Abstract
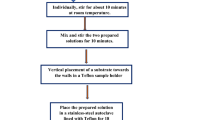
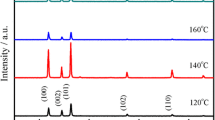
The hydrothermal method was used to synthesize Zn0.99−xNixCu0.01O (x = 0.00 to 0.05 with a 0.01 increment) nanorods. The X-ray diffraction method was used to provide the structural analysis. It was observed that all Ni/Cu co-doped ZnO nanorods are single phases. The Scanning Electron Microscope and Electron Dispersive Spectroscopy were employed to monitor the surface morphology, shapes, size, and elemental compositions of the Ni/Cu co-doped ZnO nanorods. The Fourier Transform Infrared studies were performed and detailed. The UV-Spectrophotometer was used to obtain the optical properties of the nanorods. The energy band gaps of Ni/Cu-doped ZnO nanorods were calculated and their effects on optical properties were discussed. Five different models were used to calculate the refractive index. Multi-doped (Ni and Cu) ZnO nanorods were successfully produced using the hydrothermal method and their structural, band gap and refractive indexes were discussed for optoelectronic and sensor applications.


















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article.
References
E. Asikuzun, O. Ozturk, L. Arda, A.T. Tasci, F. Kartal, C. Terzioglu, High-quality c-axis oriented non-vacuum Er doped ZnO thin films. Ceram. Int. 2, 8085–8091 (2016)
C. Boyraz, N. Doğan, L. Arda, Microstructure and magnetic behavior of (Mg/Ni) co-doped ZnO nanoparticles. Ceram. Int. 43, 15986–15991 (2017)
S. Demirozu Senol, Influence of Mg doping on the structural, optical, and electrical properties of Zn 0.95 Li 0.05 O Nanoparticles. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 16, 138–145 (2019)
I.P. Duru, E. Ozugurlu, L. Arda, Size effect on magnetic properties of Zn0.95−x Mgx Ni0.05 O nanoparticles by Monte Carlo simulation. Ceram. Int. 45(5), 5259–5265 (2019)
S.D. Senol, E. Ozugurlu, L. Arda, The effect of cobalt and boron on the structural, microstructural, and optoelectronic properties of ZnO nanoparticles. Ceram. Int. 46, 7033–7044 (2020)
U. Ozgur, Y.I. Alivov, C. Liu, A. Teke, M.A. Reshchikov, S. Dogan, V. Avrutin, S.J. Cho, H. Morkoc, A comprehensive review of ZnO materials and devices. J. Appl. Phys. 98, 041301 (2005)
A. Guler, L. Arda, N. Dogan, C. Boyraz, E. Ozugurlu, The annealing effect on microstructure and ESR properties of (Cu/Ni) codoped ZnO nanoparticles. Ceram. Int. 45, 1737–1745 (2019)
A.K.T. Taha, Md. Amir, M.A. Al-Messiere, A. Baykal, S. Karakus, A. Kilislioglu, Development of novel nano-ZnO enhanced polymeric membranes for water purification. J. Inorg. Organometall. Polym. Mater. 29, 979–988 (2019)
Y. Slimani, A. Selmi, E. Hannachi, M.A. Almessiere, A. Baykal, I. Ercan, Impact of ZnO addition on structural, morphological, optical, dielectric and electrical performances of BaTiO3 ceramics. J. Mater. Sci. 30, 9520–9530 (2019)
M. Tosun, L. Arda, Effect of temperature and film thickness on structural and mechanical properties of c-axis oriented Zn0.95Mg0.05O thin films. Ceram. Int. 45(13), 16234–16243 (2019)
I. Gonzalez-Valls, M. Lira-Cantu, Vertically-aligned nanostructures of ZnO for excitonic solar cells: a review. Energy Environ. Sci. 2(1), 19–34 (2009)
E. Asikuzun, A. Donmez, L. Arda, O. Cakiroglu, O. Ozturk, D. Akcan, M. Tosun, S. Ataoglu, C. Terzioglu, Structural and mechanical properties of (Co/Mg) co-doped nano ZnO. Ceram. Int. 41, 6326–6334 (2015)
K.S. Syed Ali, R. Saravanan, S. Israel, M. Acikgoz, L. Arda, Localized ferromagnetic charge ordering through charge density analysis in nano sized diluted magnetic semiconductor Co2+:ZnO. Physica B 405, 1763–1769 (2010)
M. Tosun, S. Ataoglu, L. Arda, O. Ozturk, E. Asikuzun, D. Akcan, O. Cakiroglu, Structural and mechanical properties of ZnMgO nanoparticles. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 590, 416–422 (2014)
