Abstract
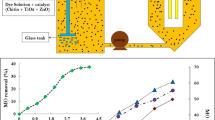
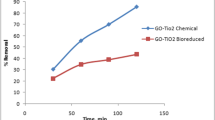
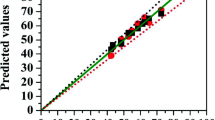
Due to the increase of environmental pollution by various industries in recent decades, preparing drinking water has become one of the most vital issues for many countries. The organic pollutant, such as different azo dyes, is one of the most important issues. Using photocatalyst materials is considered to be an optimal solution to prevent environmental pollution. In this work, novel ternary catalysts of CoFe2O4/TiO2/Au were synthesized for the photocatalytic reduction of methyl orange (MO) under UV light illumination. The localized surface plasmon resonance (LSPR) property of Au nanoparticles is widely exploited for their photocatalytic activities. In this research, both CoFe2O4 and TiO2 nanoparticles (NPs) were prepared by sol–gel method. Hydrothermal treatment was also used to synthesize the nanocomposite. Au nanoparticles were successfully loaded on the CoFe2O4/TiO2 surface to get CoFe2O4/TiO2/Au magnetic nanocomposites. To characterize the shape of the structure, morphology, purity, and particle size of the nanocomposite, scanning and transmission electron microscopy (SEM and TEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), Zeta potential analysis, dynamic light scattering (DLS), photoluminescence spectroscopy (PL), Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET), and Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy were employed. Alternating gradient field magnetometer (AGFM) studies show the superparamagnetic properties of the CoFe2O4 nanostructures. Finally, we investigated the catalytic performance and recyclability in reducing MO of synthesized nanocomposites by monitoring a UV–visible spectrophotometer. The composite catalysts can then be easily separated from the reaction solution using a magnet bar and ultimately reused. We used artificial neural network (ANN) to remove expensive experimental research and tried solving and predicting the novel phenomena with huge factors. Initially, information about the degradation of MO was gathered by experimental analyses. We then tried shaping and calculating the special algorithm that could find the best relation and high percentage of accuracy between input variables. The genetic algorithm as one of the most popular algorithms in an artificial world was selected to predict and train the model. In conclusion, the experimental results determined that the CoFe2O4/TiO2/Au magnetic nanocomposites were successfully synthesized and it exhibited a useful effect on the removal of azo dyes from the contaminated solutions. According to the prediction of removal efficiency of pollution by artificial neural network, the results show that using this algorithm has a high percentage of accuracy to investigate the experimental results of the current research.




















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this article.
References
Q. Wang, M. Zhang, C. Chen, W. Ma, J. Zhao, Photocatalytic aerobic oxidation of alcohols on TiO2: the acceleration effect of a Brønsted acid. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 49, 7976–7979 (2010)
D.A. Nicewicz, D.W. MacMillan, Merging photoredox catalysis with organocatalysis: the direct asymmetric alkylation of aldehydes. Science 322, 77–80 (2008)
A. Tanaka, K. Hashimoto, H. Kominami, Preparation of Au/CeO2 exhibiting strong surface plasmon resonance effective for selective or chemoselective oxidation of alcohols to aldehydes or ketones in aqueous suspensions under irradiation by green light. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 134, 14526–14533 (2012)
A. Albini, M. Fagnoni, Green chemistry and photochemistry were born at the same time. Green Chem. 6, 1–6 (2004)
