Abstract
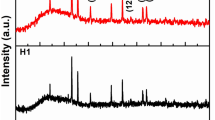
Fe5C2 particle is a promising magnetic material, but there are few reports on pure phase Fe5C2 particle with adjustable morphology. Herein, pure phase Fe5C2 magnetic materials with different morphologies were prepared by a simple ethylenediamine carbonization method. This method included the preparation of FeC2O4·2H2O precursors with different morphologies and the co-calcination process of ethylenediamine and the precursors. At the same time, the optimum experimental conditions for the formation of pure phase Fe5C2 particles with different morphologies were investigated. More importantly, the magnetic properties of Fe5C2 particles and the electrocatalytic activities of Fe5C2 particles as electrocatalysts for the hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) are improved by adjusting the morphologies of Fe5C2 particles. The saturation magnetization (Ms) and coercivity (Hc) of Fe5C2 particle with the cuboid rod-like structure can reach 134.53 emu/g and 305.93 Oe, respectively, demonstrating good soft magnetic properties at 298 K. Simultaneously, the Fe5C2 particle with the porous cuboid rod-like structure exhibits efficient HER activity (225 mV for j = − 10 mA cm−2). In this work, a simple and generalized Fe5C2 particle synthesis method is proposed, and new explorations are provided for the further applications of Fe5C2 particles with different morphologies in the fields of magnetism and catalysis.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. Zhu, Y. Ju, J. Xu, Z. Yang, S. Gao, Y. Hou, Magnetic nanomaterials: chemical design, synthesis, and potential applications. Acc. Chem. Res. 51(2), 404–413 (2018)
X. Wang, K. Zhu, Y. Ju, Y. Li, W. Li, J. Xu, Y. Hou, Iron carbides: magic materials with magnetic and catalytic properties. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 489, 165432 (2019)
Y. Zhong, X. Xia, F. Shi, J. Zhan, J. Tu, H.J. Fan, Transition metal carbides and nitrides in energy storage and conversion. Adv. Sci. 3(5), 1500286 (2016)
Y. Tian, L. Xu, J. Qian, J. Bao, C. Yan, H. Li, H. Li, S. Zhang, Fe3C/Fe2O3 heterostructure embedded in N-doped graphene as a bifunctional catalyst for quasi-solid-state zinceair batteries. Carbon 146, 763–771 (2019)
Z. Ye, P. Zhang, X. Lei, X. Wang, N. Zhao, H. Yang, Iron Carbides and Nitrides: Ancient Materials with Novel Prospects. Chemistry 24(36), 8922–8940 (2018)
W. Tang, Z. Zhen, C. Yang, L. Wang, T. Cowger, H. Chen, T. Todd, K. Hekmatyar, Q. Zhao, Y. Hou, J. Xie, Fe5C2 nanoparticles with High MRI contrast enhancement for tumor imaging. Small 10, 1245–1249 (2014)
J. Yu, C. Yang, J. Li, Y. Ding, L. Zhang, M.Z. Yousaf, J. Lin, R. Pang, L. Wei, L. Xu, F. Sheng, C. Li, G. Li, L. Zhao, Y. Hou, Multifunctional Fe5C2 nanoparticles: a targeted theranostic platform for magnetic resonance imaging and photoacoustic tomography-guided photothermal therapy. Adv. Mater 26, 4114–4120 (2014)
J. Yu, Y. Ju, L. Zhao, X. Chu, W. Yang, Y. Tian, F. Sheng, J. Lin, F. Liu, Y. Dong, Y. Hou, Multistimuli-regulated photochemothermal cancer therapy remotely controlled via Fe5C2 nanoparticles. ACS Nano 10, 159–169 (2016)
H. Liang, H. Xing, Z. Ma, H. Wu, Tailoring high-electroconductivity carbon cloth coated by nickel cobaltate/nickel oxide: a case of transition from microwave shielding to absorption. Carbon 183, 138–149 (2021)
T. Hou, B. Wang, Z. Jia, H. Wu, D. Lan, Z. Huang, A. Feng, M. Ma, G. Wu, A review of metal oxide-related microwave absorbing materials from the dimension and morphology perspective. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 30(12), 10961–10984 (2019)
X. Li, M. Li, X. Lu, W. Zhu, H. Xu, J. Xue, F. Ye, Y. Liu, X. Fan, L. Cheng, A sheath-core shaped ZrO2-SiC/SiO2 fiber felt with continuously distributed SiC for broad-band electromagnetic absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 419, 129414 (2021)
