)
R.C. Kell, A.C. Greenham, G.C.E. Olds, High-permittivity temperature-stable ceramic dielectrics with low microwave loss. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 56(7), 352–354 (1973)
M.T. Sebastian, K.P. Surendran, Tailoring the microwave dielectric properties of Ba(Mg1/3Ta2/3)O3 ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 26(10–11), 1791–1799 (2006)
F. Liu, L.J. Cheng, H. Li, S.J. Liu, Ordering-induced domains in sub-micron-sized Ba (Zn1/3Ta2/3) O3–BaZrO3 microwave ceramics. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 32(21), 26126–26136 (2021)
Y. Yu, Y.J. Wang, W.J. Guo, C.Q. Zhu, A. Ji, H. Wu et al., Grain size engineered 0.95 MgTiO3–0.05 CaTiO3 ceramics with excellent microwave dielectric properties and prominent mechanical performance. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 105(1), 299–307 (2022)
C.S. Hsu, C.L. Huang, K.H. Chiang, Microwave dielectric properties of B2O3 doped LaAlO3 ceramics at low sintering temperature. J. Mater. Sci. 38(16), 3495–3500 (2003)
X.K. Liu, L. He, M.X. Yu, R.Z. Zuo, Temperature-stable and ultralow-loss (1–x) CaSmAlO4–xSr2TiO4 microwave dielectric solid-solution ceramics. J. Mater. Sci. 56(23), 13190–13197 (2021)
X.Q. Liu, X.M. Chen, Y. Xiao, Preparation and characterization of LaSrAlO4 microwave dielectric ceramics. Mater. Sci. Eng.: B. 103(3), 276–280 (2003)
Y. Xiao, X.M. Chen, X.Q. Liu, Microstructures and microwave dielectric characteristics of CaRAlO4 (R= Nd, Sm, Y) ceramics with tetragonal K2NiF4 structure. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 87(11), 2143–2146 (2004)
I.M. Reaney, D. Iddles, Microwave dielectric ceramics for resonators and filters in mobile phone networks. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 89(7), 2063–2072 (2006)
D. Cruickshank, 1–2 GHz dielectrics and ferrites: overview and perspectives. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 23(14), 2721–2726 (2003)
X.C. Fan, M.M. Mao, X.M. Chen, Microstructures and microwave dielectric properties of the CaSmAlO4-based ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 91(9), 2917–2922 (2008)
S. He, K.G. Wang, X.J. Zhou, S. Hu, X.W. Luan, S.C. Zhou et al., Microwave dielectric properties of Ca1.15Sm0.85Al0.85Ti015O4 ceramics prepared by reaction sintering. Ceram. Int. 47(11), 15580–15584 (2021)
F. Lichtenberg, A. Herrnberger, K. Wiedenmann, Synthesis, structural, magnetic and transport properties of layered perovskite-related titanates, niobates and tantalates of the type AnBnO3n+ 2, A′ Ak−1BkO3k+1 and AmBm−1O3m. Prog. Solid State Chem. 36(4), 253–387 (2008)
S.N. Ruddlesden, P. Popper, The compound Sr3Ti2O7 and its structure. Acta Crystallogr. 11(1), 54–55 (1958)
Y.L. Liu, J.R. Liu, Q. Sun, D.W. Wang, K.R. Adair, J.N. Liang et al., Insight into the microstructure and ionic conductivity of cold sintered NASICON solid electrolyte for solid-state batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 11(31), 27890–27896 (2019)
Y.L. Liu, Q. Sun, D.W. Wang, K. Adair, J.N. Liang, X.L. Sun, Development of the cold sintering process and its application in solid-state lithium batteries. J. Power Sourc. 393, 193–203 (2018)
R.D. Shannon, Revised effective ionic radii and systematic studies of interatomic distances in halides and chalcogenides. Acta Crystallogr. 32(5), 751–767 (1976)
A.K. Chatterjee, G.I. Zhmoidin, The phase equilibrium diagram of the system CaO-Al2O3-CaF2. J. Mater. Sci. 7(1), 93–97 (1972)
S.H. Lei, H.Q. Fan, X.H. Ren, J.W. Fan, L.T. Ma, H.L. Tian, Microstructure, phase evolution and interfacial effects in a new Zn0.9Mg0.1TiO3-ZnNb2O6 ceramic system with greatly induced improvement in microwave dielectric properties. Scr. Mater. 146, 154–159 (2018)
