Abstract
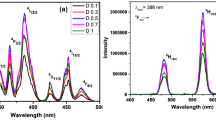
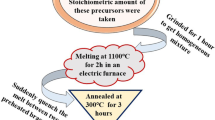
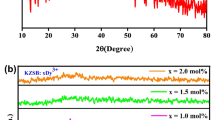
In this research work, Dy3+ doped alkali zinc alumino borosilicate (AZABS) glasses have been prepared via melt quenching technique. A series of AZABS glasses of varying concentrations of dysprosium (Dy3+) (0.1–2.5 mol%) was prepared. It was found that under UV excitation, 0.5 mol% Dy3+ doped glass exhibited maximum luminescence intensity. Subsequent photoluminescence studies like emission/excitation spectra, temperature-dependent photoluminescence and decay kinetics were also performed. The value of direct bandgap as calculated from Tauc Plot for 0.5 mol% of Dy3+ ions doped AZABS glass is 2.85 eV. Yellow to blue ratio and colorimetry analysis have showed that the as-prepared glasses are capable of producing cool white light. Application of Dexter theory showed that the energy transfer mechanism between the dopant ions in the glass matrix was of dipole–dipole nature. It is proposed that these Dy3+ doped AZABS glasses can be used as prospective materials in optoelectronic device applications such as solid-state lighting and w-LEDs.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available on request from the corresponding author, [Prof. A.S. Rao]. The data are not publicly available due to restrictions, e.g. their containing information that could compromise the privacy of research participants.
References
K. Swapna, S. Mahamuda, A.S. Rao, T. Sasikala, P. Packiyaraj, L.R. Moorthy, G.V. Prakash, Luminescence characterization of Eu3+ doped zinc alumino bismuth borate glasses for visible red emission applications. J. Lumin. 156, 80–86 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2014.07.022
K. Annapoorani, K. Marimuthu, Spectroscopic properties of Eu3+ ions doped Barium telluroborate glasses for red laser applications. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 463, 148–157 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2017.03.004
S. Arunkumar, K. Marimuthu, Structural and luminescence studies on Eu3+: B2O3-Li2O-MO-LiF (M=Ba, Bi, Pb and Zn) glasses. AIP Conf. Proc. 1447, 573–574 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4710133
S. Mahamuda, K. Swapna, M. Venkateswarlu, A. Srinivasa Rao, S. Shakya, G. Vijaya Prakash, Spectral characterisation of Sm3+ ions doped Oxy-fluoroborate glasses for visible orange luminescent applications. J. Lumin. 154, 410–424 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2014.05.017
S. Mahamuda, K. Swapna, A. Srinivasa Rao, T. Sasikala, L. Rama Moorthy, Reddish-orange emission from Pr3+ doped zinc alumino bismuth borate glasses. Phys. B Condens. Matter 428, 36–42 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2013.07.010
A.K. Vishwakarma, M. Jayasimhadri, Pure orange color emitting Sm3+ doped BaNb2O6 phosphor for solid—state lighting applications. J. Lumin. 176, 112–117 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2016.03.025
C.B. Annapurna Devi, S. Mahamuda, M. Venkateswarlu, K. Swapna, A. Srinivasa Rao, G. Vijaya Prakash, Dy3+ ions doped single and mixed alkali fluoro tungsten tellurite glasses for LASER and white LED applications. Opt. Mater. (Amst.) 62, 569–577 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2016.11.016
N. Deopa, A.S. Rao, S. Mahamuda, M. Gupta, M. Jayasimhadri, D. Haranath, G.V. Prakash, Spectroscopic studies of Pr3+ doped lithium lead alumino borate glasses for visible reddish orange luminescent device applications. J. Alloys Compd. 708, 911–921 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.03.020
R. Bajaj, M. Gupta, R. Nagarajan, A.S. Rao, G.V. Prakash, Strong structural phase sensitive rare-earth photoluminescence color flips in KLaF4:RE3+ (RE3+ = Eu3+, Er3+/Yb3+) nanocrystals. Dalton Trans. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1039/d0dt01179g
