Abstract
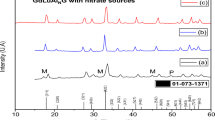
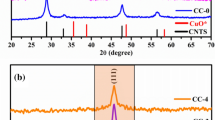
In this paper, we report the synthesis of multicomponent Cu2ZnxFe1 − xSnS4 (CZFTS) (0 ≤ x ≤ 1) powders and the effect of zinc content on their physical properties. Cu2FeSnS4, Cu2Zn0.25Fe0.75SnS4, Cu2Zn0.5Fe0.5SnS4, Cu2Zn0.75Fe0.25SnS4 and Cu2ZnSnS4 materials were successfully synthesized by solid-state reaction method. The five materials were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), Raman spectroscopy, energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS), diffuse reflectance spectroscopy (DRS) and photoluminescence (PL). XRD and Raman measurements showed that all CZFTS powders were polycrystalline in nature, with a preferential orientation along the (112) plane. We also found that a structural transition from stannite (x = 0) to kesterite (x = 1) occurred with increasing the zinc content. The EDS analysis revealed that the obtained compositions of the synthesized powders were very close to the expected theoretical stoichiometry. The band gap energy of CZFTS powders varied on the basis of a parabolic increasing trend from 1.21 to 1.39 eV (DRS) and from 1.32 to 1.42 eV (PL) depending on the zinc content. The band gap tunability of CZFTS materials is an important property that can be used in multi-junction CZFTS based solar cells. The hot probe method showed that all CZFTS ingots were a p-type conductivity. These interesting properties confer the CZFTS materials the capacity to be used as absorber layer in solar cells.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data sharing not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
References
P. Jackson, D. Hariskos, E. Lotter, S. Paetel, R. Wuerz, R. Menner, W. Wischmann, M. Powalla, New world record efficiency for Cu(In,Ga)Se2 thin-film solar cells beyond 20%. Res. Appl. 19, 894–897 (2011)
M.A. Green, K. Emery, Y. Hishikawa, W. Warta, E.D. Dunlop, Solar cell efficiency tables (version 42). Res. Appl. 21, 827–837 (2013)
C. Nefzi, M. Souli, Y. Cuminal, N. Kamoun-Turki, Effect of substrate temperature on physical properties of Cu2FeSnS4 thin films for photocatalysis applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 254, 114509 (2020)
R.J. Deokate, H.S. Chavan, H. Im, A.I. Inamdar, Spray-deposited kesterite Cu2ZnSnS4 (CZTS): Optical, structural, and electrical investigations for solar cell applications. Ceramics Internationa, 795–802 (2022)
X. Zhang, N. Bao, K. Ramasamy, Y.A. Wang, Y. Wang, B. Linb, A. Gupta, Crystal phase-controlled synthesis of Cu2FeSnS4 nanocrystals with a band gap of around 1.5 eV. Chem. Commun. 48, 4956–4958 (2012)
X. Song, X. Ji, M. Li, W. Lin, X. Luo, H. Zhang, A review on development prospect of CZTS based thin film solar cells. Int. J. Photoenergy 2014, 1–11 (2014)
S. Chen, H. Tao, Y. Shen, L. Zhu, X. Zeng, J. Tao, T. Wang, Facile synthesis of single crystalline sub-micron Cu2ZnSnS4 (CZTS) powders using solvothermal treatment. Royal Soc. Chem. 5, 6682 (2015)
B. Ananthoju, J. Mohapatra, M.K. Jangid, D. Bahadur, N.V. Medhekar, M. Aslam, Cation/Anion Substitution in Cu2ZnSnS4 for Improved Photovoltaic Performance. Sci. Rep. 6, 35369 (2016)
A.M. Alanazi, F. Alam, A. Salhi, M. Missous, A.G. Thomas, P. O’Brien, D.J. Lewis, A molecular precursor route to quaternary chalcogenide CFTS (Cu2FeSnS4) powders as potential solar absorber materials. Royal Soc. Chem. 9, 24146–24153 (2019)
G. Bousselmi, N. Khemiri, S. Ahmadi, A. Cantarero, M. Kanzari, Cation Substitution of Copper by Silver in the Earth-Abundant Compound Cu2ZnSnS4: Comparative Study of Structural, Morphological, and Optical Properties. J. Electron. Mater. 50, 1527–1534 (2021)
W. Wang, M.T. Winkler, O. Gunawan, T. Gokmen, T.K. Todorov, Y. Zhu, D.B. Mitzi, Device characteristics of CZTSSe thin-film solar cells with 12.6% efficiency. Adv. Energy Mater. 4, 1301465 (2013)
R.R. Prabhakar, N.H. Loc, M.H. Kumar, P.P. Boix, S. Juan, R.A. John, S.K. Batabyal, L.H. Wong, Facile water-based spray pyrolysis of earth-abundant Cu2FeSnS4 thin films as an efficient counter electrode in dye-sensitized solar cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 6, 17661–17667 (2014)