C. Athanasekou, G.E. Romanos, S.K. Papageorgiou, G.K. Manolis, F. Katsaros, P. Falaras, Photocatalytic degradation of hexavalent chromium emerging contaminant via advanced titanium dioxide nanostructures. Chem. Eng. J. 318, 171–180 (2017)
I. Bibi, N.K. Niazi, G. Choppala, E.D. Burton, Chromium(VI) removal by siderite (FeCO3) in anoxic aqueous solutions: an X-ray absorption spectroscopy investigation. Sci. Total Environ. 640, 1424–1431 (2018)
H.X. Han, C. Shi, N. Zhang, L. Yuan, G.P. Sheng, Visible-light-enhanced Cr(VI) reduction at Pd-decorated silicon nanowire photocathode in photoelectrocatalytic microbial fuel cell. Sci. Total Environ. 639, 1512–1519 (2018)
M. Barjasteh-Moghaddam, A. Habibi-Yangjeh, Effect of operational parameters on photodegradation of methylene blue on ZnS nanoparticles prepared in presence of an ionic liquid as a highly efficient photocatalyst. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 8, 169–175 (2011)
A. Ajmal, I. Majeed, R.N. Malik, M. Iqbal, M.A. Nadeem, I. Hussain et al., Photocatalytic degradation of textile dyes on Cu2O-CuO/TiO2 anatase powders. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 4(2), 2138–2146 (2016)
Sh. Masoumi, G. Nabiyouni, D. Ghanbari, Photo-degradation of congored, acid brown and acid violet: photo catalyst and magnetic investigation of CuFe2O4–TiO2–Ag nanocomposites. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 27, 11017–11033 (2016)
A.L. Luna, M.A. Valenzuela, C. Colbeau-Justin, P. Vázquez, J.L. Rodriguez, J.R. Avendaño et al., Photocatalytic degradation of gallic acid over CuO–TiO2 composites under UV/Vis LEDs irradiation. Appl. Catal. A 521, 140–148 (2016)
T. Xin, M. Ma, H. Zhang, J. Gu, S. Wang, M. Liu, Q. Zhang, A new approach to quality function deployment planning with financial consideration. Appl. Surf. Sci. 288, 51 (2014)
S.J. Zhang, W.X. Huang, X.L. Fu, X.Z. Zheng, S.G. Meng, X.J. Ye, S.F. Chen, Photocatalytic organic transformations: Simultaneous oxidation of aromatic alcohols and reduction of nitroarenes on CdLa2S4 in one reaction system. Appl. Catal. B 233, 14 (2018)
V.M. Mboula, V. Hequet, Y. Andres, Y. Gru, R. Colin, J.M. Dona-Rodriguez, L.M. Pastrana-Martinez, A.M.T. Silva, M. Leleu, A.J. Tindall, S. Mateos, P. Falaras, Photocatalytic degradation of estradiol under simulated solar light and assessment of estrogenic activity. Appl. Catal. B 162, 437–444 (2015)
M. Tountas, Y. Topal, A. Verykios, A. Soultati, A. Kaltzoglou, T.A. Papadopoulos, F. Auras, K. Seintis, M. Fakis, L.C. Palilis, D. Tsikritzis, S. Kennou, A. Fakharuddin, L. Schmidt-Mende, S. Gardelis, M. Kus, P. Falaras, D. Davazoglou, P. Argitis, M. Vasilopoulou, A silanol-functionalized polyoxometalate with excellent electron transfer mediating behavior to ZnO and TiO2 cathode interlayers for highly efficient and extremely stable polymer solar cells. J. Mater. Chem. C 6, 1459–1469 (2018)
A. Toumazatou, M.K. Arfanis, P.A. Pantazopoulos, A.G. Kontos, P. Falaras, N. Stefanou, V. Likodimos, Slow-photon enhancement of dye sensitized TiO2 photocatalysis. Mater. Lett. 197, 123–126 (2017)
M.K. Arfanis, P. Adamou, N.G. Moustakas, T.M. Triantis, A.G. Kontos, P. Falaras, Photocatalytic degradation of salicylic acid and caffeine emerging contaminants using titania nanotubes. Chem. Eng. J. 310, 525–536 (2017)
M. Pelaez et al., Use of selected scavengers for the determination of NF-TiO2 reactive oxygen species during the degradation of microcystin-LR under visible light irradiation. J. Mol. Catal. A 425, 183–189 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcata.2016.09.035
V. Likodimos, A. Chrysi, M. Calamiotou, C. Fernandez-Rodriguez, J.M. DonaRodriguez, D.D. Dionysiou, P. Falaras, Microstructure and charge trapping assessment in highly reactive mixed phase TiO2 photocatalysts. Appl. Catal. B 192, 242–252 (2016)
