Abstract
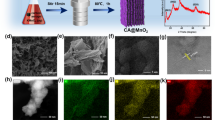
Nitrogen-doped porous carbon with parallel macropore channels is prepared from Luffa sponge through a facile one-step carbonization process. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy measurement indicates that nitrogen is doped into the carbonized product of Luffa sponge. The pore structure and morphology characterizations demonstrate that the obtained Luffa sponge-based nitrogen-doped porous carbon (LSNPC) has a high surface area and unique hierarchical porous architecture containing parallel macropore channels and mesopores/micropores developed on the macropore channel wall. The as-prepared LSNPC is employed to fabricate the counter electrode for dye-sensitized solar cells (DSCs). The combination of nitrogen doping, unique hierarchical porous architecture, and high surface area endows LSNPC counter electrode with superior electrocatalytic activity for the I−/I3− redox reaction. Consequently, the DSC based on LSNPC counter electrode delivers a power conversion efficiency of 6.92%, which is comparable to the efficiency of the cell based on the conventional Pt counter electrode.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The authors declare that all data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article.
References
B. O’Regan, M. Grätzel, A low-cost, high-efficiency solar cell based on dye- sensitized colloidal TiO2 films. Nature 353, 737–740 (1991)
K. Sharma, V. Sharma, S.S. Sharma, Dye-sensitized solar cells: fundamentals and current status. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 3, 381 (2018)
M. Kokkoneen, P. Talbi, J. Zhou, S. Asgari, J. Halme, A. Hagfeldt, G. Hashmi, Advanced research trends in dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Mater. Chem. A 9, 10527–10545 (2021)
N. Sharifi, F. Tajabadi, N. Taghavinia, Recent developments in dye-sensitized solar cells. Chem Phys Chem 15, 3902–3927 (2014)
K. Kakiage, Y. Aoyama, T. Yano, K. Oya, J. Fujisawa, M. Hanaya, Highly-efficient dye-sensitized solar cells with collaborative sensitization by silyl-anchor and carboxy-anchor dyes. Chem. Commun. 51, 15894–15897 (2015)
S. Mathew, A. Yella, P. Gao, R. Humphry-Baker, N. Ashari-Astani, I. Tavernelli, U. Rothlisberger, M.K. Nazeeruddin, M. Grätzel, Dye-sensitized solar cells with 13% efficiency achieved through the molecular engineering of porphyrin sensitizers. Nat. Chem. 6, 242–247 (2014)
D. Kuang, J. Brillet, P. Chen, M. Takata, S. Uchida, H. Miura, K. Sumioka, S.M. Zakeeruddin, M. Grätzel, Application of highly ordered TiO2 nanotube arrays in flexible dye-sensitized solar cells. ACS Nano 6, 1113–1116 (2008)
https://www.nrel.gov/pv/assets/pdfs/best-research-cell-efficiencies.20200803.pdf
J. Wu, Z. Lan, J. Lin, M. Huang, L. Fan, G. Lou, Y. Xie, Y. Wei, Counter electrodes in dye-sensitized solar cells. Chem. Soc. Rev. 46, 5975–6023 (2017)
V. Dao, H. Choi, Pt nanourchins as efficient and robust counter electrode materials for dye-sensitized solar cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8, 1004–1010 (2016)
T. Chen, T. Liu, J. Ren, T. He, Y. Cao, N. Wang, Z. Guo, Synergistic carbon nanotube aerogel-Pt nanocomposites toward enhanced energy conversion in dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Mater. Chem. A 4, 3238–3244 (2016)
L. Kavan, J. Yum, M. Grätzel, Graphene-based cathodes for liquid-junction dye sensitized solar cells: electrocatalytic and mass transport effects. Electrochim. Acta 128, 349–359 (2014)
F. Lodermeyer, M. Prato, R.D. Costa, D.M. Guldi, Facile and quick preparation of carbon nanohorn-based counter electrodes for efficient dye-sensitized solar cells. Nanoscale 8, 7556–7561 (2016)
N. Narudin, P. Ekanayake, Y. Soon, H. Nakajima, C. Lim, Enhanced properties of low-cost carbon black-graphite counter electrode in DSSC by incorporating binders. Sol. Energy 225, 237–244 (2021)
W. Hou, Y. Xiao, G. Han, D. Fu, R. Wu, Serrated, flexible and ultrathin polyaniline nanoribbons: an efficient counter electrode for the dye-sensitized solar cell. J. Power Sources 322, 155–162 (2016)
D. Kim, S.E. Atanasov, P. Lemaire, K. Lee, G.N. Parsons, Platinum-free cathode for dye-sensitized solar cells using poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDOT) formed via oxidative molecular layer deposition. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 7, 3866–3870 (2015)
G. Yue, X. Zhang, L. Wang, J. Wu, J. Lin, M. Huang, Z. Lan, Highly efficient and stable dye-sensitized solar cells based onnanographite/polypyrrole counter electrode. Electrochim. Acta 129, 229–236 (2014)
T. Xu, D. Kong, H. Tang, A. Gurung, K. Kou, L. Chen, Q. Qiao, W. Huang, Transparent MoS2/PEDOT composite counter electrodes for bifacial dye-sensitized solar cells. ACS Omega 5, 8687–8696 (2020)
X. Meng, Ch Yu, B. Lu, J. Yang, J. Qiu, Dual integration system endowing two-dimensional titanium disulfide with enhanced triiodide reduction performance in dye-sensitized solar cells. Nano Energy 22, 59–69 (2016)
