Abstract
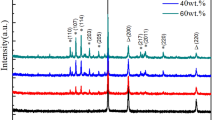
In order to optimize microwave absorption performance at low matching thickness, polyvinyl pyrrolidone-induced carbothermal reduction has been utilized to successfully convert NiFe2O4/Fe2O3/Ni composite spheres into FeNi/Fe/C-based composites. The results show that with the increase dosage of polyvinyl pyrrolidone, the reduction degree would first increase and then decrease, which leads to the change of composition and morphology. In detail, Fe3O4 can be found in S-0.3, S-0.4, and S-0.6, revealing lower reduction degree. And S-0.5 contains only FeNi, Fe, and C, indicating highest reduction degree. Moreover, smooth carbon layers can be observed on the particle surface for S-0.5, while the other samples exhibit rough surface decorated with particle clusters. The changing trend of graphitic degree is in line with reduction degree, and saturation magnetization basically increases with the increase dosage of polyvinyl pyrrolidone. As for electromagnetic properties, S-0.5 possesses strongest dielectric loss and magnetic loss, while the other samples own similar loss ability except in high frequency range, which should be ascribed to dielectric relaxation. Owing to synergetic effect of conduction loss, interfacial polarization, dipolar polarization, natural resonance, exchange resonance, eddy current loss, and appropriate impedance, the as-synthesized FeNi/Fe/C-based composites hold great potential in evading radar detection and reducing electromagnetic pollution. This work may offer novel insights into the design and application of high-performance magnetic metal-based microwave absorbing materials derived from controllable reduction of ferrites.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
X. Yang, B. Fan, X. Tang et al., Interface modulation of chiral PPy/Fe3O4 planar microhelixes to achieve electric/magnetic-coupling and wide-band microwave absorption. Chem. Eng. J 430, 132747 (2022)
Q. Chang, H. Liang, B. Shi et al., Ethylenediamine-assisted hydrothermal synthesis of NiCo2O4 absorber with controlled morphology and excellent absorbing performance. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 588, 336–345 (2021)
Q. Chang, H. Liang, B. Shi et al., Sodium oxalate-induced hydrothermal synthesis of wood-texture-column-like NiCo2O4 with broad bandwidth electromagnetic wave absorption performance. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 600, 49–57 (2021)
Z. Lou, Q. Wang, U. Kare et al., Biomass-derived carbon heterostructures enable environmentally adaptive wideband electromagnetic wave absorbers. Nano-Micro Lett. 14, 11 (2022)
Y. Zhang, S. Gao, Y. Wang, Metal-organic framework derived magnetic carbon Ni@C octahedron composite as an excellent microwave absorber. Compos. Commun. 31, 101135 (2022)
J. He, S. Gao, Y. Zhang et al., N-doped residual carbon from coal gasification fine slag decorated with Fe3O4 nanoparticles for electromagnetic wave absorption. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 104, 98–108 (2022)
Q. Chang, H. Liang, B. Shi et al., Microstructure induced dielectric loss in lightweight Fe3O4 foam for electromagnetic wave absorption. Iscience 25, 103925 (2022)
B. Deng, Z. Liu, F. Pan et al., Electrostatically self-assembled two-dimensional magnetized MXene/hollow Fe3O4 nanoparticle hybrids with high electromagnetic absorption performance and improved impendence matching. J. Mater. Chem. A 9, 3500–3510 (2021)
J. Liu, Z. Jia, W. Zhou et al., Self-assembled MoS2/magnetic ferrite CuFe2O4 nanocomposite for high-efficiency microwave absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 429, 132253 (2022)
J.H. Park, J.C. Ro, S.J. Suh, Fe/Co ratio dependent excellent microwave absorption of FeCo alloys with a wide bandwidth in the high-frequency region. Mater. Res. Bull. 145, 111513 (2022)
