Abstract
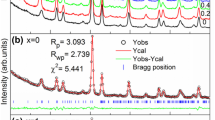
Aurivillius intergrowth multiferroic phases are inspiring to many researchers owing to their scientific and technological application point of view. We have synthesized the intergrowth of promising three-layered Bi3.25La0.75Ti3O12 (BLT) and four-layered Bi4NdTi3Fe0.7Co0.3O15 (BNTF) compounds. The X-ray diffraction (XRD) data was analyzed by comparing our data with a standard eight-layered compound (Bi9Ti6FeO27) and the lattice parameters were evaluated. Showing a shoulder peak at maximum XRD intensity peak (1 1 8) is considered to be a signature of intergrowth formation. Scanning electron microscopic images have shown non-uniform disk-like grains with no preferential orientation. In order to extract information about relaxation species, Nyquist plots (Cole–Cole plots) were drawn at different temperatures. AC activation energies were evaluated from \(\sigma\)ac vs. 1000/T plots, drawn at 10 kHz, 50 kHz and 100 kHz. Based on the impedance studies it is concluded that the hopping mechanism prefers through the doubly ionized oxygen atom vacancies and this phenomenon is corroborated to dielectric relaxation. Room temperature magnetic measurements display a weak ferromagnetic order. The intergrowth compound (BLT–BNTF) displayed ME coefficient (= 0.123 mV/cm–Oe) at lower magnetic fields. This is the most striking factor and helpful to fabricate room temperature Magnetoelectric sensors.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data sets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
D. Song, J. Yang, Y. Wang, Focus on the ferroelectric Polarization behavior of four-layered Aurivillius multiferroic thin film. Ceram. Int. 45, 15695–15702 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.02.054
D.L. Zhang, W.C. Huang, Z.W. Chen, W.B. Zhao, L. Feng, M. Li, Y.W. Yin, S.N. Dong, X.G. Li, structure evaluation and multiferroic properties in Cobalt doped Bi4NdTi3Fe1-xCoxO15- Bi3NdTi2Fe1-xCoxO12-δ Intergrowth Aurivillius Compounds. Sci. Rep. 7, 43540 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep43540
P. Mandal, M.J. Pitcher, J. Alaria, H. Niu, P. Borisov, P. Stamenov, J.B. Claridge, M.J. Rosseinky, Designing switchable polarization and magnetization at room temperature in an oxide. Nature 525, 363–366 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14881
W. Eerenstein, N.D. Mathur, J.F. Scott, Multiferroics: a magnetic twist for ferroelectricity. Nature 442, 759–765 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat1804
F.J. Yang, P. Su, C. Wei, X.Q. Chen, C.P. Yang, W.Q. Cao, Large magnetic response in (Bi4Nd)Ti4(Fe0.5Co0.5)O15 ceramic at room-temperature. J. Appl. Phys. 110, 126102 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3671418
X. Zuo, E. He, Z. Hui, J. Bai, J. Yang, Z. Xuebin, J. Dai, Magnetic, dielectric and magneto-dielectric properties of Aurivillius phase Bi4.25Nd0.75FeTi2(NbCo)0.5O15 ceramics. J. Mater. Sci: Mater. Electron. 30, 16337–16346 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-02004-6
H. Ju, Y. Lee, K.-T. Kim, I.H. Choi, C.J. Roh, S. Son, P. Park, J.H. Kim, T.S. Jung, J.H. Kim, K.H. Kim, J.-G. Park, J.S. Lee, Possible persistence of multiferroic order down to bilayer limit of van der Waals Material NiI2. Nano Lett. 21(12), 5126–5132 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.nanolett.1c01095
B. Sun, Y. Liu, P. Chen, Room-temperature multiferroic properties of single-crystalline FeWO4 nanowires. Scr. Mater. 89, 17–20 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2014.06.030
B. Sun, P. Han, W. Zhao, Y. Liu, P. Chen, White-light-controlled magnetic and ferroelectric properties in multiferroic BiFeO3 square nanosheets. J. Phys. Chem. C 118(32), 18814–18819 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1021/jp5064885