G. Wang, S. Hou, C. Yan, Y. Lin, S. Liu, Three-dimensional porous vanadium nitride nanoribbon aerogels as Pt-free counter electrode for high-performance dye-sensitized solar cells. Chem. Eng. J. 322, 611–617 (2017)
M. Wu, J. Bai, Y. Wang, A. Wang, L. Wang, Z. Wang, A. Hagfeldt, T. Ma, High-performance phosphide/carbon counter electrode for both iodide and organic redox couples in dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Mater. Chem. 22, 11121–11127 (2012)
Y. Duan, Q. Tang, J. Liu, B. He, L. Yu, Transparent metal selenide alloy counter electrodes for high-efficiency bifacial dye-sensitized solar cells. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 53, 14569–14574 (2014)
B. Pang, M. Zhang, C. Zhou, J. Feng, Y. Chen, L. Yu, L. Dong, Heterogeneous FeNi3/NiFe2O4 nanoparticles with modified graphene as electrocatalysts for high performance dye-sensitized solar cells. Chem. Eng. J. 405, 126944 (2021)
J. Zhang, S. Kuang, S. Nian, G. Wang, The effect of carbonization temperature on the electrocatalytic performance of nitrogen-doped porous carbon as counter electrode of dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 26, 6913–6919 (2015)
D. Yang, Ch Kim, M. Song, J. Lee, M. Ju, J. Yu, N-doped hierarchical hollow mesoporous carbon as metal-free cathode for dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Phys. Chem. C 118, 16694–16702 (2014)
L. Li, C. Wang, J. Liao, A. Manthiram, Dual-template synthesis of N-doped macro/mesoporous carbon with an open-pore structure as a metal-free catalyst for dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Power Sources 300, 254–260 (2015)
M. Chen, L. Shao, Y. Liu, T. Ren, Z. Yuan, Nitrogen-doped ordered cubic mesoporous carbons as metal-free counter electrodes for dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Power Sources 283, 305–313 (2015)
Y. Zhang, S. Liu, X. Zheng, Y. Xu, F. Kang, Q. Yang, J. Liu, Biomass organs control the porosity of their pyrolyzed carbon. Adv. Funct. Mater. 27, 1604687 (2017)
G. Wang, J. Bi, M. Lei, J. Liu, W. Zhang, Hierarchical porous carbon obtained from directly carbonizing carex meyeriana for high-performance supercapacitors. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 32, 21278–21287 (2021)
J. Sun, J. Niu, M. Liu, M. Dou, F. Wang, Biomass-derived nitrogen-doped porous carbons with tailored hierarchical porosity and high specific surface area for high energy and power density supercapacitors. Appl. Surf, Sci. 427, 807–813 (2018)
A.K. Mondal, K. Kretschmer, Y. Zhao, C. Wang, B. Sun, G. Wang, Nitrogen-doped porous carbon nanosheets from eco-friendly eucalyptus leaves as high performance electrode materials for supercapacitors and lithium ion batteries. Chem. Eur. J. 23, 3683–3690 (2017)
V.O.A. Tanobe, T.H.D. Sydenstricker, M. Munaro, S.C.A. Amico, Comprehensive characterization of chemically treated brazilian sponge-gourds (luffa cylindrica), Polym. Test 24, 474–482 (2005)
N. Xiao, J. Song, Y. Wang, Y. Zhou, Z. Liu, M. Li, J. Qiu, Nitrogen-doped porous carbon with well-balanced charge conduction and electrocatalytic activity for dye-sensitized solar cells. Carbon 128, 201–204 (2017)
M. Zhou, F. Pu, Z. Wang, S. Guang, Nitrogen-doped porous carbons through KOH activation with superior performance in supercapacitors. Carbon 68, 185–194 (2014)
A. Sahasrabudhe, S. Kapri, S. Bhattacharyya, Graphitic porous carbon derived from human hair as ‘green’ counter electrode in quantum dot sensitized solar cells. Carbon 107, 395–404 (2017)
S. Jiao, J. Du, Z. Du, W. Jiang, Z. Pan, Y. Li, X. Zhong, Nitrogen-Doped mesoporous carbons as counter electrodes in quantum dot sensitized solar cells with a conversion efficiency exceeding 12%. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 8, 559–564 (2017)
P. Zhai, T. Wei, Y. Chang, Y. Huang, W. Yeh, H. Su, S. Feng, High electrocatalytic and wettable nitrogen-doped microwave-exfoliated graphene nanosheets as counter electrode for dye-sensitized solar cells. Small 10, 3347–3353 (2014)
J.D. Roy-Mayhew, D.J. Bozym, C. Punckt, I.A. Aksay, Functionalized graphene as a catalytic counter electrode in dye-sensitized solar cells. ACS Nano 4, 6203–6211 (2010)
P. Joshi, L. Zhang, Q. Chen, H. Feng, Q. Qiao, Electrospun carbon nanofibers as low-cost counter electrode for dye-sensitized soalr cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2, 3572–3577 (2010)
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by XF. The first draft of the manuscript was written by DW and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fu, X., Wang, D. Nitrogen-doped porous carbon with parallel macropore channels derived from Luffa sponge as counter electrode of high-performance dye-sensitized solar cells. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 33, 5224–5232 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-07711-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-07711-1