L. Chen, L. Luo, Z. Chen, M. Zhang, J.A. Zapien, C.S. Lee, S.T. Lee, ZnO/Au composite nanoarrays as substrates for surface-enhanced raman scattering detection. J. Phys. Chem. C 114, 93–100 (2009)
X. Ma, K. Zhao, H. Tang, Y. Chen, C. Lu, W. Liu, Z. Tang, New insight into the role of gold nanoparticles in Au@CdS core–shell nanostructures for hydrogen evolution. Small 10, 4664–4670 (2014)
J. Guo, Y. Zhang, L. Shi, Y. Zhu, M.F. Mideksa, K. Hou, Z. Tang, Boosting hot electrons in hetero-superstructures for plasmon-enhanced catalysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 139, 17964–17972 (2017)
P. Lu, C.T. Campbell, Y. Xia, A sinter-resistant catalytic system fabricated by maneuvering the selectivity of SiO2 deposition onto the TiO2 surface versus the Pt nanoparticle surface. Nano Lett. 13, 4957–4962 (2014)
Y. Dai, L. Byungkwon, Y. Yong, C.M. Cobley, W. Li, C.E. Chul, G. Benjamin, P.T. Fanson, C.T. Campbell, Y. Sun, A sinter-resistant catalytic system based on platinum nanoparticles supported on TiO2 nanofibers and covered by porous silica. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 49, 8165–8168 (2010)
C. Zhang, F. Liu, Y. Zhai, H. Ariga, N. Yi, Y. Liu, K. Asakura, M. Flytzani-Stephanopoulos, H. He, Alkali-metal-promoted Pt/TiO2 opens a more efficient pathway to formaldehyde oxidation at ambient temperatures. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 124, 9628–9632 (2012)
A.V. Humbe, J.S. Kounsalye, S.B. Somvanshi, A. Kumar, K.M. Jadhav, Cation distribution, magnetic and hyperfine interaction studies of Ni–Zn spinel ferrites: role of Jahn Teller ion (Cu2+) substitution. Mater. Adv. 1(4), 880–890 (2020)
A. Shabani, G. Nabiyouni, J. Saffari et al., Photo-catalyst Fe3O4/TiO2 nanocomposites: green synthesis and investigation of magnetic nanoparticles coated on cotton. J. Mater. Sci. 27, 8661–8669 (2016)
P.B. Kharat, S.B. Somvanshi, P.P. Khirade, K.M. Jadhav, Induction heating analysis of surface-functionalized nanoscale CoFe2O4 for magnetic fluid hyperthermia toward noninvasive cancer treatment. ACS Omega 5(36), 23378–23384 (2020)
A. Hassani, P. Eghbali, Ö. Metin, Sonocatalytic removal of methylene blue from water solution by cobalt ferrite/mesoporous graphitic carbon nitride (CoFe2O4/ mpg-C3N4) nanocomposites: response surface methodology approach. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 25, 32140–32155 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3151-3
I. Ibrahim, A. Kaltzoglou, C. Athanasekou, F. Katsaros, E. Devlin, A.G. Kontos, N. Ioannidis, M. Perraki, P. Tsakiridis, L. Sygellou, M. Antoniadou, P. Falaras, Magnetically separable TiO2/CoFe2O4/Ag nanocomposites for the photocatalytic reduction of hexavalent chromium pollutant under UV and artificial solar light. Chem. Eng. J. 381, 122730 (2020)
A.R. Chavan, P.P. Khirade, S.B. Somvanshi, S.V. Mukhamale, K.M. Jadhav, Eco-friendly green synthesis and characterizations of CoFe2-x AlxO4 nanocrystals: analysis of structural, magnetic, electrical, and dielectric properties. J. Nanostruct. Chem. 11(3), 469–481 (2021)
N. Eskandari, G. Nabiyouni, S. Masoumi, D. Ghanbari, Preparation of a new magnetic and photo-catalyst CoFe2O4–SrTiO3 perovskite nanocomposite for photo-degradation of toxic dyes under short time visible irradiation. Composit. Part B 176, 107343 (2019)
S.B. Somvanshi, S.A. Jadhav, M.V. Khedkar, P.B. Kharat, S.D. More, K.M. Jadhav, Structural, thermal, spectral, optical and surface analysis of rare earth metal ion (Gd3+) doped mixed Zn–Mg nano-spinel ferrites. Ceram. Int. 46(9), 13170–13179 (2020)
M. Houshiar, F. Zebhi, Z. Jafari Razi, A. Alidoust, Z. Askari, Synthesis of cobalt ferrite (CoFe2O4) nanoparticles using combustion, coprecipitation, and precipitation methods: a comparison study of size, structural, and magnetic properties. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 371, 43–48 (2014)
