Abstract
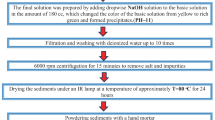
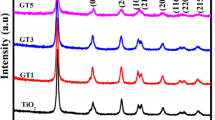
In this present work, titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles were prepared by a standard solid-state reaction technique. The structural analysis by the XRD pattern confirms a single rutile phase tetragonal structure. According to scanning electron microscopy analysis, the prepared sample shows uniform morphology with a mean particle size of 120–160 nm. The elemental analyses by energy dispersive spectroscopy confirm the absence of any impurity in the prepared sample. The UV–vis absorption data reveal that the band gap value of the synthesized compound was found to be 2.94 eV. From the optical transmittance spectrum, the average transmittance of the prepared sample in the visible range was found to be 55%. The field and temperature dependence of magnetization reveals a weak ferromagnetic behavior, with saturation magnetization of 0.002 µB and coercivity of 930 Oe. Most likely, the presence of defects and/or oxygen vacancies is thought to be responsible for this particular behavior. Dielectric properties observations reveal that the sample exhibits low dielectric loss in the higher frequency region, which is compatible with the Maxwell and Wagner model.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that supports the findings of this study are available within the article.
References
L. Chouhan, S.K. Srivastava, A comprehensive review on recent advancements in d0 ferromagnetic oxide materials for spintronics application. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 147, 106768 (2022)
A.J. Haider, Z.N. Jameel, I.H.M. Al-Hussaini, Review on titanium dioxide applications. Energy Proc. 157, 17–19 (2019)
P. Du, A. Bueno-Lopez, M. Verbaas, A.R. Almeida, M. Makkee, J.A. Moulijn, G. Mul, The effect of surface OH-population on the photocatalytic activity of rare-earth-doped P25-TiO2 in methylene blue degradation. J. Catal. 260(1), 75–80 (2008)
L. Chouhan, S.K. Srivastava, Observation of room temperature d0 ferromagnetism, band-gap widening, zero dielectric loss and conductivity enhancement in Mg-doped TiO2 (rutile + anatase) compounds for spintronics applications. J. Solid State Chem. 307, 122828 (2022)
G. Madras et al., J Am Ceram Soc. 90, 250–255 (2007)
L. Chouhan, G. Bouzerar, S.K. Srivastava, Effect of Mg-doping in tailoring d0 ferromagnetism of rutile TiO2 compounds for spintronics application. J. Mater. Sci: Mater. Electron. 32(8), 11193–11201 (2021)
B. O’regan, M. Gratzel, A low-cost, high-efficiency solar cell based on dye-sensitized colloidal TiO2 films. Nature 353, 737–740 (1991)
T. Fuyuki et al., Effects of small amount of water. J. Electrochem. Soc. 135, 248–250 (1988)
L. Chouhan, S.K. Panda, S. Bhattacharjee, B. Das, A. Mondal, B.N. Parida, R. Brahma, M.K. Manglam, M. Kar, G. Bouzerar, S.K. Srivastava, Room temperature d0 ferromagnetism, zero dielectric loss, and ac-conductivity enhancement in p-type Ag-doped SnO2 compounds. J. Alloys Compounds 870, 159515 (2021)
M. Thaidun, B.V. Rao, L.R.M. Reddy, G.V. Chalapathi, Structural, dielectric and optical properties of sputtered TiO2 nano-films. IOSR J. Appl. Phys 4(2), 49–53 (2013)
B. Sun, Y. Chen, L. Tao, H. Zhao, G. Zhou, Y. Xia, H. Wang, Y. Zhao, ACS Appl. Mater. Interf. 11(2), 2071–2081 (2018)
Y. Yu, F. Yang, S. Mao, S. Zhu, Y. Jia, L. Yuan, M. Salmen, B. Sun, Effect of anodic oxidation time on resistive switching memory behavior based on amorphous TiO2 thin films device. Chem. Phys. Lett. 706, 477–482 (2018)
Y. Xia, B. Sun, Y. Wei, B. Tao, Y. Zhao, Simple sol-gel method synthesis of 3-dimension Li4Ti5O12-TiO2 nanostructures using butterfly wings as biotemplates for high rate performance lithium-ion batteries. J. Alloys Compd. 705, 58–63 (2017)
M. Dubey, R. Kumar, S.K. Srivastava, M. Joshi, Visible light induced photodegradation of chlorinated organic pollutants using highly efficient magnetic Fe3O4/TiO2 nanocomposite. Optik 243, 167309 (2021)
M.H. Kafshgari, D. Kah, A. Mazare et al., Anodic titanium dioxide nanotubes for magnetically guided therapeutic delivery. Sci Rep 9, 13439 (2019)