Y. Qiao, P. Chen, Luminescence, energy transfer, and color adjustment of CaO-CaF2-Al2O3 glass co-doped with CeO2 and Sm2O3. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 552, 120461 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2020.120461
J. Dahiya, A. Hooda, A. Agarwal, S. Khasa, Tuneable colour flexibility in Dy3+ & Eu3+ co-doped lithium fluoride bismuth borate glass system for solid state lighting applications. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 576, 121237 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2021.121237
R.H.A. Bergh, G. Craford, A. Duggal, The promise and challenge of solid-state lighting. Phys. Today 54, 42–47 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1445547
G. Zissis, Energy consumption and environmental and economic impact of lighting: the current situation. Handb. Adv. Light. Technol. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-00176-0
N. Deopa, A.S. Rao, Photoluminescence and energy transfer studies of Dy3+ ions doped lithium lead alumino borate glasses for w-LED and laser applications. J. Lumin. 192, 832–841 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2017.07.052
K. Jha, M. Jayasimhadri, Spectroscopic investigation on thermally stable Dy3+ doped zinc phosphate glass for white light emitting diodes. J. Alloys Compd. 688, 833–840 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.07.024
K. Jha, A.K. Vishwakarma, M. Jayasimhadri, D. Haranath, Multicolor and white light emitting Tb3+/Sm3+ co-doped zinc phosphate barium titanate glasses via energy transfer for optoelectronic device applications. J. Alloys Compd. 719, 116–124 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.05.076
H. Masai, Y. Yamada, Y. Suzuki, K. Teramura, Y. Kanemitsu, T. Yoko, Narrow energy gap between triplet and singlet excited states of SN2+ in borate glass. Sci. Rep. 3, 1–7 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep03541
Y. Zhang, C. Lu, L. Sun, Z. Xu, Y. Ni, Influence of Sm2O3 on the crystallization and luminescence properties of boroaluminosilicate glasses. Mater. Res. Bull. 44, 179–183 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2008.03.004
H.M. Gomaa, H.A. Saudi, I.S. Yahia, M.A. Ibrahim, H.Y. Zahran, Optik Influence of exchanging CeO2 with Cu2O3 on structural matrix, shielding, and linear / nonlinear optical parameters of the cerium-sodium borate glass. Optik (Stuttg.) 249, 168267 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2021.168267
N.S. Prabhu, V. Hegde, A. Wagh, M.I. Sayyed, O. Agar, S.D. Kamath, Physical, structural and optical properties of Sm3+ doped lithium zinc alumino borate glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 515, 116–124 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2019.04.015
J. Rajagukguk, J. Kaewkhao, M. Djamal, R. Hidayat, Suprijadi, Y. Ruangtaweep, Structural and optical characteristics of Eu3+ ions in sodium-lead-zinc-lithium-borate glass system. J. Mol. Struct. 1121, 180–187 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2016.05.048
W. Bao, X. Yu, T. Wang, H. Zhang, C. Su, Tb3+ / Eu3+ co-doped Al2O3 – B2O3 – SrO glass ceramics: preparation, structure and luminescence properties. Opt. Mater. (Amst.) 122, 111772 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2021.111772
N. Deopa, A.S. Rao, Spectroscopic studies of Sm3+ ions activated lithium lead alumino borate glasses for visible luminescent device applications. Opt. Mater. (Amst) 72, 31–39 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2017.04.067
H. Gui, C. Li, C. Lin, Q. Zhang, Z. Luo, L. Han, J. Liu, T. Liu, A. Lu, Glass forming, crystallization, and physical properties of MgO-Al2O3-SiO2-B2O3 glass-ceramics modified by ZnO replacing MgO. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 39, 1397–1410 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2018.10.002
N.F. Yusof, K.H.K. Bulat, N.A. Badarulzaman, M.A.A.M. Nor, The effect of boron oxide on concentration of iron ion released from SiO2-B2O3-Na2CO3-Fe2O3 Glass System. Int. J. Curr. Res. Sci. Eng. Technol. 1, 130 (2018). https://doi.org/10.30967/ijcrset.1.s1.2018.130-134