P. Bonazzi, L. Bindi, G.P. Bernardini, S. Menchetti, A model for the mechanism of incorporation of Cu, Fe and Zn in the stannite – kësterite series, Cu2FeSnS4 – Cu2ZnSnS4. Can. Mineral. 41, 639–647 (2003)
S. Schorr, H.J. Hoebler, M.A. Tovar, Neutron diffraction study of the stannite kesterite solid solution series. Eur. J. Min. 19, 65 (2007)
D.B. Khadka, J.H. Kim, Structural transition and band gap tuning of Cu2(Zn,Fe)SnS4 chalcogenide for photovoltaic application. J. Phys. Chem. C 118, 14227–14237 (2014)
A.G. Kannan, T.E. Manjulavalli, M. Thambidurai, K. Habeeba, D.V.E. GnanaKumari, A study on the Cu-poor and Zn-poor CZTS nanoparticles and its influence on the photoconversion efficiency of non-toxic ZnO buffer layer solar cell. Materials Today: Proceedings 47, 1128–1132 (2021)
S. Engberg, J. Symonowicz, J. Schou, S. Canulescu, K. M. Ø Jensen, Characterization of Cu2ZnSnS4 Particles Obtained by the Hot-Injection Method. ACS Omega 5, 10501–10509 (2020)
D. Ramírez-Ceja, L.A. Gonzalez, M. Pech-Canul, Cu2ZnSnS4 nanoparticles synthesized via reaction media with glycine. Ceram. Int. 5, 5071–5078 (2021)
S.A. Vanalakar, S.M. Patil, V.L. Patil, S.A. Vhanalkar, P.S. Patil, J.H. Kim, Simplistic eco-friendly preparation of nanostructured Cu2FeSnS4 powder for solar photocatalytic degradation. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 229, 135–143 (2018)
M. Isacfranklin, R. Yuvakkumar, G. Ravi, B. Saravanakumar, M. Pannipara, A.G. Al-Sehemi, D. Velauthapillai, Quaternary Cu2FeSnS4/PVP/rGO Composite for Supercapacitor Applications. ACS Omega 6, 9471–9481 (2021)
C. Yan, C. Huang, J. Yang, F. Liu, J. Liu, Y. Lai, J. Li, Y. Liu, Synthesis and characterizations of quaternary Cu2FeSnS4 nanocrystals. Chem. Commun. 48, 2603–2605 (2012)
G.L. Agawane, S.W. Shin, S.A. Vanalakar, A.V. Moholkar, J.H. Kim, Next generation promising Cu2(ZnxFe1-x)SnS4 photovoltaic absorber material prepared by pulsed laser deposition technique. Mater. Lett. 137, 147–149 (2014)
P. Kevin, M.A. Malik, P. O’Brien, The controlled deposition of Cu2(ZnyFe1-y)SnS4, Cu2(ZnyFe1-y)SnSe4and Cu2(ZnyFe1-y)(SxSe1-x)4 thin films by AACVD: potential solar cell materials based on earth abundant elements. J. Mater. Chem. C 3, 5733–5741 (2015)
C. Huang, Y. Chan, F. Liu, D. Tang, J. Yang, Y. Lai, J. Li, Y. Liu, Synthesis and characterization of multicomponent Cu2(FexZn1-x)SnS4 nanocrystals with tunable bandgap and structure. J. Mater. Chem. A 1, 5402–5407 (2013)
W. Wang, H. Shen, J. Chen, W. Chen, X. He, Synthesis and properties of Cu2(FexZn1-x)SnS4 nanocrystals by microwave irradiation assisted solvothermal method. Adv. Powder Technol. 26, 275–279 (2015)
Z. Shadrokh, A. Yazdani, H. Eshghi, Solvothermal synthesis of Cu2ZnxFe1-xSnS4 nanoparticles and the influence of annealing conditions on drop-casted thin films. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 31, 12 (2016)
M. Sebai, I. Trabelsi, M. Kanzari, Comparative study of electrical properties of Cu2 ZnxFe1-xSnS4 thin films. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 240, 55–61 (2019)
V. Trifiletti, G. Tseberlidis, M. Colombo, A. Spinardi, S. Luong, M. Danilson, M. Grossberg, O. Fenwick, S. Binetti, Growth and Characterization of Cu2Zn1-xFexSnS4 Thin Films for Photovoltaic Applications. Materials 13, 1471 (2020)
T. Shibuya, Y. Goto, Y. Kamihara, M. Matoba, K. Yasuoka, L.A. Burton, A. Walsh, From kesterite to stannite photovoltaics: Stability and band gaps of the Cu2(Zn,Fe)SnS4 alloy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 104, 021912 (2014)
G. Gurieva, S. Niedenzu, N. Siminel, A. Franza, S. Schorr, The kesterite–stannite structural transition as a way to avoid Cu/Zn disorder in kesterites: the exemplary case of the Cu2(Zn,Mn)SnSe4, Faraday Discuss. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1039/d2fd00042c
P. Scherrer, Bestimmung der Grösse und der inneren Struktur von Kolloidteilchen mittels Röntgenstrahlen. Nachr. Ges Wiss Göttingen 26, 98 (1918)
J.I. Langford, A.J.C. Wilson, Scherrer after Sixty Years: A Survey and Some New Results in the Determination of Crystallite Size. J. Appl. Cryst. 11, 102 (1978)
S. Ahmadi, N. Khemiri, A. Cantarero, M. Kanzari, Influence of calcination on the structural properties of earth abundant Cu2ZnSnS4. J. Alloys Compd. 852, 156714 (2021)
