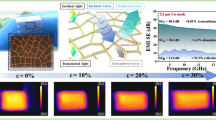
Abstract
Structural microwave absorption material has become one of the key research directions for microwave absorption materials since they have a combination of mechanical properties, microwave absorption properties and excellent designability. To this end, this work was conducted to prepare two kinds of modified carbonyl iron powders, KH550-CIP and EP@CIP, by surface modification of carbonyl iron powder (CIP) with silane coupling agent (KH550) and epoxy sizing agent, respectively, and to prepare CIP/GF/CF/EP laminate-structured absorption composites using a vacuum-assisted molding process (VARI). Then the effects of CIP surface modification on the microscopic morphology, mechanical properties and microwave absorption properties of the composites were investigated. The modified CIP/GF/CF/EP composite has increased strength, reduced modulus and a significantly larger effective absorption bandwidth, making it a structural absorbing material with practical applications. It is found that KH550-CIP/GF/CF/EP is more outstanding in absorption performance with the minimum reflection loss value of − 31.6 dB at 16.44 GHz and the effective bandwidth of 4.56 GHz, while EP@CIP/GF/CF/EP was more improved in mechanical properties with the tensile strength of 366 MPa, flexural strength of 320.6 MPa, compressive strength of 275.5 MPa, and interlayer shear strength of 33.68 MPa.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Y. Cheng, G. Ji, Z. Li et al., Facile synthesis of FeCo alloys with excellent microwave absorption in the whole Ku-band: effect of Fe/Co atomic ratio. J. Alloys Compd. 704, 289–295 (2017)
L. Ye, Y. Lu, Z. Su et al., Functionalized composite structures for new generation airframes: a review. Compos. Sci. Technol. 65(9), 1436–1446 (2005)
S. Geetha, K.K.S. Kumar, C.R.K. Rao et al., EMI shielding: methods and materials-a review. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 112(4), 2073–2086 (2009)
G. Wang, Z. Gao, S. Tang et al., Microwave absorption properties of carbon nanocoils coated with highly controlled magnetic materials by atomic layer deposition. ACS Nano 6(12), 11009–11017 (2012)
H. Wang, F. Meng, F. Huang et al., Interface modulating CNTs@PANi hybrids by controlled unzipping of the walls of CNTs to achieve tunable high-performance microwave absorption. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 11(12), 12142–12153 (2019)
T. Han, R. Luo, G. Cui, L. Wang, Effect of SiC nanowires on the high-temperature microwave absorption properties of SiCf/SiC composites. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 39, 1743–1756 (2019)
Y. Qian, Z. Yao, H. Lin, J. Zhou, Mechanical and microwave absorption properties of 3D-printed Li0.44Zn0.2Fe2.36O4/polylactic acid composites using fused deposition modeling. J. Mater. Sci. 29, 19296–19307 (2018)
D. Micheli, A. Vricella, R. Pastore et al., Ballistic and electromagnetic shielding behaviour of multifunctional Kevlar fiber reinforced epoxy composites modified by carbon nanotubes. Carbon 104, 141–156 (2016)
M. Crespo, N. Méndez, M. González et al., Synergistic effect of magnetite nanoparticles and carbon nanofibres in electromagnetic absorbing composites. Carbon 74, 63–72 (2014)
A. Hazarika, B.K. Deka, K. Kong et al., Microwave absorption and mechanical performance of α-MnO2 nanostructures grown on woven Kevlar fiber/reduced graphene oxide-polyaniline nanofiber array-reinforced polyester resin composites. Composites B 140, 123–132 (2018)
A. Shah, A. Ding, Y. Wang et al., Enhanced microwave absorption by arrayed carbon fibers and gradient dispersion of Fe nanoparticles in epoxy resin composites. Carbon 96, 987–997 (2016)
D. Micheli, C. Apollo, R. Pastore et al., X-Band microwave characterization of carbon-based nanocomposite material, absorption capability comparison and RAS design simulation. Compos. Sci. Technol. 70(2), 400–409 (2010)
M. Chen, Z. Yong, Y. Pan et al., Gradient multilayer structural design of CNTs/SiO2 composites for improving microwave absorbing properties. Mater. Des. 32(5), 3013–3016 (2011)
J.H. Oh, K.S. Oh, C.G. Kim et al., Design of radar absorbing structures using glass/epoxy composite containing carbon black in x-band frequency ranges. Composites B 35(1), 49–56 (2004)
X. Shen, H. Liu, Z. Wang et al., Microwave absorption properties of a double-layer absorber based on nanocomposite BaFe12O19/α-Fe and nanocrystalline α-Fe microfibers. Chin. Phys. B 07(23), 746–751 (2014)
F. Xu, M. Li, Q. Huo et al., Microwave absorbing properties and structural design of microwave absorbers based on polyaniline and polyaniline/magnetite nanocomposite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 374, 311–316 (2015)
Y. Gao, X. Gao, J. Li et al., Microwave absorbing and mechanical properties of alternating multilayer carbonyl iron powder-poly(vinyl chloride) composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 135(12), 45846 (2018)
C. Wu, W. Lee, Curing and thermal properties of copolymer epoxy resins prepared by copolymerized bisphenol-A and epichlorohydrin with liquefied Dendrocalamus latiflorus. Polym. J. 42(9), 711–715 (2010)
Y. Feng, T. Qiu, J. Zhang et al., Effects of silane coupling agent on microstructure and mechanical properties of EPDM/carbonyl iron microwave absorbing patch. J Wuhan Univ Technol 21(4), 78–82 (2006)
X. Weng, X. Lv, B. Li et al., One-pot preparation of reduced graphene oxide/carbonyl iron/polyvinyl pyrrolidone ternary nanocomposite and its synergistic microwave absorbing properties. Mater. Lett. 188(1), 280–283 (2017)
G. Bergman, Unexpected Stress Corrosion Failures of High Quality FRP Process Equipment (NACE International, Houston, 2004)
S. Huang, G. Chen, M. Deng et al., Electromagnetic shielding effectiveness of graphite-carbon fiber cement based materials. J. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 38(4), 549–552 (2010)
K. Qian, Z. Yao, H. Lin et al., The influence of Nd substitution in Ni–Zn ferrites for the improved microwave absorption properties. Ceram. Int. 46(1), 227–235 (2020)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51702158), Open Fund of Key Laboratory of Materials Preparation and Protection for Harsh Environment (Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics), Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (56XCA20013-5)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
WZ performed writing—original draft and writing—review & editing. XZ performed conceptualization, data curation and formal analysis. ZY and JZ performed funding acquisition, Investigation, methodology and project administration.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, W., Yao, Z., Zhang, X. et al. Fabrication and properties of structural microwave absorption composites based on VARI process. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 33, 5127–5137 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-07701-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-07701-3