Abstract
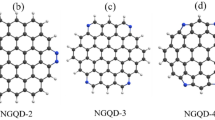
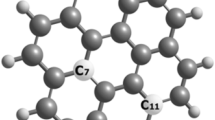
The photoluminescence quantum yield of graphene quantum dots (GQDs) is usually very low because the fast electron–hole recombination converts electronic energy into thermal energy. This problem can be addressed by controlling the surface chemistry of the GQDs through the manipulation of the oxidation configurations. The optoelectronic properties of GQDs functionalized with hydroxyl groups at different sites of the GQDs are investigated in this work using density-functional theory (DFT) and linear response time-dependent DFT calculations. We also calculated the non-radiative decay rates of GQDs with different oxidation configurations. Our results show that the center-oxidized configurations lead to a larger perturbation of the conjugated π-system, reducing the band gap and the red-shift of the absorption spectra. The addition of solvent leads to red-shifts in the absorption spectra and increased intensities for some center-oxidized configurations. In contrast, only the red-shifts occur in the absorption spectra for the edge-oxidized configurations. Placement of the hydroxyl group in the basal plane of the GQD accelerates the non-radiative decay, while the placement of the hydroxyl group at the edges of the GQD suppresses the non-radiative decay. The current calculations shed light on the relationship between the surface chemistry and the photoluminescence efficiency of GQDs.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
M.H. Facure, R. Schneider, L.A. Mercante, D.S. Correa, A review on graphene quantum dots and their nanocomposites: from laboratory synthesis towards agricultural and environmental applications. Environ. Sci. Nano 7(12), 3710–3734 (2020)
T.A. Tabish, C.J. Scotton, D.C.J. Ferguson, L. Lin, A.v. der Veen, S. Lowry, M. Ali, F. Jabeen, M. Ali, P.G. Winyard, Biocompatibility and toxicity of graphene quantum dots for potential application in photodynamic therapy. Nanomedicine 13, 1923–1937 (2018)
Q. Liu, B. Guo, Z. Rao, B. Zhang, J.R. Gong, Strong two-photon-induced fluorescence from photostable, biocompatible nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots for cellular and deep-tissue imaging. Nano Lett. 13(6), 2436–2441 (2013)
M.X. Liu, Y. Nuri, Y. Maksym, J. Maximilian, V. Wood, E.H. Sargent, Colloidal quantum dot electronics, Nature. Electronics 4, 548–558 (2021)
S. Campuzano, P. Yáñez-Sedeño, J.M. Pingarrón, Carbon dots and graphene quantum dots in electrochemical biosensing. Nanomaterials 9(4), 634 (2019)
S.H. Yoon, S. Kim, H.J. Woo, J. Kim, Y.W. Kim, S. Seo, E. Yoo, J.W. Cho, Y.J. Song, Y.J. Choi, Flexible quantum dot light-emitting diodes without sacrificing optical and electrical performance. Appl. Surf. Sci. 566, 150614 (2021)
S. Sarthik, B.L. Sovan, B. Koushik, S.K., Nikhil, Graphene quantum dots-ornamented waterborne epoxy-based fluorescent adhesive via reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer-mediated miniemulsion polymerization: a potential material for art conservation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 13(30), 36307–36319 (2021)
S. Wang, Z. Li, X. Xu, G. Zhang, Y. Li, Q. Peng, Amino-functionalized graphene quantum dots as cathode interlayer for efficient organic solar cells: quantum dot size on interfacial modification ability and photovoltaic performance. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 6(3), 1801480 (2019)
D. Du, K. Wang, Y. Wen, Y. Li, Y.Y. Li, Photodynamic graphene quantum dot: reduction condition regulated photoactivity and size dependent efficacy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 8(5), 3287–3294 (2016)
