Abstract
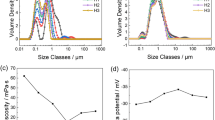
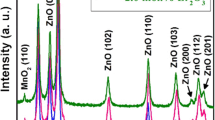
The aim of this work is to find a proper grinding medium that produce the best suspension of additives in order to fabricated ZnO varistors with excellent comprehensive electrical properties. For this, the effect of various kind of milling media (alumina, zirconia, and agate) in the milling times of 2, 6, and 12 h on particle size distribution, contamination amount, and zeta potential of additives suspensions was explored. Furthermore, the relation between these parameters with the microstructures and electrical properties of ZnO varistors was elaborated. Results showed that, for same milling times, the additives suspension obtained by zirconia medium produced the smallest size of particles with the most absolute value of zeta potential. The contamination amount was minimum in agate samples. In the instrument detection limit, the XRD results reveal that there is no variation in the phase compositions of the all ZnO varistors. The SEM images confirmed that the type of milling medium has a major effect on the morphology and the grain size of varistor samples. The excellent comprehensive electrical performance which are Eb: 325 V/mm, α: 68, JL: 2 µA/cm2, Kr: 1.5 along with an excellent discharge capability was acquired for those samples prepared by the zirconia medium after 6 h milling. Therefore, these results corroborate that the zirconia medium is the best choice for production of ZnO varistors with highly outstanding non-Ohmic characteristics.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author, upon reasonable request.
References
M. Matsouka, non-ohmics property of zinc ceramics. Jpn J. Appl. Phys. 10, 736 (1971)
D.R. Clarke, Varistor ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 82, 485 (1999)
T.K. Gupta, Application of zinc oxide varistors. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 73, 1817 (1990)
F. Greuter, ZnO Varistors from Grain Boundaries to Power Applications (Wiley, Hoboken, 2021), pp.157–234. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119529538
J. Li, S. Li, P. Cheng, M.A. Alim, Advances in ZnO–Bi2O3 based varistors. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 26, 4782–4809 (2015)
J. He, Metal Oxide Varistors: From Microstructure to Macro-characteristics (Wiley, Boschstr, 2019), pp.31–65
C. Thambiliyagodage, R. Wijeseker, Ball milling—a green and sustainable technique for the preparation of titanium based materials from ilmenite. Curr. Res. Green Sustain. Chem. 5, 100236 (2022)
C. Suryanarayana, Mechanical alloying and milling. Prog. Mater. Sci. 46, 1–184 (2001)
C.P. Fah, J. Wang, Effect of high-energy mechanical activation on the microstructure and electrical properties of ZnO-based varistors. Solid State Ion. 132, 107–117 (2000)
M.C. Kelleher, M.S.J. Hashmi, The effect of vibratory milling on the powder properties of zinc oxide varistors. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 201, 645–650 (2008)
Y. Yan, X. Ren, Q. Cheng, X. Ruan, M. Wang, W. Yu, Z. Yao, Effects of sizes of additive particles on suspensions, microstructures, and electrical properties of ZnO varistors. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 00, 1–8 (2020)
X. Ruan, X. Ren, W. Zhou, Q. Cheng, Z. Yao, W. Yu, L. Jin, L. Shi, Effects of dispersant content and pH on dispersion of suspension, microstructures and electrical properties of ZnO varistors. Ceram. Int. 46, 14134–14142 (2020)
Z. Li, X. Ren, X. Wang, W. You, M. Zhong, A. Kong, X. Lao, H. Jiang, W. Yu, L. Jin, Z. Yao, L. Shi, Effectively enhanced comprehensive electrical performance of ZnO varistors by a fast combinatorial refinement method. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 133, 105945 (2021)
W.J. Cai, G.R. Li, Q.R. Yin, Analysis of ZnO varistors prepared from high-energy mechanical activation. J. Electroceram. 21, 234–237 (2008)
H.Y. Liu, H. Kong, X.M. Ma, W.Z. Shi, Microstructure and electrical properties of ZnO-based varistors prepared by high-energy ball milling. J. Mater. Sci. 42, 2637–2642 (2007)
J. Zhu, G. Qi, L. Wang, H. Yang, F. Wang, Influence of intensive milling on the microstructure and electrical properties of ZnO–Bi2O3-based varistors. Ceram. Int. 38, S463–S466 (2012)
X. Dong, T. Dong-mei, J. Lei, Y. Hong-ming, Z. Guo-ping, C. Xiao-nong, Effects of high-energy ball milling oxide-doped and varistor ceramic powder on ZnO varistor. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 22, 1423–1431 (2012)
