Abstract
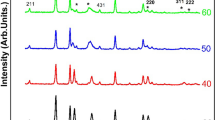
The use of nickel oxide as a complementary electrode in electrochromic devices is found to be widespread because of its high coloration efficiency and low materials cost. In the present work, we investigate the properties exhibited by radio frequency (RF) magnetron sputtered nickel oxide (NiO) thin films. The optical, vibrational and morphological characteristics of prepared nickel oxide thin films are tuned with different RF powers (100 W, 150 W and 200 W). The deposited nickel oxide films’ photoluminescence spectra reveal broad band-edges, Ultra-violet emission at 365 nm accompanied by defect-related, at 420 nm (DLE1) and 485 nm (DLE2) which occurred due to deep-level-emission (DLE). The Raman peaks centred at 560 cm−1 are related to 1-phonon longitudinal optic (LO) mode. The peak observed at 1100 cm−1 corresponds to the 2-phonon LO mode of nickel oxide, which is due to the defects of nickel vacancy or an increase in Ni3+ ions. Field emission scanning electron microscopy characterization reveals the prepared films are uniform and pinhole free nature, resulting in a high quality film. The EDX spectrum confirms the purity of the nickel thin film obtained.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request. Compliance with Ethical Standards.
References
P.M.S. Monk, R.J. Mortimer, D.R. Rosseinsky, Electrochromism and Electrochromic Devices (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2007), p. 421
P.R. Somani, S. Radhakrishnan, Electrochromic materials and devices: present and future. Mater. Chem. Phys. 77, 117 (2003)
G. Sonmez, Polymeric electrochromics. Chem. Commun. 42, 5251 (2005)
Q. Liu, Q. Chen, Q. Zhang, Y. Xiao, X. Zhong, G. Dong, M.P.D. Ogletree, H. Terryn, K. Baert, F. Reniers, X. Diao, In-situ electrochromic efficiency of nickel oxide thin film: origin of electrochemical process and electrochromic degradation. J. Mater. Chem. C6, 646 (2018)
E.O. Polat, O. Balcı, C. Kocabas, Graphene based flexible electrochromic devices. Sci. Rep. 4, 6484 (2014)
C.G. Granqvist, Oxide electrochromics: an introduction to devices and materials. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. C 99, 1 (2012)
C.J. Wang, M. Shim, P. Guyot-Sionnest, Electrochromic nanocrystal quantum dots. Science 291, 2390 (2001)
A. Llordes, G. Garcia, J. Gazquez, D.J. Milliron, Tunable near-infrared and visible-light transmittance in nanocrystal-in-glass composites. Nature 500, 323 (2013)
M. Nikolou, A.L. Dyer, T.T. Steckler, E.P. Donoghue, Z. Wu, N.C. Heston, A.G. Rinzler, D.B. Tanner, J.R. Reynolds, Dual n- and p-type dopable electrochromic devices employing transparent carbon nanotube electrodes. Chem. Mater. 21, 5539 (2009)
S.I. Cho, W.J. Kwon, S.J. Choi, P. Kim, S.A. Park, J. Kim, S.J. Son, R. Xiao, S.H. Kim, S.B. Lee, Nanotube-based ultrafast electrochromic display. Adv. Mater. 17, 171 (2005)
F.H. Wang, M.E. Itkis, E. Bekyarova, R.C. Haddon, Charge-compensated, semiconducting single-walled carbon nanotube thin film as an electrically configurable optical medium. Nat. Photon. 7, 460 (2013)
R.J. Mortimer, Electrochromic materials. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 41, 241 (2011)
W.S. Choi, M.F. Chisholm, D.J. Singh, T. Choi, G.E. Jellison, H.N. Lee, Wide band gap tunability in complex transition metal oxides by site-specific substitution. Nat. Commun. 3, 689 (2012)
M.Z. Sialvi, R.J. Mortimer, G.D. Wilcox, A.M. Teridi, T.S. Varley, K.G.U. Wijayantha, C.A. Kirk, Electrochromic and colorimetric properties of Nickel (II) oxide Thin films prepared by aerosol-assisted chemical vapor deposition. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 5, 5675 (2013)
F. Cao, G.X. Pan, X.H. Xia, P.S. Tang, H.F. Chen, Hydrothermal-synthesized mesoporous nickel oxide nanowall arrays with enhanced electrochromic application. Electrochim. Acta. 111, 86 (2013)
D. Ma, G. Shi, H. Wang, Q. Zhang, Y. Li, Hierarchical NiO microflake films with high coloration efficiency, cyclic stability and low power consumption for applications in a complementary electrochromic device. Nanoscale 5, 4808 (2013)
J. Zhang, G. Cai, D. Zhou, H. Tang, X. Wang, C.D. Gu, J.P. Tu, Co-doped NiO nanoflake array films with enhanced electrochromic properties. J. Mater. Chem. C 2, 7013 (2014)
S. Pereira, A. Gonçalves, N. Correia, J. Pinto, L. Pereira, R. Martins, E. Fortunato, Electrochromic behavior of NiO thin films deposited by e-beam evaporation at room temperature. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 120, 109 (2014)
K.S. Usha, R. Sivakumar, C. Sanjeeviraja, Optical constants and dispersion energy parameters of NiO thin films prepared by radio frequency magnetron sputtering technique. J. Appl. Phys. 114, 123501 (2013)