L. Khomenkova, V.I. Kushnirenko, M.M. Osipyonok et al., Structural, electrical and luminescent properties of ZnO: Li films fabricated by screen-printing method on sapphire substrate. Phys Status Solidi C 12, 1144–1147 (2015)
I.V. Markevich, T.R. Stara, V.O. Bondarenko, Influence of Mg content on defect-related luminescence of undoped and doped MgZnO ceramics. Semicond. Phys. Quantum Electron. Optoelectron. 18, 344–348 (2015)
S. Choopun, R.D. Vispute, W. Yang, R.P. Sharma, T. Venkatesan, H. Shen, Realization of band gap above 5.0 eV in metastable cubic-phase MgxZn1−x O alloy films Appl. Phys. Lett. 80, 1529–1531 (2002)
V. Srikant, V. Sergo, D.R. Clarke, Epitaxial aluminum-doped zinc-oxide thin film on saphire: effect of substrate orientation. J. Am. Cerm. Soc. 78, 1931–1934 (1995)
S. Boumaza, A. Boudjemaa, A. Bouguelia, R. Bouarab, M. Trari, Visible light-induced hydrogen evolution on new hetero-system ZnFe2O4/SrTiO3. Appl. Energy. 87, 2230–2236 (2010)
R. Dom, R. Subasri, K. Radha, P.H. Borse, Synthesis of solar active nanocrystalline ferrite, MFe2O4 (M: Ca, Zn, Mg) photocatalyst by microwave irradiation. Solid State Commun. 151, 470–473 (2011)
S. Ida, K. Yamada, T. Matsunaga, H. Hagiwara, Y. Matsumoto, T. Ishihara, Preparation of p-Type CaFe2O4 photocathodes for producing hydrogen from water. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 132, 17343 (2010)
K. Vanheusden, W.L. Warren, C.H. Seager, D.R. Tallant, J.A. Voigt, Mechanisms behind green photoluminescence in ZnO phosphor powders. Appl Phys. 79, 7983–7990 (1996)
M. Andres-Vergés, A. Mifsud, C.J. Serna, Formation of rod-like zinc oxide microcrystals in homogeneous solutions. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 86, 959–963 (1990)
T. Pandiyarajan, R. Udayabhaskar, B. Karthikeyan, Role of Fe doping on structural and vibrational properties of ZnO nanostructures. Appl. Phys. A 107, 411–419 (2012)
F. Ahmed, S. Kumar, N. Arshi, M.S. Anwar, B.H. Koo, C.G. Lee, Doping effects of Co2+ ions on structural and magnetic properties of ZnO nanoparticles. Microelectron. Eng. 89, 129–132 (2012)
L. Arda, M. Acikgoz, N. Dogan, D. Akcan, O. Cakiroglu, Synthesis, characterization and ESR studies of Zn1-x Co x O nanoparticles. J. Supercond. Novel Magn. 27(3), 799–804 (2014)
Z.K. Heiba, L. Arda, M.B. Mohamed, Structural and magnetic properties of Zn0.95 Cr0.05 O annealed at different temperatures. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 389, 153–156 (2015)
S.D. Senol, O. Ozturk, C. Terzioğlu, Effect of boron doping on the structural, optical and electrical properties of ZnO nanoparticles produced by the hydrothermal method. Ceram. Int. 41(9), 11194–11201 (2015)
J. Li, L. Zhang, J. Zhu, W. Hao, Aligned ZnO: Co nanorod arrays: electrophoretic deposition fabrication and magnetic manipulation. Ceram. Int. 41, 3456–3460 (2015)
R. He, B. Tan, C. Ton-Hhat, M. Phillips, T. Tsuzuki, Physical structure and optical properties of Co-doped ZnO nanoparticles prepared by co-precipitation. J. Nanoparticle Res. 15, 2030 (2013)
S.D. Senol, C. Boyraz, E. Ozugurlu, A. Gungor, L. Arda, Band gap engineering of Mg doped ZnO nanorods prepared by a hydrothermal method. Cryst. Res. Technol. 3, 1800233 (2019)
L. Arda, The effects of Tb doped ZnO nanorod: An EPR study. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 475, 493–501 (2019)
D.P. Yu, X.S. Sun, C.S. Lee, I. Bello, S.T. Lee, H.D. Gu, K.M. Leung, G.W. Zhou, Z.F. Dong, Z. Zhang, Synthesis of boron nitride nanotubes by means of excimer laser ablation at high temperature. Appl. Phys. Lett. 72, 1966 (1998)
X.F. Duan, C.M. Lieber, Laser-assisted catalytic growth of single crystal GaN nanowires. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 122, 188 (2000)
