Abstract
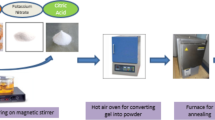
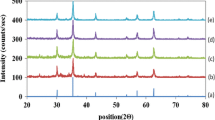
In recent years, alkali metal substituted spinel magnesium ferrites have been considered as potential materials for the fabrication of hydroelectric cells for the generation of green electricity without using any electrolyte. The purpose of potassium substitution was to observe the crystallite size variation, stretching molecular bonds, micro strain, porosity, defect centres, the surface morphology and HEC behavior of the prepared ferrites as monovalent potassium leads to occupying the octahedral site of Fe and Mg, which acts as reactive site for absorption and dissociation of the water molecule. The crystallite size and porosity of entire samples Mg1−xKxFe2O4 (x = 0.0–0.4) were found using Scherer’s equation between 11.15 and 36.20 nm and 22–53%, respectively, in XRD analysis, which decreased with the increase in alkali metal content. This decrease in lattice constant and unit cell volume may have been due to the compressive stress developed within the crystal structure, resulting in the negative strain as evident from W–H plot. Rietveld refinement was executed for pure and highest doped samples from the available XRD data to achieve the refined diffraction parameters. The FTIR analysis revealed the shift of molecular bands towards lower wavenumbers with the increase in K+ content. The SEM micrographs show agglomeration in the materials and porosity in the synthesized samples, and further, a decrease in grain size from 1.264 to 0.79 μm. The porous structure enhances the chemidissociation of water molecules followed by physisorption to generate the electric current. The PL spectra showed the emission wavelength between 275 and 400 nm, which indicates the presence of oxygen vacancies, leading to the chemidissociation of water molecules. Nanoparticles of the compositions have been investigated for hydroelectric cell application. The voltage–current characteristics performance of all the compositions fabricated as hydroelectric cells reveals the offload current and open circuit voltage between 1.4 and 7.8 mA and 0.74 and 0.86 V, respectively.















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
A. Nigam, S.J. Pawar, Structural, magnetic, and antimicrobial properties of zinc doped magnesium ferrite for drug delivery applications. Ceram. Int. l 46, 4058–4064 (2020)
P.T. Thakur, R. Sharma, M. Kumar, S.C. Katyal, P.B. Barman, V. Sharma, P. Sharma, Structural, morphological, magnetic and optical study of co-precipitated Nd3+ doped Mn-Zn ferrite nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 479, 317–325 (2019)
W. Montha, W. Maneeprakorn, N. Buatong, I.M. Tang, W.P. On, Synthesis of doxorubicin-PLGA loaded chitosan stabilized (Mn, Zn) Fe2O4 nanoparticles: biological activity and pH-responsive drug release. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 59, 235–240 (2016)
J. Wu, W. Jiang, Y. Shen, W. Jiang, R. Tian, Synthesis and characterization of mesoporous magnetic nanocomposites wrapped with chitosan gatekeepers for pH sensitive controlled release of doxorubicin. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 70, 132–140 (2017)
A. Bigham, F. Foroughi, M. Motamedi, M. Rafienia, Multifunctional nanoporous magnetic zinc silicate-ZnFe2O4 core-shell composite for bone tissue engineering applications. Ceram. Int. 44, 11798–11806 (2018)
G. Wang, F. Zhou, X. Li, J. Li, Y. Ma, J. Mu, Z. Zhang, H. Che, X. Zhang, Controlled synthesis of L-cysteine coated cobalt ferrite nanoparticles for drug delivery. Ceram. Int. 44, 13588–13594 (2018)
E.M.M. Ramosn, V.G. Chavez, B.I. Macias-Martínez, C.M. Lopez-Badillo, L.A. García-Cerda, Synthesis and characterization of maghemite nanoparticles for hyperthermia applications. Ceram. Int. 41, 397–402 (2015)
S. Praveen Kumar, K. Sakthipandi, R. Gayathiri, M. Sridhar Panday, V. Rajendran, Inorganic and nano-metal chemistry volume 47, 278–287 (2017)
A. Hossain, P. Bandyopadhyay, A. Karmakar, A.A. Ullah, R.K. Manavalan, K. Sakthipandi, N. Alhokbany, S.M. Alshehri, J. Ahmed, Ceram. Int. 48, 7325–7343 (2022)
D. Wei, Writable electrochemical energy source basedon graphene oxide. Sci. Rep. 5, 15173 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep15173
N. Miljkovic, D.J. Preston, R. Enright, E.N. Wang, Jumping-droplet electrostatic energy harvesting. Appl. Phys. Lett. 105, 013111 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4886798
Q. Meng, Y. Kenayeti, D.D.L. Chung, Battery in the formof a cement-matrix composite. Cem. Concr. Compos. 32, 829 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2010.08.009
A. Byrne, N. Holmes, B. Norton, Cement based batteriesand their potential for use in low power operations. Mater. Sci. Eng. 96, 012073 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/96/1/012073
