Abstract
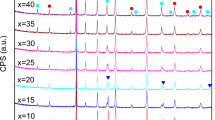
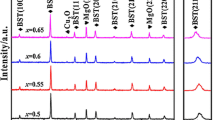
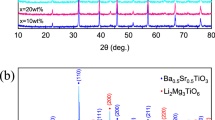
Spark plasma sintering (SPS) process was employed to synthesize Ba0.5Sr0.5TiO3-Mg2SiO4-MgO composite at 1200 °C for 5 min. We systematically investigated the effect of this sintering method on the dielectric properties of the samples. Experiment results show that while the dielectric content increases, the permittivity of the composite presents a decreasing tend monotonously; however, the tunability first increases abnormally and then decreases. Most importantly, the composite ceramics exhibits higher tunability than undoped Ba0.5Sr0.5TiO3. The interdiffusion in Ba0.5Sr0.5TiO3-Mg2SiO4-MgO composite was controlled via SPS process and enables us to produce composites with lower permittivity and relatively higher tunability simultaneously, which is hard to realize through traditional solid-state reaction method. Our findings reveal that the improved tunability is derived mainly from the low sintering temperature and short sintering time in SPS, which greatly suppress the doping effects. This provides valuable insights for future development of tunable applications.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data sharing not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
References
K.J. Choi, M. Biegalski, Y.L. Li, A. Sharan, J. Schubert, R. Uecker, P. Reiche, Y.B. Chen, X.Q. Pan, V. Gopalan, L.Q. Chen, D.G. Schlom, C.B. Eom, Science 306, 1005 (2004)
R.P. Jimenez, J.P. Rino, B. Fraygola, J.A. Eiras, J. Appl. Phys. 113, 074109 (2013)
A.K. Tagantsev, V.O. Sherman, K.F. Astafiev, J. Venkatesh, N. Setter, J. Electroceram. 11, 5 (2003)
A. Ahmed, I.A. Goldthorpe, A.K. Khandani, Appl. Phys. Rev. 2, 011302 (2015)
Z.Q. Gu, S. Pandya, A. Samanta, S. Liu, G. Xiao, C.J.G. Meyers, A.R. Damodaran, H. Barak, A. Dasgupta, S. Saremi, A. Polemi, L.Y. Wu, A.A. Podpirka, A. Will-Colel, C.J. Hawley, P.K. Davies, R.A. York, I. Grinberg, L.W. Martin, J.E. Spanier, Spanier. Nature 560, 622 (2018)
C.H. Lee, N.D. Orloff, T. Birol, Y. Zhu, V. Goian, E. Rocas, R. Haislmaier, E. Vlahos, J.A. Mundy, L.F. Kourkoutis, Y.F. Nie, M.D. Biegalski, J.S. Zhang, M. Bernhagen, N.A. Benedek, Y. Kim, J.D. Brock, R. Uecker, X.X. Xi, V. Gopalan, D. Nuzhnyy, S. Kamba, J.C. Booth, C.J. Fennie, D.G. Schlom, Nature 502, 532 (2013)
L.C. Sengupta, S. Sengupta, IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelect. Freq. Contr. 44, 792 (1997)
L.C. Sengupta, S. Sengupta, Mater. Res. Innov. 2, 278 (1999)
W. Chang, L.C. Sengupta, J. Appl. Phys. 92, 3941 (2002)
Y.Y. He, Y.B. Xu, T. Liu, C.L. Zeng, W.P. Chen, IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Contr. 57, 1505 (2010)
Y.Y. He, J.Y. Zhao, Y.B. Xu, C.N. Li, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 96, 1203 (2013)
X.J. Chou, J.W. Zhai, X. Yao, Appl. Phys. Lett. 91, 122908 (2007)
P. Liu, J.L. Ma, L. Meng, J. Li, L.F. Ding, J.L. Wang, H.W. Zhang, Mater. Chem. Phys. 114, 624 (2009)
A.B. Kozyrev, A.D. Kanareykin, E.A. Nenasheva, V.N. Osadchy, D.M. Kosmin, Appl. Phys. Lett. 95, 012908 (2009)
E.A. Nenasheva, N.F. Kartenko, I.M. Gaidamaka, O.N. Trubitsyna, S.S. Redozubov, A.I. Dedyk, A.D. Kanareykin, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 30, 395 (2010)
E.A. Nenasheva, N.F. Kartenko, I.M. Gaidamaka, S. Redozubov, A.B. Kozyrev, A.D. Kanareykin, Ferroelectrics 506, 174 (2017)
M. Lei, Z.J. Feng, Z. He, B.X. Liu, Y.Y. He, B.Y. Li, Y.B. Xu, Ceram. Int. 41, 8791 (2015)
X.M. Ma, S.S. Li, Y.Y. He, T. Liu, Y.B. Xu, J. Alloy. Compd. 739, 755 (2018)
Y.Y. He, Y.K. Peng, Y.B. Xu, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 102, 2706 (2019)
M.W. Zhang, J.W. Zhai, B. Shen, X. Yao, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 94, 3883 (2011)
B. Su, T.W. Button, J. Appl. Phys. 95, 1382 (2004)
V.O. Sherman, A.K. Tagantsev, N. Setter, D. Iddles, T. Price, J. Appl. Phys. 99, 074104 (2006)
U.C. Chung, C. Elissalde, M. Maglione, C. Estournès, M. Paté, J.P. Ganne, Appl. Phys. Lett. 92, 042902 (2008)
C. Elissalde, M. Maglione, C. Estournès, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 90, 973 (2007)
Y.Y. He, Y.K. Peng, X.M. Ma, Y.B. Xu, Materialia 5, 100217 (2019)
J.J. Zhang, J.W. Zhai, H.T. Jiang, X. Yao, Ferroelectrics 388, 74 (2009)
Y. Chen, X.L. Dong, R.H. Liang, J.T. Li, Y.L. Wang, J. Appl. Phys. 98, 064107 (2005)
Q.W. Zhang, J.W. Zhai, X. Yao, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 93, 2560 (2010)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China under grant numbers 61671214 and 61401152. The authors wish to acknowledge the Analytical and Testing Center in Huazhong University of Science and Technology for XRD and ESEM analysis.
Funding
Funding was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China, (Grant Nos. 61671214, 61401152).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by ZX and ZF. The first draft of the manuscript was written by ZX, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Z., Fu, Z., Ling, F. et al. Simultaneously with lower permittivity and higher tunability achieved in Ba0.5Sr0.5TiO3-Mg2SiO4-MgO composite ceramics prepared by spark plasma sintering. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 33, 23630–23638 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-09123-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-09123-7