S.B. Somvanshi, S.R. Patade, D.D. Andhare, S.A. Jadhav, M.V. Khedkar, P.B. Kharat, P.P. Khirade, K.M. Jadhav, Hyperthermic evaluation of oleic acid coated nano-spinel magnesium ferrite: Enhancement via hydrophobic-to-hydrophilic surface transformation. J. Alloys Compd. 835, 155422 (2020)
S. Ayyappan, S. Mahadevan, P. Chandramohan, M.P. Srinivasan, J. Philip, B. Raj, Influence of Co2þ ion concentration on the size, magnetic properties, and purity of CoFe2O4 spinel ferrite nanoparticles. J Phys. Chem. C 114, 6334–6341 (2010)
S.B. Somvanshi, P.B. Kharat, M.V. Khedkar, K.M. Jadhav, Hydrophobic to hydrophilic surface transformation of nano-scale zinc ferrite via oleic acid coating: Magnetic hyperthermia study towards biomedical applications. Ceram. Int. 46(6), 7642–7653 (2020)
X. Wang, Z. Zhang, Y. Zhao, K. Xia, Y. Guo, Z. Qu, R. Bai, A mild and facile synthesis of amino functionalized CoFe2O4@SiO2 for Hg(II) removal. Nanomaterials 8, 14 (2018)
S.R. Patade, D.D. Andhare, S.B. Somvanshi, S.A. Jadhav, M.V. Khedkar, K.M. Jadhav, Self-heating evaluation of superparamagnetic MnFe2O4 nanoparticles for magnetic fluid hyperthermia application towards cancer treatment. Ceram. Int. 46(16), 25576–25583 (2020)
M. Mylarappa, V.V. Lakshmi, K.R. Vishnu Mahesh, N. Raghavendra, H.P. Nagaswarupa, Cyclic voltammetry, impedance and thermal properties of CoFe2O4 obtained from waste Li-ion batteries. Mater. Today 5, 22425–22432 (2018)
M.M. Ismail, S.N. Rafeeq, J.M.A. Sulaiman et al., Electromagnetic interference shielding and microwave absorption properties of cobalt ferrite CoFe2O4/polyaniline composite. Appl. Phys. A 124, 380 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-018-1808-x
S.B. Somvanshi, M.V. Khedkar, P.B. Kharat, K.M. Jadhav, Influential diamagnetic magnesium (Mg2+) ion substitution in nano-spinel zinc ferrite (ZnFe2O4): thermal, structural, spectral, optical and physisorption analysis. Ceram. Int. 46(7), 8640–8650 (2020)
Sh. Mirzaee, S.F. Shayesteh, Ultrasound induced strain in ultrasmall CoFe2O4@ polyvinyl alcohol nanocomposites. Ultrasound Sonochem. 40, 583–586 (2018)
B. Somvanshi, S.P.B. Kharat, T.S. Saraf, S.B. Somwanshi, S.B. Shejul, K.M. Jadhav, Multifunctional nano-magnetic particles assisted viral RNA-extraction protocol for potential detection of COVID-19. Mater. Res. Innovat. 25(3), 169–174 (2021)
A.B. Bhosale, S.B. Somvanshi, V.D. Murumkar, K.M. Jadhav, Influential incorporation of RE metal ion (Dy3+) in yttrium iron garnet (YIG) nanoparticles: Magnetic, electrical and dielectric behaviour. Ceram. Int. 46(10), 15372–15378 (2020)
G.G. Bessegato, M.D. Cooke, P.A. Christensen, D. Wood, M.V.B. Zanoni, Synthesis and electrochemical characterization of Si/TiO2/Au composite anode: Efficient oxygen evolution and hydroxyl radicals generation. Electrochim. Acta 370, 137742 (2021)
N. Fehn, E. Vahidzadeh, K. Shankar, U. Heiz, A. Kartouzian, Surface second harmonic generation spectra of titania coated Au NPs. Appl. Surf. Sci. 581, 152381 (2022)
M. Yan, Y. Wu, X. Liu, Photocatalytic nanocomposite membranes for high-efficiency degradation of tetracycline under visible light: an imitated core-shell Au-TiO2-based design. J. Alloys Compd 855, 157548 (2021)
X. Yu, H. Qiu, Z. Wang, B. Wang, Q. Meng, S. Sun, Y. Tang, K. Zhao, Constructing the Z-scheme TiO2/Au/BiOI nanocomposite for enhanced photocatalytic nitrogen fixation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 556, 149785 (2021)
S. Zeng, E. Vahidzadeh, C.G. VanEssen, P. Kar, R. Kisslinger, A. Goswami, Y. Zhang, N. Mahdi, S. Riddell, A.E. Kobryn, S. Gusarov, P. Kumar, K. Shankar, Optical control of selectivity of high rate CO2 photoreduction via interband- or hot electron Z-scheme reaction pathways in Au-TiO2 plasmonic photonic crystal photocatalyst. Appl. Catal. B 267, 118644 (2020)