M.I. Miranda-López, M.B. Hernández, P. Zambrano-Robledo, L. García-Ortiz, S. García-Villarreal, C. Gómez Rodríguez, J.A. Aguilar-Martínez. (2018) Effect of milling speed and time on electrical properties and microstructure of SnO2-Co3O4-Dy2O3-Ta2O5 varistors. Ceramics International 44:23185–23190
M. Broseghini, M. D’Incau, L. Gelisio, N.M. Pugno, P. Scardi, Effect of jar shape on high-energy planetary ball milling efficiency: simulations and experiments. Mater. Des. 110, 365–374 (2016)
M. Asachi, E. Nourafkan, A. Hassanpour, A review of current techniques for the evaluation of powder mixing. Adv. Powder Technol. 29, 1525–1549 (2018)
C.H. Zhang, M.S. Li, D. Xu, Y.F. Chen, Y.L. Liu, K. Zhang, Microstructure and electrical properties of ZnO–Bi2O3-based varistor ceramics by different high-energy ball milling time. Adv. Mater. Res. 490–495, 3391–3395 (2012)
Y.W. Lao, S.T. Kuo, W.H. Tuan, Influence of ball milling on the sintering behaviour of ZnO powder. Ceram. Int. 35, 1317–1320 (2009)
D. Xu, X.N. Cheng, M.S., L.Y. Wang, Shi, Microstructure and electrical properties of ZnO-Bi2O3-doped ZnO-Bi2O3 based varistor ceramics. Adv. Mater. Res. 79–82, 2007–2010 (2009)
M. Maleki Shahraki, S.A. Shojaee, A. Nemati, M. A. Faghihi Sani, High voltage SnO2 varistors prepared from nanocrystalline powders. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 21, 199–205 (2011)
S. Bernik, N. Daneu, A. Recnik, Inversion boundary induced grain growth in TiO2 or Sb2O3 doped ZnO-based varistor ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 24, 3703–3708 (2004)
S. Bernik, N. Daneu, Characteristics of ZnO-based varistor ceramics doped with Al2O3. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 27, 3161–3170 (2007)
H. Bai, M. Li, Z. Xu, R. Chu, J. Hao, H. Li, C. Chen, G. Li, Influence of SiO2 on electrical properties of the highly nonlinear ZnO–Bi2O3–MnO2 varistors. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 37, 3965–3971 (2017)
H. Bai, M. Zhang, Z. Xu, R. Chu, J. Hao, H. Li, Y. Gong, G. Li, The effect of SiO2 on electrical properties of low-temperature sintered ZnO–Bi2O3–TiO2–Co2O3–MnO2-based ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 100, 1057–1064 (2016)
D. Xu, K. He, L. Jiao, B. Chen, S. Mu, W. Wu, X. Sun, Y. Yang, Microstructure and electrical properties of ZrO2-doped ZnO varistor ceramics. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 27, 767–771 (2016)
C. Kim, J. Kim, Microstructure and electrical properties of ZnO–ZrO2–Bi2O3–M3O4 (M = Co, Mn) varistors. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 24, 2537–2546 (2004)
N. Daneu, S. Bernik, A. Rečnik, Inversion boundary induced grain growth in ZnO ceramics: from atomic-scale investigations to microstructural engineering. J. Phys. Conf. Ser 326, 012003 (2011)
H. Shouxiang, W. Shiliang, X. Yuchun, L. Xingjiao, Effect of aluminum doping on the electrical properties of ZnO varistors, in IEEE Transactions on Components, Hybrids, and Manufacturing Technology. CHMT-8 (1985), pp. 525–529
M. Maleki Shahraki, M. A.Bahrevar, S.M.S. Mirghafourian, The effect of TiO2 addition on microstructure and electrical properties of SnO2 varistors prepared from nanomaterials. Ceram. Int. 41, 6920–6924 (2015)
J. He, S. Li, J. Lin, L. Zhang, K. Feng, L. Zhang, W. Liu, J. Li, Reverse manipulation of intrinsic point defects in ZnO-based varistor ceramics through Zr-stabilized high ionic conducting III-Bi2O3 intergranular phase. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 38, 1614–1620 (2018)
S. Li, J. Lin, J. He, W. Liu, Influences of lithium on the defect structures and electrical properties of ZnO–Bi2O3 based varistors. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 28, 13905–13911 (2017)
M. Abdollahi, M.R. Nilforoushan, M. Maleki Shahraki, M. Delshad Chermahini, M. Moradizade, The degradation behavior of high-voltage SnO2 based varistors sintered at different temperatures. Ceram. Int. 46, 11577–11583 (2020)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
FA, AA, FN, MKJ study conceptualization and writing original draft the manuscript. MMS superviser, writing and editing the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare they have no conflict of interest.
Research involving animal rights
This article does not contain any studies involving animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Abedsaeidi, F., Amini, A., Norouzian, F. et al. The effect of grinding media on suspensions, microstructures, and comprehensive electrical properties of ZnO varistors. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 33, 21727–21736 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-08960-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-08960-w