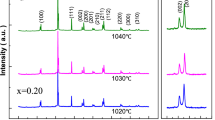
Abstract
We investigate the effect of fluorine doping on the optical bandgap and Young’s modulus of binary Bi2O3–SiO2 and Bi2O3–B2O3 glasses. Colorless Bi2O3–BiF3–SiO2 and Bi2O3–BiF3–B2O3 glasses, with very small photoelasticity and elastic constants compared with pure silica glass, are potential alternatives to lead-containing oxide glass in the development of optical components using polarization control in the visible wavelength range. The effects of fluorine doping are summarized for blueshifts in the optical bandgaps of up to ~ 0.3 eV from ~ 3.6 eV. The applied photoelastic constants remained small at ± (0.02–0.07) × 10−12 Pa−1, and the Young’s moduli were ~ 70 GPa after doping. However, no conclusive connection to the structural effect of fluorine doping, as examined by Fourier-transform infrared and Raman scattering spectroscopies, was made, although there is clear evidence of the compatible properties of wide optical bandgap, very small photoelastic constant, and large elastic constant.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data sharing and data citation are encouraged. All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
H. Hosono, M. Mizuguchi, H. Kawazoe, T. Ogawa, Effects of fluorine dimer excimer laser radiation on the optical transmission and defect formation of various types of synthetic SiO2 glasses. Appl. Phys. Lett. 74(19), 2755–2757 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.124004
L. Vaccaro, M. Cannas, S. Girard, A. Alessi, A. Morana, A. Boukenter, Y. Ouerdane, R. Boscaino, Influence of fluorine on the fiber resistance studied through the nonbridging oxygen hole center related luminescence. J. Appl. Phys. 113(19), 193107 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4807163
K. Suzuki, G. Tricot, B. Revel, A. Saitoh, Properties and structure of SnO−SiO2 and SnO−SnF2−SiO2 glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 527, 119706 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2019.119706
K. Hayashi, Y. Ishibashi, T. Shimizu, T. Asahi, A. Saitoh, Correlation with one- and two-photon absorptions in Bi2O3 containing B2O3 and SiO2 glasses with zero photoelastic constant. Appl. Phys. Express (2019). https://doi.org/10.7567/1882-0786/ab40f4
A. Saitoh, M. Itadani, K. Suzuki, H. Takebe, H. Hosono, Optical properties and zero photoelastic constant of ns2-type metal cation containing oxide glasses. Opt. Quantum. Electron. 51, 302 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-019-2024-4
A. Saitoh, S. Kitani, S. Matsuishi, H. Kawaji, H. Takebe, H. Hosono, Structure and photoelastic constant of binary ns2-type metal cation containing silicate glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 521, 1195261–1195265 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2019.119526
H. Terasaki, N. Umeda, M. Tsukiji, Stabilized transverse Zeeman laser as a new light source for optical measurement. Appl. Opt. 19(3), 435–441 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-3093(94)90349-2
A. Saitoh, U. Hoppe, R.K. Brow, G. Tricot, Y. Hashida, H. Takebe, The structure and properties of xZnO–(67–x)SnO–33P2O5 glasses: (III) Photoelastic behavior. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 498, 173–176 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2018.06.016
Z. Pan, D.O. Henderson, S.H. Morgan, Vibrational spectra of bismuth silicate glasses and hydrogen-induced reduction effects. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 171(2), 134–140 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-3093(94)90349-2
Y. Kuromitsu, H. Yoshida, H. Takebe, K. Morinaga, Interaction between alumina and binary glasses. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 80(6), 1583–1587 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1151-2916.1994.tb07019.x
V.L. Stolyarova, A.L. Shilov, S.I. Lopatin, S.M. Shugurov, High-temperature mass spectrometric study and modeling of thermodynamic properties of binary glass-forming systems containing Bi2O3. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 28(7), 801–810 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1002/rcm.6842
L. Maya, crystalline compounds and glasses in the system B2O3-NaF-NaBF4. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 60(7–8), 323–328 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1151-2916.1977.tb15552.x