E. Azaceta, S. Chavhan, P. Rossi, M. Paderi, S. Fantini, M. Ungureanu, O. Miguel, H.J. Grande, R. Tena-Zaera, NiO cathodic electrochemical deposition from an aprotic ionic liquid: building metal oxide n–p heterojunctions. Electrochim. Acta 71, 39 (2012)
M. Wu, Y. Huang, C. Yang, J. Jow, Electrodeposition of nanoporous nickel oxide film for electrochemical capacitors. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 32, 4153 (2007)
F. Vera, R. Schrebler, E. Muñoz, C. Suarez, P. Cury, H. Gómez, R. Córdova, R.E. Marotti, E.A. Dalchiele, Preparation and characterization of eosin band erythrosine J-sensitized nanostructured NiO thin film photocathodes. Thin Solid Films 490, 182 (2005)
X. Hou, J. Williams, K.-L. Choy, Processing and structural characterization of porous reforming catalytic films. Thin Solid Films 495, 262 (2006)
R.C. Korosec, P. Bukovec, Sol–gel prepared NiO thin films for electrochromic applications. Acta Chim. Slov. 53, 136 (2006)
H. Lee, Y.T. Huang, M.W. Horn, S.P. Feng, Engineered optical and electrical performance of rf–sputtered undoped nickel oxide thin films for inverted perovskite solar cells. Sci. Rep. 8, 5590 (2018)
K.S. Usha, R. Sivakumar, C. Sanjeeviraja, Effect of substrate temperature on structural and optical properties of nickel tungsten oxide thin films. J. Mater. Sci. 26, 1033 (2015)
A. Manikandan, J.J. Vijaya, L.J. Kennedy, Comparative investigation of NiO nano- and microstructures for structural, optical and magnetic properties. Physica E 49, 117–123 (2013)
C.D. Guerra, A. Remon, J.A. Garcia, J. Piqueras, Cathodoluminescence and photoluminescence spectroscopy of NiO. Phys. Status Solidi A 163, 497 (1997)
P. Gupta, M. Ramrakhiani, Influence of the particle size on the optical properties of CdSe nanoparticles. Open Nanosci. J. 3, 15 (2009)
C.H. Ho, Y.M. Kuo, C.H. Chan, Y.R. Ma, Optical characterization of strong UV luminescence emitted from the excitonic edge of nickel oxide nanotowers. Sci. Rep. 5, 15856 (2015)
L.Q. Jing, F.L. Yuan, H.G. Hou, B.F. Xin, W.M. Cai, H.G. Fu, Relationships of surface oxygen vacancies with photoluminescence and photocatalytic performance of ZnO nanoparticles. Sci. China Chem. 48, 25 (2005)
D.Y. Jiang, J.M. Qin, X. Wang, S. Gao, Q.C. Liang, J.X. Zhao, Optical properties of NiO thin films fabricated by electron beam evaporation. Vacuum 86, 1083 (2012)
P. Colomban, Raman analyses and “Smart” imaging of nanophases and nanosized materials. Spectrosc. Europe 15/6, 8 (2003)
G. Gouadec, Ph. Colomban, Raman spectroscopy of nanomaterials: how spectra relate to disorder, particle size and mechanical properties. Prog. Cryst. Growth Charact. Mater. 53, 1 (2007)
N.M. Ulmane, A. Kuzmin, I. Sildos, M. Pärs, Polarisation dependent Raman study of single-crystal nickel oxide. Cent. Eur. J. Phys. 9, 1096 (2011)
W.J. Duan, S.H. Lu, Z.L. Wu, Y.S. Wang, Size effects on properties of NiO nanoparticles grown in alkalisalts. J. Phys. Chem. C 116, 26043 (2012)
D.A. Wruck, M. Rubin, Structure and electronic properties of electrochromic NiO films. J. Electrochem. Soc. 140, 1097 (1993)
S. Kasap, P. Capper, Springer Handbook of Electronic and Photonic Materials (Springer, New York, 2017)
Acknowledgements
K.S. Usha is grateful to the Department of Science and Technology, New Delhi, India for funding via Innovation in Science Pursuit for Inspired Research (INSPIRE). A grateful acknowledgement is given by an author, R.S to the Department of Education, Government of India for the financial support under RUSA—Phase 2.0 Scheme (Ref. No.: F. 24-51/2014-U, Policy (TNMulti-Gen), dt. 09.10.2018).
Funding
The research leading to these results have received funding from “Innovation in Science Pursuit for Inspired Research (INSPIRE)” funded by Department of Science and Technology, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by KSU. The first draft of the manuscript was written by KSU, RS and CS edited the entire draft. RS supervized the whole work and edited the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
The authors declare that there are no competing financial interest and also they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that influence the work reported in this work.
Compliance with ethical standards
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Usha, K.S., Sivakumar, R. & Sanjeeviraja, C. Preparation of pure NiO thin film by radio frequency magnetron sputtering technique and investigation on its properties. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 33, 16136–16143 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-08504-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-08504-2