Z.J. Zhou, Z.B. Liu, Z.R. Li, X.R. Huang, C.C. Sun, Shape effect of graphene quantum dots on enhancing second-order nonlinear optical response and spin multiplicity in NH2–GQD–NO2 systems. J. Phys. Chem. C 115(33), 16282–16286 (2011)
L. Kittiratanawasin, S. Hannongbua, The effect of edges and shapes on band gap energy in graphene quantum dots. Integr. Ferroelectr. 175(1), 211–219 (2016)
S.P. Wang, Y. Li, Z.X. Zhang, Y. Zhang, Y. Wang, S.M. Kong, H.C. Li, W. Jian, F.Q. Bai, H.X. Zhang, Computational studies on the materials combining graphene quantum dots and Pt complexes with adjustable luminescence characteristics. Inorg. Chem. 60, 1480–1490 (2021)
P. Cui, Y. Xue, Tuning non-radiative recombination loss by selective oxidation patterns of epoxy groups bound to different sites of graphene quantum dots. Chem. Eng. J. 431, 134052 (2022)
P. Cui, Y. Xue, The role of center-N-doping in non-radiative recombination loss of nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots. Mater. Sci. Semiconductor Process. 139, 106323 (2022)
Z. Gan, H. Xu, Y. Hao, Mechanism for excitation-dependent photoluminescence from graphene quantum dots and other graphene oxide derivates: consensus, debates and challenges. Nanoscale 8(15), 7794–7807 (2016)
A.L. Exarhos, M.E. Turk, J.M. Kikkawa, Ultrafast spectral migration of photoluminescence in graphene oxide. Nano Lett. 13(2), 344–349 (2013)
S. Chen, N. Ullah, T. Wang, R. Zhang, Tuning the optical properties of graphene quantum dots by selective oxidation: a theoretical perspective. J. Mater. Chem. C 6(25), 6875–6883 (2018)
A. Sheely, B. Gifford, S. Tretiak, A. Bishop, Tunable optical features of graphene quantum dots from edge functionalization. J. Phys. Chem. C 125(17), 9244–9252 (2021)
P. Cui, Y. Xue, Role of edge nitrogen doping in non-radiative decay dynamics of graphene quantum dots: a Fermi’s golden rule analysis, Applied. Nanoscience 11, 2837–2845 (2021)
J. Shen, Y. Zhu, X. Yang, J. Zong, J. Zhang, C. Li, One-pot hydrothermal synthesis of graphene quantum dots surface-passivated by polyethylene glycol and their photoelectric conversion under near-infrared light. New J. Chem. 36(1), 97–101 (2012)
H. Tetsuka, R. Asahi, A. Nagoya, K. Okamoto, I. Tajima, R. Ohta, A. Okamoto, Optically tunable amino-functionalized graphene quantum dots. Adv. Mater. 24(39), 5333–5338 (2012)
L.L. Li, J. Ji, R. Fei, C.Z. Wang, Q. Lu, J.R. Zhang, L.P. Jiang, J.J. Zhu, A facile microwave avenue to electrochemiluminescent two-color graphene quantum dots. Adv. Func. Mater. 22(14), 2971–2979 (2012)
M.A. Sk, A. Ananthanarayanan, L. Huang, K.H. Lim, P. Chen, Revealing the tunable photoluminescence properties of graphene quantum dots. J. Mater. Chem. C 2(34), 6954–6960 (2014)
X. Wen, P. Yu, Y.R. Toh, X. Hao, J. Tang, Intrinsic and extrinsic fluorescence in carbon nanodots: ultrafast time-resolved fluorescence and carrier dynamics. Adv. Opt. Mater. 1(2), 173–178 (2013)
M.X. Gao, C.F. Liu, Z.L. Wu, Q.L. Zeng, X.X. Yang, W.B. Wu, Y.F. Li, C.Z. Huang, A surfactant-assisted redox hydrothermal route to prepare highly photoluminescent carbon quantum dots with aggregation-induced emission enhancement properties. Chem. Commun. 49(73), 8015–8017 (2013)
H. Abdelsalam, H. Elhaes, M.A. Ibrahim, First principles study of edge carboxylated graphene quantum dots. Physica B 537, 77–86 (2018)
S. Daryabari, S. Mansouri, J. Beheshtian, M. Karimkhani, A computational study on the novel defects of graphene quantum dot as a promising anode material for sodium ion battery. Mater. Chem. Phys. 265, 12448 (2021)
B. Liu, Y. Gao, M.A. Jabed, S. Kilina, G. Liu, W. Sun, Lysosome targeting bis-terpyridine ruthenium (II) complexes: photophysical properties and in vitro photodynamic therapy. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 3(9), 6025–6038 (2020)
A.J.W. Frisch, USA, 25p, gaussian 09W Reference, (2009).