P.H. Fang, C.R. Robbins, B. Aurivillius, Ferroelectricity in the compound Bi4Ti3O12. Phys. Rev. 126(3), 892–892 (1962). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRev.126.892
B. Aurivillius, P.H. Fang, Ferroelectricity in the compound Ba2Bi4Ti5O18. Phys. Rev. 126(3), 893–896 (1962). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRev.126.893
C. Pirovano, Modelling the crystal structures of Aurivillius phases. Solid State Ion. 140(1–2), 115–123 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-2738(01)00699-3
A. Moure, Review and perspectives of Aurivillius stucturea as a lead-free piezoelectric systems. Appl. Sci. 8(1), 62 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3390/app8010062
K.R. Kendall, C. Navas, J.K. Thomas, H.-C. zur Loye, Recent developments in oxide ion conductors: Aurivillius phases. Chem. Mater. 8, 642–649 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1021/cm9503083
J.-B. Li, Y.-P. Huang, H.-B. Jin, G.-H. Rao, J.-K. Liang, Inhomogeneous structure and magnetic properties of Aurivillius ceramics Bi4Bin-3Ti3Fen+3O3n+3. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 96, 3920–3925 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1111/jace.12614
X. Mao, W. Wang, X. Chen, Y. Lu, Multiferroic properties of layer-structured Bi5Fe0.5Co0.5Ti3O15 ceramics. Appl. Phys. Lett. 95, 082901 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3213344
H. Uchida, R. Ueno, H. Funakubo, S. Koda, Crystal structure and ferroelectric properties of rare-earth substituted BiFeO3 thin films. J. Appl. Phys. 100(1), 014106 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2210167
E. Venkata Ramana, N.V. Prasad, D.M. Tobaldi, Z. Janez, M.K. Singh, J.H. Maria, M.P. Seabra, G. Prasad, M.V. Valente, Effect of samarium and vanadium co-doping on structure, ferroelectric and photocatalytic properties of bismuth titanate. RSC Adv. 7, 9680–9692 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1039/C7RA00021A
B. Shobhan Babu, G. Prasad, G.S. Kumar, N.V. Prasad, Studies on samarium modified SrBi4Ti4O15 Aurivillius ferroelectric ceramics. Ferroelectrics 572(1), 106–117 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1080/00150193.2020.1868876
Zulhadjri, T.P. Wendari, R. Ramadhani, Y.E. Putri, Imelda, La3+ substitution induced structural transformation in CaBi4Ti4O15 Aurivillius phases: synthesis, morphology, dielectric and optical properties. Ceram. Int. 47(16), 23549–23557 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.05.072
H. Sun, Y. Wu, T. Yao, Y. Lu, H. Shen, F. Huang, X. Chen, Electrical and magnetic properties of Aurivillius phase Bi5Fe1-xNixTi3O15 thin films prepared by chemical solution deposition. J. Alloys Compd. 765, 27–36 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.06.167
W. Fan, X. Jiang, C. Chen, X. Huang, X. Nie, X. Wang, Electrical properties and Curie temperature of Li/Ce co-doped BaBi4Ti4O15–Bi4Ti3O12 intergrowth ceramics. Ceram. Int. 48, 2833–2842 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.10.073
Y. Liu, X. Zhou, Z. Jia, H. Wu, G. Wu, Oxygen vacancy-induced dielectric polarization prevails in the electromagnetic wave-absorbing mechanism for Mn-based MOFs-derived composites. Adv. Funct. Mater. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202204499
S. Zhang, Z. Jia, Bo. Cheng, Z. Zhao, Lu. Feng, Wu. Guanglei, Recent progress of perovskite oxides and their hybrids for electromagnetic wave absorption: a mini-review. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-022-00458-7
Y. Liu, Z. Jia, Q. Zhan, Y. Dong, Xu. Qimeng, Wu. Guanglei, Magnetic manganese-based composites with multiple loss mechanisms towards broadband absorption. Nano Res. 15, 5590–5600 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-022-4287-5
Z. Jia, M. Kong, Yu. Bowen, Y. Ma, J. Pan, Wu. Guanglei, Tunable Co/ZnO/C@MWCNTs based on carbon nanotube-coated MOF with excellent microwave absorption properties. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 127, 153–163 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2022.04.005