R.K. Kotnala, J. Shah, Green hydroelectrical energy source based on water dissociation by nanoporous ferrite. Int. J. Energy Res. 40, 1652–1661 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1002/er.3545
J. Shah, K.C. Verma, A. Agarwal, R.K. Kotnala, Novel application of multiferroic compound for green electricity generation fabricated as hydroelectric cell. Mater. Chem. Phys. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2019.122068
S. Saini, J. Shah, R.K. Kotnala, K.L. Yadav, Nickel substituted oxygen deficient nanoporous lithium ferrite based green energy device hydroelectric cell. J. Alloy Compd. 827, 154334 (2020)
R. Gupta, J. Shah, R. Singh, R.K. Kotnala, Nonphotocatalytic water splitting process to generate green electricity in alkali doped zinc oxide based hydroelectric cell. Energy Fuels 35, 9714–9726 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.energyfuels.1c01164
J. Shah, S. Jain, B. Gahtori, C. Sharma, R.K. Kotnala, Water splitting on the mesoporous surface and oxygen vacancies of iron oxide generates electricity by hydroelectric cell. Mater. Chem. Phys. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2020.123981
P. Kumar, S. Vashishth, I. Sharma, V. Verma, Porous SnO2 ceramic-based hydroelectric cells for green power generation. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 32, 1052–1060 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-04880-9
R. Gupta, J. Shah, R. Das, S. Saini, R.K. Kotnala, Defect-mediated ionic hopping and green electricity generation in Al2 – xMgxO3-based hydroelectric cell. J. Mater. Sci. 56, 1600–1611 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-020-05280-4
R.K. Kotnala, R. Gupta, A. Shukla, S. Jain, A. Gaur, J. Shah, Metal oxide based hydroelectric cell for electricity generation by water molecule dissociation without electrolyte/acid. J. Phys. Chem. C 122, 18841–18849 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.8b04999
P. Heidari, S.M. Masoudpanah, Structural, magnetic and optical properties and photocatalytic activity of magnesium-calcium ferrite powders. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 148, 109681 (2021)
A. Goldman, Modem Ferrite Technology, 2nd edn. (Springer, Pittsburgh, 2006)
H.M. Widatallah, F.A.S. Al-Mamari, N.A.M. Al-Saqri, A.M. Gismelseed, I.A. Al- Omari, T.M.H. Al-Shahumi, A.F. Alhaj, A.M. Abo, E. Ata, M.E. Elzain, Mossbauer and magnetic studies of Mg1þ2xSbxFe2–3xO4 spinel ferrites. Mater. Chem. Phys. 140, 97–103 (2013)
Q. Lin, Y. He, J. Lin, F. Yang, L. Wang, J. Dong, Structural and magnetic studies of Mg substituted cobalt composite oxide catalyst Co1 – xMgxFe2O4. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 469, 89–94 (2019)
S.B. Somvanshi, S.R. Patade, D.D. Andhare, S.A. Jadhav, M.V. Khedkar, P.B. Kharat, P.P. Khirade, K.M. Jadhav, Hyperthermic evaluation of oleic acid coated nano-spinel magnesium ferrite: enhancement via hydrophobic-to-hydrophilic surface transformation. J. Alloy Compd. 835, 155422 (2020)
T. Ajeesha, A. Ashwini, A. Mary George, J. Manikandan, Y. Arul Mary, M.A. Slimani, A. Almessiere, Baykal, Nickel substituted MgFe2O4 nanoparticles via co-precipitation method for photocatalytic applications. Phys. B: Condens. Matter 606, 412660 (2021)
B.D. Cardoso, A. Rodrigues, B.G. Almeida, C.O. Amorim, V.S. Amaral, E. Castanheira, P. Coutinho, Stealth magneto liposomes based on calcium-substituted magnesium ferrite nanoparticles for curcumin transport and release. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21, 3641 (2020)
A. Lagashetty, A. Pattar, S.K. Ganiger, Heliyon (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e01760
E.E. Ateia, A.A.H. El-Bassuony, G. Abdellatif et al., The impact of Ni substitution on the structural and magnetic properties of Mg nano-ferrite. Silicon 10, 1687–1696 (2018)
E. Fantozzi, E. Rama, C. Calvio, B. Albini, P. Galinetto, M. Bini, Silver doped magnesium ferrite nanoparticles: physico-chemical characterization and antibacterial activity. Materials 14, 2859 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma1411285
N. Okasha, Influence of silver doping on the physical properties of Mg ferrites. J. Mater. Sci. 43, 4192–4197 (2008)
S.B. Das, V. Kumar, M.M. Siddiqui, N. Kumar, R.K. Singh, R. Kumar, Structural characterization and investigation of magneto-optic and multiferroic properties of nanostructured CoFe2O4 prepared by sol–gel derived facile chemical route. Mater. Today: Proc. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2021.07.234
V. Kumar, N. Kumar, S.B. Das, R.K. Singh, K. Sarkar, M. Kumar, Mater. Today: Proc. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2021.05.215
K. Sarkar, V. Kumar, S. Mukherjee, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 31, 14314–14321 (2020)
K. Sarkar, V. Kumar, S.B. Das, M. Kumar, A. Manash, C. Biswas, S. Mukherjee, Mater. Today: Proc. 44, 2459–2465 (2021)