K. Matusita, R. Yokota, T. Kimijima, T. Komatsu, C. Ihara, Composional trends in photoelastic constants of borate glasses. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 67(4), 261–265 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1151-2916.1984.tb18843.x
A. Saitoh, K. Hayashi, K. Hanzawa, S. Ueda, S. Kawachi, J. Yamaura, K. Ide, J. Kim, G. Tricot, S. Matsuishi, K. Mitsui, T. Shimizu, M. Mori, H. Hosono, H. Hiramatsu, Origins of the coloration from structure and valence state of bismuth oxide glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 560, 12072001–12072014 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2021.120720
P.K. Gupta, C.R. Kurkjian, Intrinsic failure and non-linear elastic behavior of glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 351(27), 2324–2328 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2005.05.029
A. Makishima, J.D. Mackenzie, Direct calculation of Young’s modulus of glass. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 12, 35–45 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-3093(73)90053-7
A. Bajaj, A. Khanna, B. Chen, J.G. Longstaffe, U.W. Zwanziger, J.W. Zwanziger, Y. Gómez, F. González, Structural investigation of bismuth borate glasses and crystalline phases. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 355(1), 45–53 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2008.09.033
A. Winterstein-Beckmann, D. Möncke, D. Palles, E.I. Kamitsos, L. Wondraczek, A Raman-spectroscopic study of indentation-induced structural changes in technical alkali-borosilicate glasses with varying silicate network connectivity. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 405, 196–206 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2014.09.020
B. Suresh, M. SrinivasaReddy, A. SivaSeshaReddy, Y. Gandhi, V. RaviKumar, N. Veeraiah, Spectroscopic features of Ni2+ ion in PbO–Bi2O3–SiO2 glass system. Spectrochimica Acta Part A 141, 263–271 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2015.01.058
S. Shibata, T. Kitagawa, M. Horiguchi, Fabrication of fluorine-doped silica glasses by the sol-gel method. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 100(1), 269–273 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-3093(88)90030-0
P. Tarte, Infra-red spectra of inorganic aluminates and characteristic vibrational frequencies of AlO4 tetrahedra and AlO6 octahedra. Spectrochim. Acta, Part A 23(7), 2127–2143 (1967). https://doi.org/10.1016/0584-8539(67)80100-4
R. Iordanova, Y. Dimitriev, V. Dimitrov, S. Kassabov, D. Klissurski, Glass formation and structure in the V2O5–Bi2O3–Fe2O3 glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 204(2), 141–150 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-3093(96)00416-4
P. McMillan, Structural studies of silicate glasses and melts-applications and limitations of Raman spectroscopy. Am. Miner. 69, 622–644 (1984)
D.M. Krol, E.M. Rabinovich, Raman study of fluorine-doped silica gels. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 82(1), 143–147 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-3093(86)90122-5
M. Kyoto, Y. Ohoga, S. Ishikawa, Y. Ishiguro, Characterization of fluorine-doped silica glasses. J. Mater. Sci. 28(10), 2738–2744 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00356211
L. Baia, R. Stefan, W. Kiefer, S. Simon, Structural characteristics of B2O3–Bi2O3 glasses with high transition metal oxide content. J. Raman Spectrosc. 36(3), 262–266 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-3093(02)01042-6
S. Hazra, S. Mandal, A. Ghosh, Properties of unconventional lithium bismuthate glasses. Phys. Rev. B 56(13), 8021–8025 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.56.8021
K.C. Sekhar, B. Kavitha, N. Narsimlu, V. Sathe, M.A. Alothman, I.O. Olarinoye, M.S. Al-Buriahi, M. Shareefuddin, Enhancement of shielding ability using PbF2 in Fe-reinforced bismuth borate glasses. J. Mater. Sci. 32(18), 23047–23065 (2021)
C.P.E. Varsamis, N. Makris, C. Valvi, E.I. Kamitsos, Short-range structure, the role of bismuth and property–structure correlations in bismuth borate glasses. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 23(16), 10006–10020 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1039/D1CP00301A
I.Z. Hager, M. El-Hofy, Investigation of spectral absorption and elastic moduli of lithium haloborate glasses. Physica Status Solidi (A) 198(1), 7–17 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1002/pssa.200305958