M. Li, X. Fan, H. Xu, F. Ye, J. Xue, X. Li, L. Cheng, Controllable synthesis of mesoporous carbon hollow microsphere twined by CNT for enhanced microwave absorption performance. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 59, 164–172 (2020)
M. Zhu, X. Yan, H. Xu, Y. Xu, L. Kong, Highly conductive and flexible bilayered MXene/cellulose paper sheet for efficient electromagnetic interference shielding applications. Ceram. Int. 47(12), 17234–17244 (2021)
O. Malina, P. Jakubec, J. Kaslik, J. Tucek, R. Zboril, A simple high-yield synthesis of high-purity Hägg carbide (χ-Fe5C2) nanoparticles with extraordinary electrochemical properties. Nanoscale 9, 10440–10446 (2017)
S. Yao, C. Yang, H. Zhao, S. Li, L. Lin, W. Wen, J. Liu, G. Hu, W. Li, Y. Hou, D. Ma, Reconstruction of the wet chemical synthesis process: the case of Fe5C2 nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 121, 5154–5160 (2017)
C. Yang, H. Zhao, Y. Hou, D. Ma, Fe5C2 nanoparticles: a facile bromide-induced synthesis and as an active phase for Fischer-Tropsch synthesis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 134, 15814–15821 (2012)
S. Li, P. Ren, C. Yang, X. Liu, Z. Yin, W. Li, H. Yang, J. Li, X. Wang, Y. Wang, R. Cao, L. Lin, S. Yao, X. Wen, D. Ma, Fe5C2 nanoparticles as low-cost HER electrocatalyst: the importance of Co substitution. Sci. Bull. 63, 1358–1363 (2018)
X. Fan, Z. Peng, R. Ye, H. Zhou, X. Guo, M3C (M: Fe Co, Ni) nanocrystals encased in graphene nanoribbons: an active and stable bifunctional electrocatalyst for oxygen reduction and hydrogen evolution reaction. ACS Nano 9, 7407–7418 (2015)
Z. Wen, S. Ci, F. Zhang, X. Feng, S. Cui, S. Mao, S. Luo, Z. He, J. Chen, Nitrogen-enriched core-shell structured Fe/Fe3C-C nanorods as advanced electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction reaction. Adv. Mater. 24, 1399–1404 (2012)
Z. Jia, D. Ren, L. Xu, Generalized preparation of metal oxalate nano/submicro-rods by facile solvothermal method and their calcined products. Mater. Lett. 76, 194–197 (2012)
Z. Ye, Y. Qie, Z. Fan, Y. Liu, Z. Shi, H. Yang, Soft magnetic Fe5C2-Fe3C@C as an electrocatalyst for the hydrogen evolution reaction. Dalton Trans. 48, 4636–4642 (2019)
Z. Yang, T. Zhao, X. Huang, X. Chu, T. Tang, Y. Ju, Q. Wang, Y. Hou, S. Gao, Modulating the phases of iron carbide nanoparticles: from a perspective of interfering with the carbon penetration of Fe@Fe3O4 by selectively adsorbed halide ions. Chem. Sci. 8, 473–481 (2017)
P. Zhao, W. Xu, X. Hua, W. Luo, S. Chen, G. Cheng, Facile synthesis of a N-doped Fe3C@CNT/porous carbon hybrid for an advanced oxygen reduction and water oxidation electrocatalyst. J. Phys. Chem. C 120, 11006–11013 (2016)
C. Song, S. Wu, X. Shen, X. Miao, Z. Ji, A. Yuan, K. Xu, M. Liu, X. Xie, L. Kong, G. Zhu, S. Ali Shah, Metal-organic framework derived Fe/Fe3C@N-doped-carbon porous hierarchical polyhedrons as bifunctional electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution and oxygen-reduction reactions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 524, 93–101 (2018)
C. Yang, Y.L. Hou, S. Gao, Nanomagnetism: principles, nanostructures, and biomedical applications. Chin. Phys. B 23(5), 057505 (2014)
W. Ge, W. Gao, J. Zhu, Y. Li, In situ synthesis of Hagg iron carbide (Fe5C2) nanoparticles with a high coercivity and saturation magnetization. J. Alloy. Compd. 781, 1069–1073 (2019)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (CN) (No. 51872111) and Natural Science Foundation of Jilin Province (No.20190201253JC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kong, F., Qie, Y., Liu, Y. et al. Magnetic properties and electrocatalytic properties of Fe5C2 particles with different morphologies. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 33, 884–893 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-07358-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-07358-4