T. Kikuchi, A. Watanabe, K. Uchida, A family of mixed-layer type bismuth compounds. Mater. Res. Bull. 12(3), 299–304 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1016/0025-5408(77)90148-9
T. Kobayashi, Y. Naguchi, M. Miyayama, Enhanced spontaneous polarization in super lattice stuctured Bi4Ti3O12-BaBi3Ti4O15 single crystals. Appl. Phys. Lett 86, 627 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1847693
W. Wang, S.P. Gu, X.Y. Mao, X.B. Chen, Effect of Nd modification on electrical properties of mixed-layer Aurivillius phase Bi4Ti3O12–SrBi4Ti4O15. J. Appl. Phys. 102, 024102 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2753582
J. Zhu, X.B. Chen, J.H. He, J.C. Shen, Raman scattering investigations on lanthanum-doped Bi4Ti3O12–SrBi4Ti4O15 intergrowth ferroelectrics. J. Solid State Chem. 178, 2832–2837 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssc.2005.06.028
J. Wang, L. Li, R. Peng, Z. Fu, M. Liu, Y. Lu, Structural evolution and multiferroics in Sr-doped Bi7Fe1.5Co1.5Ti3O21 ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 98(5), 1528–1535 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1111/jace.13495
V. Veenachary, E. Venkata Ramana, G.S. Kumar, G. Prasad, N.V. Prasad, Electrical studies on Bi4NdTi3Fe0.7Co0.3O15-Bi3NdTi2Fe0.7Co0.3O12–δ intergrowth Aurivillius. Trans. Ind. Ceram. Soc. 79, 113–119 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1080/0371750X.2020.1760139
H.E. Mgbemere, T.T. Akano, G.A. Schneider, Effect of bismuth titanate on the properties of potassium sodium niobate-based ceramics. J. Asian Ceram. Soc. 5(1), 49–55 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jascer.2016.12.006
W. Fan, X. Jiang, C. Chen, X. Huang, X. Nie, X. Wang, Electrical properties and Curie temperature of Li/Ce co-doped BaBi4Ti4O15–Bi4Ti3O12 intergrowth ceramics. Ceram. Int. 48(2), 2833–2842 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.10.073
B. Shobhan-Babu, S. Narendra-Babu, G. Prasad, G.S. Kumar, N.V. Prasad, Structure and dielectric properties of Sm3+ modified Bi4Ti3O12-SrBi4Ti4O15 intergrowth ferroelectrics. Process. Appl. Ceram. 14(3), 260–267 (2020). https://doi.org/10.2298/PAC2003260S
S. Sun, X. Yin, Engineered layer-stacked interfaces inside Aurivillius-type layered oxides enables superior ferroelectric property. Curr. Comput.-Aided Drug Des. 10(8), 710 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10080710
J.P. Kumar, K.S.K.R.C. Sekhar, T. Durga Rao, P.D. Babu, P. Tirupathi, Effect of sintering temperature on structural, dielectric, and electrical property studies of Bi4NdTi3FeO15 Aurivillius ceramics. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 32, 9675–9684 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-05628-9
W.C. Ferreira, G.L.C. Rodrigues, B.S. Araújo, F.A.A. de Aguiar, A.N.A. de Abreu Silva, P.B.A. Fechine, C.W. de Araujo Paschoal, A.P. Ayala, Pressure-induced structural phase transitions in the multiferroic four-layer Aurivillius ceramic Bi5FeTi3O15. Ceram. Int. 46(11), 18056–18062 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.04.122
S. Sun, Z. Chen, G. Wang et al., Nanoscale structural modulation and low-temperature magnetic response in mixed-layer Aurivillius-type oxides. Sci. Rep. 8, 871 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-19448-1
L. Sheng, X. Du, Q. Chao, P. Zheng, W. Bai, L. Li, F. Wen, W. Wu, L. Zheng, Enhanced electrical properties in Nd and Ce co-doped CaBi4Ti4O15 high temperature piezoceramics. Ceram. Int. 44, 18316–18321 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.07.044
T.P. Wendari, S. Arief, N. Mufti, A. Insani, J. Baas, G.R. Blake, Zulhadjri, Structure-property relationships in the lanthanide-substituted PbBi2Nb2O9 Aurivillius phase synthesized by the molten salt method. J. Alloys Compd. 860, 158440 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.158440