H. Zhang, T. Abdiryim, R. Jamal, J. Li, H. Liu, A. Kadir, D. Zou, Y. Che, N. Serkjan, Self-powered TiO2 NRs UV photodetectors: Heterojunction with PTTh and enhanced responsivity by Au nanoparticles. J. Alloys Compd 899, 163279 (2022)
A.P. Manuel, K. Shankar, Hot electrons in TiO2–noble metal nano-heterojunctions: fundamental science and applications in photocatalysis. Nanomaterials , (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11051249
A.A. Oladipo et al., Bifunctional composite from spent “Cyprus coffee” for tetracycline removal and phenol degradation: Solar-Fenton process and artificial neural network. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 90, 89–99 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2015.08.054
S. Mohanty, Artificial neural network based system identification and model predictive control of a flotation column. J. Process Control 19, 991–999 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jprocont.2009.01.001
M. Dolatabadi, M. Mehrabpour, M. Esfandyari, H. Alidadi, M. Davoudi, Modeling of simultaneous adsorption of dye and metal ion by sawdust from aqueous solution using of ANN and ANFIS. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 181, 72–78 (2018)
S. Al-Thyabat, On the optimization of froth flotation by the use of an artificial neural network. J. China Univ. Min. Technol. 18(3), 418–426 (2008)
F. Song, ANFIS-based fingerprint-matching algorithm. Opt. Eng. 43(8), 1814 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1117/1.1765663
D.I. Mendoza-Castillo, H.E. Reynel-Avila, F.J. Sanchez-Ruiz, R. Trejo-Valencia, J.E. Jaime-Leal, A. Bonilla-Petriciolet, Insights and pitfalls of artificial neural network modeling of competitive multi-metallic adsorption data. J. Mol. Liq. 251, 15–27 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2017.12.030
M. Tanzifi et al., Adsorption of Amido Black 10B from aqueous solution using polyaniline/SiO2 nanocomposite: experimental investigation and artificial neural network modeling. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 510, 246–261 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2017.09.055
E. Jorjani, S. Chehreh, S. Mesroghli, Prediction of microbial desulfurization of coal using artificial neural networks. Miner. Eng. 20, 1285–1292 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2007.07.003
H. Cao, G. Si, Y. Zhang, X. Ma, A hybrid controller of self-optimizing algorithm and ANFIS for ball mill pulverizing system. Int. Conf. Mechatron. Autom. 2007, 3289–3294 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICMA.2007.4304089
D. Podstawczyk, A. Witek-Krowiak, A. Dawiec, A. Bhatnagar, Biosorption of copper(II) ions by flax meal: empirical modeling and process optimization by response surface methodology (RSM) and artificial neural network (ANN) simulation. Ecol. Eng. 83, 364–379 (2015)
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by AS, GN, and DG. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Consent to participate
All authors have the consent to participate.
Consent for publication
All authors have the consent to publish.
Ethical approval
This material is the authors’ own original work, which has not been previously published elsewhere. All authors have been personally and actively involved in substantial work leading to the paper and will take public responsibility for its content.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shabani, A., Nabiyouni, G. & Ghanbari, D. Preparation and photocatalytic study of CoFe2O4/TiO2/Au nanocomposites and their applications in organic pollutant degradation and modeling by an artificial neural network (ANN). J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 33, 9885–9904 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-07978-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-07978-4