W. Tian, J. Li, Y. Liu et al., Atomic-scale layer-by-layer deposition of FeSiAl@ZnO@Al2O3 hybrid with threshold anti-corrosion and ultra-high microwave absorption properties in low-frequency bands. Nano-Micro Lett. 13, 161 (2021)
Y. Zou, Z. Qi, Z. Zheng et al., Microwave absorption properties of rare earth alloy Nd2Co17@C/Na2SiO3 composite at elevated temperature (293–723 K) in the X band. J. Phys. D 55, 155002 (2022)
J.H. Park, S. Lee, J.C. Ro et al., Yolk-shell Fe-Fe3O4@C nanoparticles with excellent reflection loss and wide bandwidth as electromagnetic wave absorbers in the high-frequency band. Appl. Surf. Sci. 573, 151469 (2022)
Y. Jiang, P. Yin, L. Zhang et al., Novel low-frequency microwave absorber of Sn-Fe-O multiphase compounds combined with Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge-derived biochar. Powder Technol. 394, 853–862 (2021)
L. Jin, P. Yi, L. Wan et al., Thickness-controllable synthesis of MOF-derived Ni@N-doped carbon hexagonal nanoflakes with dielectric-magnetic synergy toward wideband electromagnetic wave absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 427, 130940 (2022)
W. Liu, P. Duan, H. Xiong et al., Multicomponent Fe-based composites derived from the oxidation and reduction of Prussian blue towards efficient electromagnetic wave absorption. J. Mater. Chem. C 9, 5505–5514 (2021)
J. Qiao, X. Zhang, C. Liu et al., Non-magnetic bimetallic MOF-derived porous carbon-wrapped TiO2/ZrTiO4 composites for efficient electromagnetic wave absorption. Nano-Micro Lett. 13, 75 (2021)
M. Liu, L. Wu, B. Fan et al., Governing the Ni content and size of 2D layered C/Ni nanoparticle composites for enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption. Appl. Surf. Sci. 571, 151273 (2022)
M. Ma, Y. Bi, Z. Jiao et al., Facile fabrication of metal-organic framework derived Fe/Fe3O4/FeN/N-doped carbon composites coated with PPy for superior microwave absorption. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 608, 525–535 (2022)
Y. Zhou, W. Zhou, C. Ni et al., “Tree blossom” Ni/NC/C composites as high-efficiency microwave absorbents. Chem. Eng. J. 430, 132621 (2022)
Y. Li, L. Gai, G. Song et al., Enhanced properties of CoS2/Cu2S embedded N/S co-doped mesh-like carbonaceous composites for electromagnetic wave absorption. Carbon 186, 238–252 (2022)
X. Yan, D. Xue, Fabrication and microwave absorption properties of Fe0.64Ni0.36-NiFe2O4 nanocomposite. Nano-Micro Lett. 4, 176–179 (2012)
F.A. Wahaab, W. Yahya, L.L. Adebayo et al., Graphene@Ni0.5Co0.5Fe2O4 hybrid framework with enhanced interfacial polarization for electromagnetic wave absorption. J. Alloy Compd. 854, 157259 (2021)
X. Yang, B. Fan, X. Wang et al., HCl guided morphology and conductivity of chiral PPy nanostructures toward efficient electromagnetic wave absorption. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 65(4), 837–848 (2022)
Y. Ma, B. Quan, Z. Zeng et al., Multiple interface-induced evolution of electromagnetic patterns for efficient microwave absorption at low thickness. Inorg. Chem. Front. 8, 1810–1818 (2021)
B. Wang, S. Li, F. Huang et al., Construction of multiple electron transfer paths in 1D core-shell hetetrostructures with MXene as interlayer enabling efficient microwave absorption. Carbon 187, 56–66 (2022)
X. Zhang, Y. Shi, J. Xu et al., Identification of the intrinsic dielectric properties of metal single atoms for electromagnetic wave absorption. Nano-Micro Lett. 14, 27 (2022)
Z. Zhao, K. Kou, L. Zhang et al., Optimal particle distribution induced interfacial polarization in bouquet-like hierarchical composites for electromagnetic wave absorption. Carbon 186, 323–332 (2022)
P. Yang, Y. Huang, R. Li et al., Optimization of Fe@Ag core-shell nanowires with improved impedance matching and microwave absorption properties. Chem. Eng. J. 430, 132878 (2022)