Q.H. Yang, T. Luo, T. Yu, H.T. Yu, J.S. Liu, Improvement of microwave dielectric properties of Ba2Ti9O20 ceramics using [Zn1/3Nb2/3]4+ substitution for Ti4+. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 31(18), 15184–15191 (2020)
B. Tang, Q.Y. Xiang, Z.X. Fang, X. Zhang, Z. Xiong, H. Li et al., Influence of Cr3+ substitution for Mg2+ on the crystal structure and microwave dielectric properties of CaMg1-xCr2x/3Si2O6 ceramics. Ceram. Int. 45(9), 11484–11490 (2019)
M. Xiao, Q.Q. Gu, Z.Q. Zhou, P. Zhang, Study of the microwave dielectric properties of (La1−xSmx) NbO4 (x= 0–0.10) ceramics via bond valence and packing fraction. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 100(9), 3952–3960 (2017)
J. Iqbal, H.X. Liu, H. Hao, A. Ullah, M.H. Cao, Z.H. Yao, Phase, microstructure, and microwave dielectric properties of a new ceramic system:(1–x)Mg(Ti0.95Sn0.05)O3–xCaTiO3. Ceram. Int. 43(16), 14156–14160 (2017)
R.D. Shannon, Dielectric polarizabilities of ions in oxides and fluorides. J. Appl. Phys. 73(1), 348–366 (1993)
J. Guo, D. Zhou, S.L. Zou, H. Wang, L.X. Pang, X. Yao, Microwave dielectric ceramics Li2MO4−TiO2(M= Mo, W) with low sintering temperatures. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 97(6), 1819–1822 (2014)
J. Zhang, Y. Luo, Z.X. Yue, L.T. Li, Temperature stability, low loss and defect relaxation of MgO–TiO2 microwave dielectric ceramics modified by Ca0.8Sr0.2TiO3. Ceram. Int. 44(1), 141–145 (2018)
C. Zhang, R.Z. Zuo, J. Zhang, Y. Wang, Structure-dependent microwave dielectric properties and middle-temperature sintering of forsterite (Mg1–xNix)2SiO4 ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 98(3), 702–710 (2015)
S.J. Penn, N.M. Alford, A. Templeton, X.R. Wang, M.S. Xu, M. Reece et al., Effect of porosity and grain size on the microwave dielectric properties of sintered alumina. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 80(7), 1885–1888 (1997)
A. Templeton, X.R. Wang, S.J. Penn, S.J. Webb, L.F. Cohen, N.M. Alford, Microwave dielectric loss of titanium oxide. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 83(1), 95–100 (2000)
M.J. Wu, Crystal structure and microwave dielectric characteristics of Zr-substituted Ni0.5Ti0.5NbO4 ceramics. Funct. Mater. Lett. 1, 1–4 (2015)
Z.Y. Zhang, H.K. Zhu, Y. Zhang, Y.H. Chen, Z.X. Fu, K. Huang et al., Effects of the Ba3(VO4)2 additions on microwave dielectric properties of (Zr0.8Sn0.2)TiO4 ceramics. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 28(2), 2044–2048 (2017)
W. Lei, W.Z. Lu, X.C. Wang, Temperature compensating ZnAl2O4–Co2TiO4 spinel-based low-permittivity microwave dielectric ceramics. Ceram. Int. 38(1), 99–103 (2012)
S.Y. Cho, I.T. Kim, K.S. Hong, Microwave dielectric properties and applications of rare-earth aluminates. J. Mater. Res. 14(1), 114–119 (1999)
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the support from Suzhou Boom High Purity Materials Technology Co., Ltd and Sichuan Mianyang Weiqi Electronic Technology Co., Ltd.
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study concept and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were carried out by HF, HJ and TY. The first draft of the manuscript was written by HF. The study was supervised by HY. All the authors have commented on previous versions of the manuscript. Final draft read and approved by all authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, H., Jing, H., Yu, T. et al. Effect of hydration on microstructure and microwave dielectric properties of CaSmAlO4-based ceramics. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 33, 26135–26143 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-09300-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-09300-8