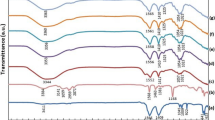
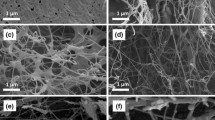
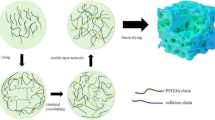
Abstract
Quasi-solid-state sodium-ion batteries (QSSNIBs) are regarded as a wise choice that balances practicality with security. However, further improvements is hindered by low ionic conductivity at room temperature. Herein, based on bacterial cellulose network, a high-strength gel polymer electrolyte (BC-GPE) for QSSNIBs is developed. The interwoven structure with abundant 3D ion transport passageways of BC-GPE make it display both high-strength (tensile strength of 36 MPa and maximum strain of 31.23%) and the inhibitory of “sodium dendrite” and “dead sodium” (an outstanding average coulombic efficiency of 98.3% and 190 cycles at 0.5 mA/cm2 and 1 mAh/cm2 in the Na/BC-GPE/SS cell). Furthermore, due to the excellent electrochemical properties of BC-GPE and the compatibility with NASICON type cathode Na3.5Mn0.5V1.5(PO4)3@C (NMVP@C), the QSSNIBs demonstrate high-rate performance and long cyclic life of 1250 cycles with a capacity decay rate of only 0.005%. All of these findings in this work can provide a novel insight for designing other high-strength GPEs and some new ideas for the potential applications of QSSNIBs in the near future.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available within the article.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
W. Xiao, J. Wang, L. Fan et al., Recent advances in Li1+xAlxTi2-x(PO4)(3) solid-state electrolyte for safe lithium batteries. Energy Storage Mater. 19, 379–400 (2019)
J. Wang, A.E. Lakraychi, X. Liu et al., Conjugated sulfonamides as a class of organic lithium-ion positive electrodes. Nat. Mater. 20, 665 (2021)
T.S. Yang, C.Z. Shu, R.X. Zheng et al., Dendrite-free solid-state Li-O-2 batteries enabled by organic-inorganic interaction reinforced gel polymer electrolyte. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 7, 17362 (2019)
Z. Zhou, C. Ding, W. Peng et al., One-step fabrication of two-dimensional hierarchical Mn2O3@graphene composite as high-performance anode materials for lithium ion batteries. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 80, 13–19 (2021)
S. Hussain, X. Yang, M.K. Aslam et al., Robust TiN nanoparticles polysulfide anchor for Li-S storage and diffusion pathways using first principle calculations. Chem. Eng. J. 391, 123595 (2020)
R. Wang, X. Dai, Z. Qian et al., boosting lithium storage in free-standing black phosphorus anode via multifunction of nanocellulose. ACS Appl. Mater Inter. 12, 31628–31636 (2020)
G. Du, M. Tao, J. Li et al., Low-operating temperature, high-rate and durable solid-state sodium-ion battery based on polymer electrolyte and Prussian Blue cathode. Adv. Energy Mater. 10, 1903351 (2020)
M. Lee, J. Hong, J. Lopez et al., High-performance sodium-organic battery by realizing four-sodium storage in disodium rhodizonate. Nat Energy. 2, 861 (2017)
W. Zhou, H. Gao, J.B. Goodenough, Low-cost hollow mesoporous polymer spheres and all-solid-state lithium, sodium batteries. Adv Energy Mater. 6, 150 (2016)
J.Y. Zhang, X.H. Yao, R.K. Misra et al., Progress in electrolytes for beyond-lithium-ion batteries. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 44, 237–257 (2020)
G.Y. Du, M.L. Tao, W. Gao et al., Preparation of MoS2/Ti3C2Tx composite as anode material with enhanced sodium/lithium storage performance. Inorg. Chem. Front. 6, 117–125 (2019)
M. Tao, Y. Zhang, R. Zhan et al., A chemically bonded CoNiO2 nanoparticles/MXene composite as anode for sodium-ion batteries. Mater. Lett. 230, 173–176 (2018)
Y. Xiao, Y.-F. Zhu, H.-R. Yao et al., A stable layered oxide cathode material for high-performance sodium-ion battery. Adv. Energy Mater. 9, 1803978 (2019)
J. Yang, M. Tang, H. Liu et al., O3-type layered Ni-rich oxide: a high-capacity and superior-rate cathode for sodium-ion batteries. Small 15, 1905311 (2019)
M. Tao, G. Du, T. Yang et al., MXene-derived three-dimensional carbon nanotube network encapsulate CoS2 nanoparticles as an anode material for solid-state sodium-ion batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A. 8, 3018–3026 (2020)
G. Tian, Z. Zhao, T. Zinkeyich et al., A crosslinked polyethyleneglycol solid electrolyte dissolving lithium bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide for rechargeable lithium batteries. Chemsuschem 12, 4708–4718 (2019)
J. Yang, H. Zhang, Q. Zhou et al., Safety-enhanced polymer electrolytes for sodium batteries: recent progress and perspectives. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 11, 17109–17127 (2019)