M. Yazawa, M. Koguchi, A. Muto, M. Ozawa, K. Hiruma, 1–x Cax Effect of one monolayer of surface gold atoms on the epitaxial growth of InAs nanowhiskers Appl. Phys. Lett. 61, 2051 (1992)
S.D. Senol, A. Guler, C. Boyraz, L. Arda, Preparation structure and magnetic properties of Mn-doped ZnO nanoparticles prepared by hydrothermal method. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-019-5030-7
J. Liu, F. Yi, Fabrication, and properties of ZnO nanorods on silicon nanopillar surface for gas sensor application. J Mater Sci 30, 11404–11411 (2019)
T.L. Lamson, S. Khan, Z. Wang et al., Patterned Synthesis of ZnO nanorod arrays for nanoplasmonic waveguide applications. Opt. Commun. 411, 53–58 (2018)
H. Fujiwara, T. Suzuki, R. Niyuki et al., ZnO nanorod array random lasers fabricated by a laser-induced hydrothermal synthesis. New J. Phys. 18, 103046 (2016)
T.S. Moss, Relations between the refractive index and energy gap of semiconductors. Phys. Status Solidi B 131, 415 (1985)
N.M. Ravindra, S. Auluck, V.K. Srivastava, On the penn gap in semiconductors. Physica Status Solidi (b) 93(2), 155–160 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1002/pssb.2220930257
R.R. Reddy, S. Anjaneyulu, Analysis of the Moss and Ravindra relations. Phys. Status Solidi B 174, 91 (1992)
V. Kumar, J. Singh, Model for calculating the refractive index of different materials. Indian J. Pure Appl. Phys. 48, 571 (2010)
P. Hervé, L. Vandamme, General relation between refractive index and energy gap in semiconductors. Infrared Phys. Technol. 35, 609 (1994)
S.D. Senol, B. Yalcin, E. Ozugurlu, L. Arda, Structure, microstructure, optical and photocatalytic properties of Mn-doped ZnO nanoparticles. Mater. Res. Express 7, 015079 (2020)
S.D. Senol, E. Ozugurlu, L. Arda, Synthesis, structure and optical properties of (Mn/Cu) co-doped ZnO nanoparticles. J. Alloys Compd. 822(5), 153514 (2020)
K. Nakamoto, Infrared and Raman Spectra of Inorganic and Coordination Compounds A and B (Wiley, New York, 1997)
M. Arshad, A. Azam, A.S. Ahmea, S. Mollah, A.H. Naqvi, J. Alloys Compd. 509, 8378–8381 (2011)
M. Ashokkumar, S. Muthukumaran, Structural, morphological and spectroscopic investigation of Mn doped Zn0.96Cu0.04O nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci. 26, 1225–1233 (2015)
F. Naccarato, F. Ricci, J. Suntivich, G. Hautier, L. Wirtz, G.-M. Rignanese, Searching for materials with a high refractive index and wide band gap: a first-principles high-throughput study. Phys. Rev. Mater. 3, 044602 (2019)
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Bolu Abant İzzet Baysal University Scientific Research Projects under Project No: BAP- 2018.03.03.1320, Bolu, Turkey, and the Research Fund of Bahcesehir University under Project No: BAP-2021.01.27 and BAP.2019-01.04, Istanbul, Turkey.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SDS: Sample Preparation, XRD, FTIR, and UV–VIS diffuse reflectance measurements and discussions, writing—review and editing; LA: writing—original draft preparation, reviewing and editing, XRD, SEM, EDS and optical properties discussions.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no potential conflicts of interest.
Research involving human and animal participants
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors. In this experiment, we did not collect any samples of human and animals.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Senol, S.D., Arda, L. The effects of Ni/Cu co-doped ZnO nanorods: structural and optoelectronic study. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 33, 20740–20755 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-08884-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-08884-5