N. Deopa, S. Saini, S. Kaur, A. Prasad, A.S. Rao, Spectroscopic investigations on Dy3+ ions doped zinc lead alumino borate glasses for photonic device applications. J. Rare Earths 37, 52–59 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jre.2018.04.013
M.H.A. Mhareb, M. Alqahtani, F. Alshahri, Y.S.M. Alajerami, N. Saleh, N. Alonizan, M.I. Sayyed, M.G.B. Ashiq, T. Ghrib, S.I. Al-Dhafar, T. Alayed, M.A. Morsy, The impact of barium oxide on physical, structural, optical, and shielding features of sodium zinc borate glass. J. Non-Cryst. Solids. 541, 120090 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2020.120090
J. Rajagukguk, B. Sinaga, J. Kaewkhao, Structural and spectroscopic properties of Er3+ doped sodium lithium borate glasses, Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 223, 117342 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2019.117342
K. Swapna, S. Mahamuda, A. Srinivasa-Rao, M. Jayasimhadri, T. Sasikala, L. Rama-Moorthy, Visible fluorescence characteristics of Dy3+ doped zinc alumino bismuth borate glasses for optoelectronic devices. Ceram. Int. 39, 8459–8465 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2013.04.028
N. Kiran, A. Suresh Kumar, White light emission from Dy3+ doped sodium-lead borophosphate glasses under UV light excitation. J. Mol. Struct. 1054–1055, 6–11 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2013.09.023
A.M. Babu, B.C. Jamalaiah, J.S. Kumar, T. Sasikala, L.R. Moorthy, Spectroscopic and photoluminescence properties of Dy3+-doped lead tungsten tellurite glasses for laser materials. J. Alloys Compd. 509, 457–462 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2010.09.058
R. Bajaj, A.S. Rao, G.V. Prakash, Photoluminescence down-shifting studies of thermally stable Eu3+ ions doped borosilicate glasses for visible red photonic device applications. J. Non-Cryst. Solids. 575, 121184 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2021.121184
S. Hemalatha, M. Nagaraja, A. Madhu, K. Suresh, N. Srinatha, Spectroscopic studies of transition metal ion-doped borate glasses for optical applications. Mater. Today Proc. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2021.08.075
W.T. Carnall, P.R. Fields, K. Rajnak, Electronic energy levels of the trivalent lanthanide aquo ions. IV. Eu8+. J. Chem. Phys. 49, 4424–4442 (1968). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1669893
P. Rekha Rani, M. Venkateswarlu, S. Mahamuda, K. Swapna, N. Deopa, A.S. Rao, Spectroscopic studies of Dy3+ ions doped barium lead alumino fluoro borate glasses. J. Alloys Compd. 787, 503–518 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.02.088
H. George, N. Deopa, S. Kaur, A. Prasad, M. Sreenivasulu, M. Jayasimhadri, A.S. Rao, Judd-Ofelt parametrization and radiative analysis of Dy3+ ions doped sodium bismuth strontium phosphate glasses. J. Lumin. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2019.116693
S. Kaur, M. Jayasimhadri, A.S. Rao, A novel red emitting Eu3+doped calcium aluminozincate phosphor for applications in w-LEDs. J. Alloys Compd. 697, 367–373 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.12.150
A.K. Vishwakarma, M. Jayasimhadri, Significant enhancement in photoluminescent properties via flux assisted Eu3+ doped BaNb2O6 phosphor for white LEDs. J. Alloys Compd. 683, 379–386 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.05.052
M. Reddi Babu, N. Madhusudhana Rao, A. Mohan Babu, N. Jaidass, C. Krishna Moorthy, L. Rama Moorthy, Effect of Dy3+ ions concentration on optical properties of lead borosilicate glasses for white light emission. Optik (Stuttg) 127, 3121–3126 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2015.12.018
C.R. Kesavulu, H.J. Kim, S.W. Lee, J. Kaewkhao, N. Chanthima, Y. Tariwong, Physical, vibrational, optical and luminescence investigations of Dy3+-doped yttrium calcium silicoborate glasses for cool white LED applications. J. Alloys Compd. 726, 1062–1071 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.08.091