J. Yue, X. Zhu, F. Han et al., Long cycle life all-solid-state sodium ion battery. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 10, 39645–39650 (2018)
D. Xu, B.R. Wang, Q. Wang et al., High-strength internal cross-linking bacterial cellulose-network-based gel polymer electrolyte for dendrite-suppressing and high-rate lithium batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 10, 17809–17819 (2018)
L. Wang, R. Zhang, H. Dai et al., Reinforce the adhesion of gel electrolyte to electrode and the interfacial charge transfer via in situ electrospinning the polymeric nanofiber matrix. Energy Technol. 9, 2000865 (2021)
Y.Y. Zhai, K. Xiao, J.Y. Yu et al., Closely packed x-poly(ethylene glycol diacrylate) coated polyetherimide/poly(vinylidene fluoride) fiber separators for lithium ion batteries with enhanced thermostability and improved electrolyte wettability. J. Power Sources. 325, 292–300 (2016)
Z.-Y. Wu, H.-W. Liang, L.-F. Chen et al., Bacterial cellulose: a robust platform for design of three dimensional carbon-based functional nanomaterials. Acc. Chem. Res. 49, 96–105 (2016)
M. Yan, W. Qu, Q. Su et al., Biodegradable bacterial cellulose-supported quasi-solid electrolyte for lithium batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 12, 13950–13958 (2020)
U. Romling, M.Y. Galperin, Bacterial cellulose biosynthesis: diversity of operons, subunits, products, and functions. Trends Microbiol. 23, 545–557 (2015)
Z. Xue, D. He, X. Xie, Poly(ethylene oxide)-based electrolytes for lithium-ion batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A. 3, 19218–19253 (2015)
N. Zhao, F. Wu, Y. Xing et al., Flexible hydrogel electrolyte with superior mechanical properties based on poly(vinyl alcohol) and bacterial cellulose for the solid-state zinc-air batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 11, 15537–15542 (2019)
Q. Zheng, H.M. Yi, X.F. Li et al., Progress and prospect for NASICON-type Na3V2(PO4)(3) for electrochemical energy storage. J. Energy Chem. 27, 1597–1617 (2018)
H.L. Xiong, C.Y. Qi, S.Q. Lv et al., The synthesis of porous Na3V2(PO4)(3) for sodium-ion storage. Chem. Eur. J. 27, 14790–14799 (2021)
Z.L. Jian, Y.S. Hu, X.L. Ji et al., NASICON-structured materials for energy storage. Adv. Mater. 29, 1601925 (2017)
S.Q. Chen, C. Wu, L.F. Shen et al., Challenges and perspectives for NASICON-type electrode materials for advanced sodium-ion batteries. Adv. Mater. 29, 1700431 (2017)
H. Xiong, G. Sun, Z. Liu et al., Polymer stabilized droplet templating towards tunable hierarchical porosity in single crystalline Na3V2(PO4)3 for enhanced sodium-ion storage. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 60, 10334–10341 (2021)
H.C. Gao, I.D. Seymour, S. Xin et al., Na3MnZr(PO4)(3): a high-voltage cathode for sodium batteries. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 140, 18192–18199 (2018)
X. Ma, X. Cao, Y. Zhou et al., Tuning crystal structure and redox potential of NASICON-type cathodes for sodium-ion batteries. Nano Res. 13, 3330–3337 (2020)
S. Hussain, M.S. Javed, S. Asim et al., Novel gravel-like NiMoO4 nanoparticles on carbon cloth for outstanding supercapacitor applications. Ceram. Int. 46, 6406–6412 (2020)
S. Hussain, N. Ullah, Y.Y. Zhang et al., One-step synthesis of unique catalyst Ni9S8@C for excellent MOR performances. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy. 44, 24525–24533 (2019)
M. Tao, G. Du, Y. Zhang et al., TiOxNy nanoparticles/C composites derived from MXene as anode material for potassium-ion batteries. Chem. Eng. J. 369, 828–833 (2019)
Acknowledgements
We appreciate the support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 22005315), Program for Experimental Technology Research of Southwest University (SYJ2022011).
Funding
This research was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 22005315), Program for Experimental Technology Research of Southwest University (SYJ2022011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
DL and GD: Methodology, Investigation, Writing—original draft. YQ and YN: Writing—review and editing. SB and MX: Conceptualization, Resources, Project administration.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, D., Du, G., Qi, Y. et al. Bacterial cellulose network based gel polymer electrolyte for quasi-solid-state sodium-ion battery. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 33, 15313–15322 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-08395-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-08395-3