B.N. Meera, J. Ramakrishna, Raman spectral studies of borate glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 159(1), 1–21 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-3093(93)91277-A
Z. Pan, D.O. Henderson, S.H. Morgan, A Raman investigation of lead haloborate glasses. J. Chem. Phys. 101(3), 1767–1774 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-3093(94)90349-2
A. Hayashi, M. Nakai, M. Tatsumisago, T. Minami, Y. Himei, Y. Miura, M. Katada, Structural investigation of SnO–B2O3 glasses by solid-state NMR and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 306(3), 227–237 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-3093(02)01169-9
D. Kline, P.J. Bray, Nuclear magnetic resonance investigations of the structure of glasses in the system NaF–Na2O–B2O3. Phys. Chem. Glasses 7, 41–51 (1966)
C. Jager, U. Haubenreisser, A reexamination of studies of the structure of NaF–Na2O–B2O3 glasses. Phys. Chem. Glasses 26, 152–156 (1985)
A. Saitoh, G. Tricot, P. Rajbhandari, S. Anan, H. Takebe, Effect of B2O3/P2O5 substitution on the properties and structure of tin boro-phosphate glasses. Mater. Chem. Phys. 149–150, 648–656 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2014.11.021
H. Mueller, The theory of photoelasticity. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 21, 27–33 (1938). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1151-2916.1938.tb15726.x
M. Tashiro, The effects of the polarisation of constituent ions on the photoelastic birefringence of the glass. J. Soc. Glass. Technol. 40, 353T-362T (1956)
W.A. Weyl, E.C. Marboe, The Constitution of Glass (Wiley-Interscience, New York, 1964)
R.D. Shannon, R.X. Fischer, Empirical electronic polarizabilities in oxides, hydroxides, oxyfluorides, and oxychlorides. Phys. Rev. B 73(23), 2351111–23511128 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.73.235111
A. Walsh, G.W. Watson, D.J. Payne, R.G. Edgell, J. Guo, P.-A. Glans, T. Learmonth, K.E. Smith, Electronic structure of the a and d phases of Bi2O3: A combined ab initio and X-ray spectroscopy study. Phys. Rev. B 73(23), 235104 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.73.235104
S. Inaba, S. Fujino, K. Morinaga, Young’s modulus and compositional parameters of oxide glasses. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 82, 3501–3507 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1151-2916.1999.tb02272.x
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Collaborative Research Project of Laboratory for Materials and Structures, Tokyo Institute of Technology. A.S. was partially supported by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) KAKENHI (Grant Numbers JP17K05041, JP21K04652). S.M. and H.H. were supported by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology (MEXT) through the Element Strategy Initiative to Form Core Research Center (Grant Number JPMXP0112101001). H.H. was partially supported by JSPS KAKENHI (Grant Number 21H04612) and Design & Engineering by Joint Inverse Innovation for Materials Architecture, MEXT.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
A.S. involved in conceptualization, methodology, writing—original draft preparation, and supervision. K.H., T.S., and S.M. performed data curation. A.S., S.M., and H.H. participated in writing—review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work.
Ethical approval
The authors attest, all the experiments and procedures carried out in current study obey the standards ethics of the research committees, both international and national. Also, they declare that the submission is an exclusive to ‘‘Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics (JMSE)’’ and not under consideration for publication elsewhere.
Informed consent
The content of the manuscript and the submission for publication in ‘‘Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics (JMSE)’’ have been approved by all co-authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hayashi, K., Shimizu, T., Matsuishi, S. et al. Effect of fluorine doping on the optical and mechanical properties of bismuth-containing silicate and borate glasses. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 33, 2242–2256 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-07508-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-07508-8