L. Mishra, A. Sharma, A.K. Vishwakarma, K. Jha, M. Jayasimhadri, B.V. Ratnam, K. Jang, A.S. Rao, R.K. Sinha, White light emission and color tunability of dysprosium doped barium silicate glasses. J. Lumin. 169, 121–127 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2015.08.063
D.L. Dexter, A theory of sensitized luminescence in solids. J. Chem. Phys. 21, 836–850 (1953). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1699044
D.L. Dexter, J.H. Schulman, Theory of concentration quenching in inorganic phosphors. J. Chem. Phys. 22, 1063–1070 (1954). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1740265
K. Linganna, C.S. Rao, C.K. Jayasankar, Optical properties and generation of white light in Dy3+-doped lead phosphate glasses. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 118, 40–48 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jqsrt.2012.12.002
M.K. Sahu, M. Jayasimhadri, Conversion of blue emitting thermally stable Ca3Bi(PO4)3 host as a color tunable phosphor via energy transfer for luminescent devices. J. Lumin. 227, 117570 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2020.117570
A. Prasad, A.S. Rao, M. Gupta, G.V. Prakash, Morphological and luminescence studies on KGdF4:Yb3+/Tb3+ up-conversion nanophosphors. Mater. Chem. Phys. 219, 13–21 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2018.07.056
A. Prasad, A.S. Rao, G.V. Prakash, A study on up-conversion and energy transfer kinetics of KGdF4: Yb3+ / Er3+ nanophosphors. J. Mol. Struct. 1205, 127647 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2019.127647
C.S. McCamy, Correlated color temperature as an explicit function of chromaticity coordinates. Color Res. Appl. 17, 142–144 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1002/col.5080170211
L. Wang, M. Xu, H. Zhao, D. Jia, Luminescence, energy transfer and tunable color of Ce3+, Dy3+/Tb3+ doped BaZn2(PO4)2 phosphors. New J. Chem. 40, 3086–3093 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/c5nj03148f
D. Xu, Z. Yang, J. Sun, X. Gao, J. Du, Synthesis and luminescence properties of double-perovskite white emitting phosphor Ca3WO6:Dy3+. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 27, 8370–8377 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-4848-z
M.K. Sahu, J. Mula, White light emitting thermally stable bismuth phosphate phosphor Ca3Bi(PO4)3:Dy3+ for solid-state lighting applications. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 102, 6087–6099 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1111/jace.16479
R. Bajaj, A.S. Rao, G.V. Prakash, Linear and nonlinear photoluminescence from thermally stable KYF4:Eu3+ cubic nanocrystals. J. Alloys Compd. 885, 160893 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.160893
Acknowledgements
The work reported in this paper has been partially supported by a Major Research Project (EMR/2016/007766) sanctioned by SERB, Department of Science and Technology, Govt. of India, New Delhi. Dr. Sumandeep Kaur is grateful to CSIR, New Delhi for the award of Research Associate fellowship (08/133(0053) 2020-EMR-I).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RB: Work plan, experimental work, manuscript writing. AP: Experimental Help, calculations. AVSY: Experimental Help, calculations. PR: Experimental Help, calculations. SK: Validation of results, Manuscript correction. ASR: Work plan, validation of results, manuscript correction.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bajaj, R., Prasad, A., Yeswanth, A.V.S. et al. Down-shifting photoluminescence studies of thermally stable Dy3+ ions doped borosilicate glasses for optoelectronic device applications. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 33, 4782–4793 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-07667-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-07667-8