S.R. Kodigala, Thin Film Solar Cells from Earth Abundant Materials: Growth and Characterization of Cu2ZnSn(SSe)4 Thin Films and Their Solar Cells (Elsevier, New York, 2014), pp. 121–122
M. Himmrich, H. Haeuseler, Far infrared studies on stannite and wurtzstannite type compounds. Spectrochimica Acta A 47, 933–942 (1991)
M. Altosaar, J. Raudoja, K. Timmo, M. Danilson, M. Grossberg, J. Krustok, E. Mellikov, Cu2Zn1–xCdxSn(Se1–ySy)4 solid solutions as absorber materials for solar cells Phys. Stat. Sol 205, 167–170 (2008)
P.A. Fernandes, P.M.P. Salomé, A. F. da Cunha, Growth and Raman scattering characterization of Cu2ZnSnS4 thin films. Thin Solid Films 517, 2519–2523 (2009)
X. Fontané, V. Izquierdo-Roca, E. Saucedo, S. Schorr, V.O. Yukhymchuk, M.Y. Valakh, A. Pérez- Rodríguez, J.R. Morante, Vibrational properties of stannite and kesterite type compounds: Raman scattering analysis of Cu2(Fe,Zn)SnS4. J. Alloys Compd. 539, 190–194 (2012)
P.A. Fernandes, P.M.P. Salomé, A.F. da Cunha, CuxSnSx+1 (x = 2, 3) thin films grown by sulfurization of metallic precursors deposited by dc magnetron sputtering. Phys. Status Solidi C 7, 901–904 (2010)
L. Yang, B. Kruse, Revised Kubelka-Munk theory. I. Theory and application. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 21, 1933–1941 (2004)
A.G. Kannan, T.E. Manjulavalli, J. Chandrasekaran, Influence of solvent on the properties of CZTS nanoparticles. Procedia Eng. 141, 15–22 (2016)
O. Khouja, A.C. Galca, K. Nouneh, M.Y. Zaki, M.E. Touhami, M. Taibi, E. Matei, C.C. Negrila, M. Enculescu, L. Pintilie, Structural, morphological and optical properties of Cu–Fe–Sn–S thin films prepared by electrodeposition at fixed applied potential. Thin Solid Films 721, 138547 (2021)
S.G. Nilange, N.M. Patil, A.A. Yadav, Growth and characterization of spray deposited quaternary Cu2FeSnS4 semiconductor thin films. Phys. B: Condens. Matter 560, 103–110 (2019)
W. Shockley, H.J. Queisser, Detailed Balance Limit of Efficiency of p-n Junction Solar Cells. J. Appl. Phys. 32, 510 (1961)
S. Chamekh, N. Khemiri, M. Kanzari, Effect of annealing under different atmospheres of CZTS thin films as absorber layer for solar cell application. SN Appl. Sci. 2, 1507 (2020)
Y. Zhang, X. Sun, P. Zhang, X. Yuan, F. Huang, W. Zhang, Structural Properties and Quasiparticle Band Structures of Cu-based Quaternary Semiconductors for Photovoltaic Applications. J. Appl. Phys. 111, 063709 (2012)
O.El Khouja, C.C. Negrila, K. Nouneh, M. Secu, M.E. Touhami, E. Matei, V. Stancu, M. Enculescu, V. Kuncser, A.C. Galca, Bulk and Surface Characteristics of Co-Electrodeposited Cu2FeSnS4 Thin Films Sulfurized at Different Annealing Temperatures. J. Alloys Compd. 906, 164379 (2022)
M.C. Benachoura, R. Bensaha, R. Moreno, Annealing duration influence on dip-coated CZTS thin films properties obtained by sol-gel method. Optik 187, 1–8 (2019)
I. Sheebha, V. Venugopal, J. James, V. Maheskumar, A. Sakunthala, B. Vidhya, Comparative studies on hierarchical flower like Cu2XSnS4 [X = Zn, Ni, Mn & Co] quaternary semiconductor for electrocatalytic and photocatalytic applications. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 45, 8139–8150 (2020)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AH Visualization, Writing & Formal analysis, NK review editing & validation, MK Supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper. The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests
Ethical approval
This material is the authors’ own original work, which has not been previously published elsewhere. The authors declare that this article does not contain any studies involving human participants performed by any of the authors. The results are appropriately placed in the context of prior and existing research.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hannachi, A., Khemiri, N. & Kanzari, M. Influence of Fe/Zn content on the structural, and optical properties of nontoxic and earth-abundant Cu2ZnxFe1 − xSnS4 (x = 0, 0.25, 0.5, 0.75 and 1) compounds. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 33, 20604–20615 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-08872-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-08872-9