M. Cossi, N. Rega, G. Scalmani, V.J. Barone, Energies, structures, and electronic properties of molecules in solution with the C-PCM solvation model. J. Comput. Chem. 24(6), 669–681 (2003)
J. Feldmann, G. Peter, E. Göbel, P. Dawson, K. Moore, C. Foxon, R. Elliott, Linewidth dependence of radiative exciton lifetimes in quantum wells. Phys. Rev. Lett. 59(20), 2337 (1987)
J. Hunger, A. Stoppa, A. Thoman, M. Walther, R. Buchner, Broadband dielectric response of dichloromethane. Chem. Phys. Lett. 471(1–3), 85–91 (2009)
B.S. Brunschwig, N. Sutin, Rate-constant expressions for nonadiabatic electron-transfer reactions. Comments Inorg. Chem. 6(4), 209–235 (1987)
V. Barone, J. Bloino, M. Biczysko, Vibrationally-resolved electronic spectra in GAUSSIAN 09. Revision a 2, 1–20 (2009)
A. Ito, T.J. Meyer, The Golden Rule. Application for fun and profit in electron transfer, energy transfer, and excited-state decay. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 14(40), 13731–13745 (2012)
G.S.M. Tong, K.T. Chan, X. Chang, C.-M. Che, Theoretical studies on the photophysical properties of luminescent pincer gold (III) arylacetylide complexes: the role of π-conjugation at the C-deprotonated [C^ N^ C] ligand. Chem. Sci. 6(5), 3026–3037 (2015)
V. Sharma, P.K. Jha, Enhancement in power conversion efficiency of edge-functionalized graphene quantum dot through adatoms for solar cell applications. Solar. Energy Mater. Solar. Cells. 200, 10990 (2019)
T. Lu, F.J.J.o.c.c. Chen, Multiwfn: a multifunctional wavefunction analyzer, 33(5) (2012) 580–592.
C.A. Guido, P. Cortona, B. Mennucci, C. Adamo, On the metric of charge transfer molecular excitations: a simple chemical descriptor. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 9(7), 3118–3126 (2013)
J. Wang, S. Cao, Y. Ding, F. Ma, W. Lu, M. Sun, Theoretical investigations of optical origins of fluorescent graphene quantum dots. Sci. Rep. 6(1), 1–5 (2016)
P. Cui, Effect of boron and nitrogen doping on carrier relaxation dynamics of graphene quantum dots. Mater. Res. Express 5(6), 065034 (2018)
C.T. Chien, S.S. Li, W.J. Lai, Y.C. Yeh, H.A. Chen, I.S. Chen, L.C. Chen, K.H. Chen, T. Nemoto, S. Isoda, Tunable photoluminescence from graphene oxide. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 51(27), 6662–6666 (2012)
S.H. Dave, C. Gong, A.W. Robertson, J.H. Warner, J.C. Grossman, Chemistry and structure of graphene oxide via direct imaging. ACS Nano 10(8), 7515–7522 (2016)
M.Z. Hossain, J.E. Johns, K.H. Bevan, H.J. Karmel, Y.T. Liang, S. Yoshimoto, K. Mukai, T. Koitaya, J. Yoshinobu, M. Kawai, Chemically homogeneous and thermally reversible oxidation of epitaxial graphene. Nat. Chem. 4(4), 305–309 (2012)
J.E. Johns, M.C. Hersam, Atomic covalent functionalization of graphene. Acc. Chem. Res. 46(1), 77–86 (2013)
J.M. Carlsson, Buckle or break. Nat. Mater. 6(11), 801–802 (2007)
L. Lin, S. Zhang, Creating high yield water soluble luminescent graphene quantum dots via exfoliating and disintegrating carbon nanotubes and graphite flakes. Chem. Commun. 48(82), 10177–10179 (2012)
J.H. Warner, E.R. Margine, M. Mukai, A.W. Robertson, F. Giustino, A.I. Kirkland, Dislocation-driven deformations in graphene. Science 337(6091), 209–212 (2012)