S. Zhang et al., Synthesis, characterization of Cr-doped TiO2 nanotubes. J. Nanoparticle Res. 10, 871–875 (2008)
J. Rodriguez-Carvajal, Recent developments of the program FULLPROF. IUCr Newslett. 26, 12–19 (2001)
B. Dey, R. Narzary, L. Chouhan, S. Bhattacharjee, B.N. Parida, A. Mondal, S. Ravi, S.K. Srivastava, Crystal structure, optical and dielectric properties of Ag: ZnO composite-like compounds. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 33, 2855–2868 (2022)
S. Shalini, N. Prabavathy, R. Balasundaraprabhu et al., Effect of Na doping on structure, morphology, and properties of hydrothermally grown one-dimensional TiO2 nanorod structures. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 28, 3500–3508 (2017)
B. Dey, R. Narzary, S.K. Panda, A. Jyotirekha Mallick, S. Ravi, M. Kar, S.K. Srivastava, Room temperature d0 ferromagnetism, band-gap reduction, and high optical transparency in p-type K-doped ZnO compounds for spintronics applications. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 148, 106798 (2022)
K. Vijayalakshmi, S.D. Jereil, Influence of Fe catalytic doping on the properties of TiO2 nanoparticles synthesized by microwave method. J. Mater. Sci: Mater. Electron. 25, 5089–5094 (2014)
F. Aslan, H. Esen, F. Yakuphanoglu, Investigation of optical properties of TiO2 nano powder. Nat Eng Sci 5, 68–73 (2020)
L. Chouhan, R. Narzary, B. Dey, S.K. Panda, M.K. Manglam, L. Roy, R. Brahma, A. Mondal, M. Kar, S. Ravi, S.K. Srivastava, Tailoring room temperature d0 ferromagnetism, dielectric, optical and transport properties in Ag-doped rutile TiO2 compounds for spintronics applications. J. Mater. Sci: Mater. Electron. 32, 28163 (2021)
C.G. Koops, On the dispersion of resistivity and dielectric constant of some semiconductors at audio frequencies. Phys. Rev. 83(1), 121 (1951)
S.K. Srivastava, M. Kar, S. Ravi, Mater. Sci. Eng.: B 147(1), 84–89 (2008)
S.K. Srivastava, M. Kar, S. Ravi, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 320, 107 (2016)
H. Wang, Z. Zong, Y. Yan, Mechanism of multi-defect induced ferromagnetism in undoped rutile TiO2. J. Appl. Phys. 115(23), 233909 (2014)
A. Chanda, K. Rout, M. Vasundhara, S.R. Joshi, J. Singh, Structural and magnetic study of undoped and cobalt doped TiO2 nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 8(20), 10939–10947 (2018)
N. Rajkumar, K. Ramachandran, Oxygen deficiency and room temperature ferromagnetism in undoped and cobalt-doped TiO2 nanoparticles. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 10(3), 513–519 (2010)
M.C. Dimri, H. Khanduri, H. Kooskora, M. Kodu, R. Jaaniso, I. Heinmaa, A. Mere, J. Krustok, R. Stern, Room-temperature ferromagnetism in Ca and Mg stabilized cubic zirconia bulk samples and thin films prepared by pulsed laser deposition. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 45, 475003 (2012)
V.B. Kamble, S.V. Bhat, A.M. Umarji, Investigating thermal stability of structural defects and its effect on d0 ferromagnetism in undoped SnO2. J. Appl. Phys. 113, 244307 (2013)
S.K. Srivastava, P. Lejay, B. Barbara, O. Boisron, S. Pailhès, G. Bouzerar, Non-magnetic impurity induced magnetism in rutile TiO2: K compounds. J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 23, 442202 (2011)
Acknowledgments
This present research work is not supported by any kind of research grant. BD would like to thank Ms. Radha Narzary, IIT Guwahati for helping in characterizing the sample.
Funding
No funding has been received to carry out this research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
BD was involved in investigation, methodology, formal analysis, and writing manuscript; SKS contributed to conceptualization, methodology, visualization, writing—review and editing, and supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors state that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Dey, B., Srivastava, S.K. Crystal structure, microstructure, optical, dielectric, and magnetic properties of TiO2 nanoparticles. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 33, 23506–23514 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-09111-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-09111-x