N. Thirumal Reddy, N.V. Prasad, G.S. Kumar, G. Prasad, Electrical studies on Zr-modified Bi3.25La0.75Ti3O12: a promising FRAM ceramic. Phase Transit. 87(12), 1246–1254 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1080/01411594.2014.948439
S.N. Padamavath, J. Omprakash, C.H. Sameera Devi, M. Vithal, G. Prasad, G.S. Kumar, Effect of simultaneous doping of Pr and Sm on electrical conductivity and relaxation process in BLSF-SrBi4Ti4O15. Ferroelectrics 474, 83–98 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1080/00150193.2015.996447
Y. Chen, J. Xu, S. Xie, Z. Tan, R. Nie, Z. Guan, Q. Wang, J. Zhu, Ion doping effects on the lattice distortion, and interlayer mismatch of Aurivillius-type bismuth titanate compounds. Materials 11(5), 821 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11050821
Q. Chang, H. Fan, C. Long, Effect of isovalent lanthanide cations compensation for volatilized A-site bismuth in Aurivillius ferroelectric bismuth titanate. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 28, 4637–4646 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-6102-0
S.K. Rout, A. Hussian, J.S. Lee, I.W. Kim, S.I. Woo, Impedance spectroscopy and morphology of SrBi4Ti4O15 ceramics prepared by soft chemical method. J. Alloys Compd. 477(1), 706–711 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2008.10.125
N.V. Prasad, G. Prasad, T. Bhimasankaram, Impedance studies on GdBi5Fe2Ti3O18 ceramic. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 15(14), 2053–2064 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1142/S0217979201004976
A.K. Jonscher, The ‘Universal’ dielectric response. Nature 267, 673–679 (1977)
J.R. Macdonald, W.B. Johnson, Fundamentals of Impedance spectroscopy. Impedance Spectrosc. Theory Exp. Appl. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119381860.ch1
D.C. Sinclair, A.R. West, Impedance and modulus spectroscopy of semiconducting BaTiO3 showing positive temperature coefficient of resistance. J. Appl. Phys. 66(8), 3850–3856 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.344049
P. Gupta, P.K. Mahapatra, R.N.P. Choudhary, Structural and electrical characteristics of rare-earth modified bismuth layer structured compounds. J. Alloys Compd. 863, 158457 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.158457
K. Dahake, P. Jain, O. Subohi, Impedance spectroscopy, dielectric, ferroelectric and electrical transport properties of Ba-doped Bi3TiNbO9 ceramics. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 32, 26770–26785 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-07054-3
E.V. Ramana, F. Figueiras, M.P.F. Graça, M.A. Valente, Observation of magnetoelectric coupling and local piezo response in modified (Na0.5Bi0.5)TiO3–BaTiO3-CoFe2O4 lead free composites. Dalton Trans. 43, 9934 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/C4DT00956H
Acknowledgements
One author (V Veenachary) is thankful to CSIR-HRDG, New Delhi for providing JRF/SRF. Partial funding by the grants from OU-DST PURSUE-II/80//2021 program is also thankfully acknowledged.
Funding
This work was partially supported by OU-DST PURSUE-II/80//2021 and CSIR-HRDG, No: 09/132(0875)/2018-EMR-I, New Delhi for providing Fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, impedance and ME measurements were made by VV. Raman spectroscopic measurements were performed by VSP. XRD and SEM measurements were made by SNB. The first draft of the manuscript was written by VV. NVP and GP reviewed and edited the manuscript, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Veenachary, V., Puli, V.S., Babu, S.N. et al. Electrical and magnetic studies on promising Aurivillius intergrowth compound. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 33, 22614–22627 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-09039-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-09039-2