S.S. Daryabari, J. Beheshtian, S. Mansouri, Helium selectivity of H-, B-, N-, and F-doped nanoporous graphene membranes in the presence of natural gas: A density functional theory study. Superlattices. Microstructures 141, 106478 (2020)
Y. Li, H. Shu, X. Niu, J. Wang, Electronic and optical properties of edge-functionalized graphene quantum dots and the underlying mechanism. J. Phys. Chem. C 119(44), 24950–24957 (2015)
Z. Zhang, K. Chang, F. Peeters, Tuning of energy levels and optical properties of graphene quantum dots. Phys Rev B 77(23), 235411 (2008)
X. Niu, Y. Li, H. Shu, J. Wang, Revealing the underlying absorption and emission mechanism of nitrogen doped graphene quantum dots. Nanoscale 8(46), 19376–19382 (2016)
W. Yang, R.G. Parr, Hardness, softness, and the fukui function in the electronic theory of metals and catalysis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 82(20), 6723–6726 (1985)
M.L. Mueller, X. Yan, B. Dragnea, L.-S. Li, Slow hot-carrier relaxation in colloidal graphene quantum dots. Nano Lett. 11(1), 56–60 (2011)
X. Li, M. Rui, J. Song, Z. Shen, H. Zeng, Carbon and graphene quantum dots for optoelectronic and energy devices: a review. Adv. Func. Mater. 25(31), 4929–4947 (2015)
W. Kong, Y. Wang, L. Wang, Y. Li, Y. Li, W. Xue, Investigation of photoluminescence behavior of reduced graphene quantum dots. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 99, 199–205 (2019)
S. Zhu, Y. Song, J. Wang, H. Wan, Y. Zhang, Y. Ning, B. Yang, Photoluminescence mechanism in graphene quantum dots: quantum confinement effect and surface/edge state. Nano Today 13, 10–14 (2017)
S. Zhu, J. Zhang, S. Tang, C. Qiao, L. Wang, H. Wang, X. Liu, B. Li, Y. Li, W. Yu, Surface chemistry routes to modulate the photoluminescence of graphene quantum dots: from fluorescence mechanism to up-conversion bioimaging applications. Adv. Func. Mater. 22(22), 4732–4740 (2012)
P. Cui, M. Jabed, D.J. Vogel, S. Kilina, Phonon-Mediated Ultrafast Hole Transfer from Photoexcited CdSe Quantum Dots to Black Dye, in computational photocatalysis modeling of photophysics and photochemistry at interfaces. ed. by D. Kilin, S. Kilina, Y. Han (American Chemical Society, Washington, 2019), pp. 137–156
P. Cui, Effects of oxidation state on charge carrier lifetimes in B, N codoped graphene oxide quantum dots. J. Phys. Chem. C 122(33), 18818–18828 (2018)
Funding
The Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities under Grant “JUSRP12029.”
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Peng Cui performed the simulation, preparation, and reviewing and editing of the original draft. Yuan Xue performed supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Research involving human/animal participants
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cui, P., Xue, Y. Influence of edge and center oxidation configurations on non-radiative relaxation in graphene quantum dots. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 33, 5024–5036 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-07691-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-07691-8