X. Cui, X. Liang, J. Chen et al., Customized unique core-shell Fe2N@N-doped carbon with tunable void space for microwave response. Carbon 156, 49–57 (2020)
H. Lv, C. Wu, F. Qin et al., Extra-wide bandwidth via complementary exchange resonance and dielectric polarization of sandwiched FeNi@SnO2 nanosheets for electromagnetic wave absorption. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 90, 1–8 (2021)
X. Zuo, Y. Zhao, H. Zhang et al., Surface modification of helical carbon nanocoil (CNC) with N-doped and Co-anchored carbon layer for efficient microwave absorption. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 608, 1894–1906 (2022)
J. Fang, Y. Ma, Z. Zhang et al., Metal-organic framework-derived carbon/carbon nanotubes mediate impedance matching for strong microwave absorption at fairly low temperatures. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 13, 33496–33504 (2021)
W. Liu, P. Duan, C. Mei et al., Melamine-induced formation of carbon nanotubes assembly on metal-organic framework-derived Co/C composites for lightweight and broadband microwave absorption. Dalton Trans. 50, 6222–6231 (2021)
S. Wang, M.Z. Ashfaq, D. Qi et al., Electromagnetic wave absorption properties of polymer-derived magnetic carbon-rich SiCN-based composite ceramics. Ceram. Int. 48, 4986–4998 (2022)
Y. Liu, E. Fan, R. Hou et al., A simple synthesis of magnetic metal implanted hierarchical porous carbon networks for efficient microwave absorption. J. Mater. Chem. C 9, 14866–14875 (2021)
H. Yuan, Y. Wang, B. Suo et al., Dielectric relaxation and magnetic resonance of nitrogen-doped graphene-coated FeNi nanoparticles on nitrogen-doped carbon nanosheets. J. Alloy Compd. 854, 157212 (2021)
Z. Tong, Z. Liao, Y. Liu et al., Hierarchical Fe3O4/Fe@C@MoS2 core-shell nanofibers for efficient microwave absorption. Carbon 179, 646–654 (2021)
Q. Zhu, X. Zhang, X. Wang et al., Hydrothermal self-assembled Fe3O4/CA core-shell composites for broadband microwave absorption. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 541, 168511 (2022)
H. Wang, Y. Zhou, H. Xing et al., Construction of flower-like core-shell Fe3O4@2H-MoS2 heterostructures: boosting the interfacial polarization for high-performance microwave absorption. Ceram. Int. 48, 9918–9926 (2022)
Y. Cao, C. Liu, Z. Xue et al., Excellent microwave absorption of Fe3O4/Ag composites attained by synergy of considerable magnetic loss and dielectric loss. Ceram. Int. 48, 5824–5830 (2022)
H. Li, C. Yang, M. Cheng et al., Multiscale design of carbon-based, high-efficiency and wide-frequency microwave-absorption composites. Ceram. Int. 47, 20467–20475 (2021)
F. Huang, S. Wang, W. Ding et al., Sulfur-doped biomass-derived hollow carbon microtubes toward excellent microwave absorption performance. J. Mater. Sci. 32, 6260–6268 (2021)
.
Funding
This work was supported by College Student’s Innovative Entrepreneurial Training Plan Program (S202110359036), Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. JZ2021HGTA0174), the Major Project of Science and Technology Innovation 2025 in Ningbo City, China (No. 2020Z062), the Science and Technology Project of State Grid Corporation of China (No. 5500-202118252A-0-0-00) and Grant Project of Shenzhen Microgate Technology Co., Ltd. (2021-2024).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Conceptualization and methodology were proposed by WL and HS. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by ZX, TZ, PJ, FL, JW, and XZ. The first draft and review of the manuscript were completed by ZX and WL. All authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xia, Z., Liu, W., Zhou, T. et al. Adjustable electromagnetic properties of FeNi/Fe/C-based composites derived from controllable carbothermal reduction. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 33, 16425–16440 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-08536-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-08536-8