K. Sarkar, V. Kumar, S. Bhushan Das, M. Kumar, R. Srivastava, Mater. Today: Proc. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2021.02.476
S. Bhushan Das, R.K. Singh, V. Kumar, N. Kumar, S. Kumar, Mater. Today: Proc. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2021.04.001
K.K. Chattopadhyay, A. Banerjee, Introduction to Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, (PHI Learning, 2009). ISBN:9788120336087
S. Saini, K.L. Yadav, J. Shah, R.K. Kotnala, ACS Appl. Energy Mater. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsaem.2c00708
T.K. Pathak, N.H. Vasoya, V.K. Lakhani, K.B. Modi, Structural and magnetic phase evolution study on needle-shaped nanoparticles of magnesium ferrite. Ceram. Int. 36, 275–281 (2010)
N.T. To Loan, N.T. Hien Lan, N.T. Thuy Hang, N.Q. Hai, D.T. Tu Anh, Vu. ThiHau, L.V. Tan, T.V. Tran, CoFe2O4 nanomaterials: effect of annealing temperature on characterization, magnetic, photocatalytic, and photo-fenton properties. Processes 7, 885 (2019)
H.Q. Alijani, S. Iravani, S. Pourseyedi et al., Biosynthesis of spinel nickel ferrite nanowhiskers and their biomedical applications. Sci. Rep. 11, 17431 (2021)
S. Rizwan, M. Umar, Z.U. Babar, S.U. Awan, M.A. ur Rehman, Selenium enriched flower-like of bismuth ferrite nanosheets assembly with associated magnetic properties. AIP Adv. 9, 055025 (2019)
A. Khan, Z. Valicsek, O. Horváth, Synthesis, characterization and application of iron (II) doped copper ferrites (CuII(x)FeII(1–x)FeIII2O4) as novel heterogeneous photo-fenton catalysts. Nanomaterials. 10, 921 (2020)
T.E.P. Alves, H.V.S. Pessoni, A. Franco Jr., The effect of Y3+ substitution on the structural, optical band-gap, and magnetic properties of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 19, 16395–16405 (2017)
M. Shakil, U. Inayat, M.I. Arshad, G. Nabi, N.R. Khalid, N.H. Tariq, A. Shah, M.Z. Iqbal, Influence of zinc and cadmium co-doping on optical and magnetic properties of cobalt ferrites. Ceram. Int. 46, 7767–7773 (2020)
N. Singh, J. Bamne, C.C. Jana, A. Malhosia, K. Taiwade, V. Chandel, F.Z. Haque, Mater. Today: Proc. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2022.05.192]
C. Pratapkumar, S.C. Prashantha, H. Nagabhushana, M.R. Anilkumar, C.R. Ravikumar, H.P. Nagaswarupa, D.M. Jnaneshwara, White light emitting magnesium aluminate nanophosphor: near ultra violet excited photoluminescence, photometric characteristics and its UV photocatalytic activity. J. Alloy Compd. 728, 1124–1138 (2017)
R.K. Kotnala, J. Shah, Lithium-substituted magnesium ferrite material based hydroelectric cell and process for preparation thereof, US 2016/0285121 A1 (2016)
E. Codorniu-HernAndez, P.G. Kusalik, Probing the mechanisms of proton transfer in liquid water:fig. 1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 110, 13697-e13698 (2013)
S.H. Chan, K.A. Khor, Z.T. Xia, A complete polarization model of a solid oxide fuel cell and its sensitivity to the change of cell component thickness. J. Power Sources 93, 130e140 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-7753(00)00556-5
A.O. Turky, M.M. Rashad, A.M. Hassan, E.M. Elnaggar, M. Bechelany, Tailoring optical, magnetic and electric behavior of lanthanum strontium manganite La1–xSrxMnO3 (LSM) nanopowders prepared via a co-precipitation method with different Sr2+ion contents. Rsc Adv. 6(22), 17980–17986 (2016)
A.O. Turkey, M.M. Rashad, A.M. Hassan, E.M. Elnaggar, M. Bechelany, Tuning the optical, electrical and magnetic properties Ba0.5Sr0.5TixM1−xO3 (BST) nanopowders. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 19(9), 6878–6886 (2017)
A.O. Turky, M.M. Rashad, A.M. Hassan, E.M. Elnaggar, M. Bechelany, Optical, electrical and magnetic properties of lanthanum strontium manganite La1–xSrxMnO3 synthesized through the citrate combustion method. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 19, 6878–6886 (2017)
Acknowledgements
Authors are grateful to Aryabhatta Center for Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, Aryabhatta Knowledge University under the Department of Higher Education, Govt. of Bihar for providing the sophisticated research facilities to execute this work.
Funding
No funding was provided for carring out this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by AM, RKS, VK, SBD, NK, JS and RKK. The first draft of the manuscript was written by AM and VK and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Manash, A., Singh, R.K., Kumar, V. et al. Studies on structural and optical behavior of nanoporous potassium-substituted magnesium ferrite nanomaterials, and their application as a hydroelectric cell. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 33, 22103–22118 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-08978-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-08978-0