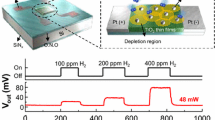
Abstract
The gas-sensing equipment experienced a greater demand in different workplace environments owing to its high capability to detect the unburnt poisonous gases in the boilers or analyzing the airborne pollution levels. The recent trend toward achieving an efficient gas sensor depends on the low-power consumption and miniaturization. In addition, emerging nanomaterials have shown great potential toward gas sensing along with their outstanding electrochemical properties. This work aims toward the sensing of hydrogen gas utilizing carbon nanotubes (CNTs) directly integrated onto a Pt microheater. The pristine CNTs detect hydrogen gas through the change in the electrical resistance. The chemical reaction between the hydrogen molecule and CNTs is promoted at high temperatures by utilizing the microheater. The suggested spray-coated CNT layer survives subsequent microfabrication processes, demonstrating a robust integration method of nanomaterials into conventional microelectromechanical systems (MEMS). CNTs integrated Pt microheater is batch fabricated using a microfabrication technique, allowing a high device yield of over 90%. The fabricated gas sensors demonstrate a low power budget of a few mW and owe a fast response time. The temperature is elevated up to 420 °C by supplying 2.19 mW power for gas sensing, and the change in the rate of resistance change reached 1.82% by supplying hydrogen gas of 10% concentration. The response and recovery time from the microheater are found to be 39 and 35 seconds, respectively. Besides, the decrease in drift factor occurs when the sensor operates at too high temperatures. The gas concentration is controlled and simultaneously the rate of resistance change is evaluated which further helps to obtain a LOD value of 1200 ppm. The Raman spectra of CNTs before and after the gas-sensing experiment confirm that there is no change or degradation of the CNTs during the experimental process. The fabricated CNTs integrated Pt microheater-based gas sensor has immense potential toward sensing hydrogen gas.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Iijima, Helical microtubules of graphitic carbon. Nature 354, 56–58 (1991)
Z. Spitalsky, D. Tasis, K. Papagelis, C. Galiotis, Carbon nanotube-polymer composites: chemistry, processing, mechanical and electrical properties. Prog. Polym. Sci. 35, 357–401 (2010)
J.N. Coleman, U. Khan, W.J. Blau, Y.K. Gun’ko, Small but strong: a review of the mechanical properties of carbon nanotube-polymer composites. Carbon 44, 1624–1652 (2006)
Y. Wang, J.T. Yeow, A review of carbon nanotube-based gas sensors. J. Sens. 2009, 24 (2009)
T. Zhang, M.B. Nix, B.Y. Yoo, M.A. Deshusses, N.V. Myung, Electrochemically functionalized single-walled carbon nanotube gas sensor. Electroanalysis 18, 1153–1158 (2006)
K.G. Ong, K. Zeng, C.A. Grimes, A wireless, passive carbon nanotube-based gas sensor. IEEE Sens. J. 2, 82–88 (2002)
R. Tang, Y. Shi, Z. Hou, L. Wei, Carbon nanotube-based chemiresistive sensors. Sensors 17, 882 (2017)
L.Q. Nguyen, P.Q. Phan, H.N. Duong, C.D. Nguyen, L.H. Nguyen, Enhancement of NH3 gas sensitivity at room temperature by carbon nanotube-based sensor coated with Co nanoparticles. Sensors 13, 1754–1762 (2013)
C. Wang, L. Yin, L. Zhang, D. Xiang, R. Gao, Metal oxide gas sensors: sensitivity and influencing factors. Sensors 10, 2088–2106 (2010)
J.H. Kim, J.G. Jeon, R. Ovalle-Robles, T.J. Kang, Aerogel sheet of carbon nanotubes decorated with palladium nanoparticles for hydrogen gas sensing. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 43, 6456–6461 (2018)
M. Baro, S. Ramaprabhu, Room temperature hydrogen gas sensing properties of mono dispersed platinum nanoparticles on graphene-like carbon-wrapped carbon nanotubes. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 43, 16421–16429 (2018)
B. Sharma, H. Yadav, J.-S. Kim, MEMS based hydrogen sensor with the highly porous Au-CNT film as a sensing material. J. Mater. Sci. 28, 13540–13547 (2017)
K. Guo, A.H. Jayatissa, Hydrogen sensing properties of multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 28, 1556–1559 (2008)
D. Jung, M. Han, G.S. Lee, Gas sensor using a multi-walled carbon nanotube sheet to detect hydrogen molecules. Sens. Actuat. A 211, 51–54 (2014)
B. Wang, L. Zhu, Y. Yang, N. Xu, G. Yang, Fabrication of a SnO2 nanowire gas sensor and sensor performance for hydrogen. J. Phys. Chem. C 112, 6643–6647 (2008)
C. Wongchoosuk, A. Wisitsoraat, D. Phokharatkul, A. Tuantranont, T. Kerdcharoen, Multi-walled carbon nanotube-doped tungsten oxide thin films for hydrogen gas sensing. Sensors 10, 7705–7715 (2010)
J. Park, I.R. Jang, K. Lee, H.J. Kim, High efficiency crumpled carbon nanotube heaters for low drift hydrogen sensing. Sensors 19, 3878 (2019)
M. Baroncini, P. Placidi, G. Cardinali, A. Scorzoni, Thermal characterization of a microheater for micromachined gas sensors. Sens. Actuat. A 115, 8–14 (2004)
L. Xu, Y. Wang, H. Zhou, Y. Liu, T. Li, Y. Wang, Design, fabrication, and characterization of a high-heating-efficiency 3-D microheater for catalytic gas sensors. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 21, 1402–1409 (2012)
A. Franco Júnior, D. Shanafield, Thermal conductivity of polycrystalline aluminum nitride (AlN) ceramics. Ceramica 50, 247–253 (2004)
R. Arsat, X. Yu, Y. Li, W. Wlodarski, K. Kalantar-Zadeh, Hydrogen gas sensor based on highly ordered polyaniline nanofibers. Sens. Actuat. B 137, 529–532 (2009)
D. Jung, D. Kim, K.H. Lee, L.J. Overzet, G.S. Lee, Transparent film heaters using multi-walled carbon nanotube sheets. Sens. Actuat. A 199, 176–180 (2013)
M.S. Dresselhaus, G. Dresselhaus, R. Saito, A. Jorio, Raman spectroscopy of carbon nanotubes. Phys. Rep. 409, 47–99 (2005)
Q. Li, J. Wu, L. Huang, J. Gao, H. Zhou, Y. Shi, Q. Pan, G. Zhang, Y. Du, W. Liang, Sulfur dioxide gas-sensitive materials based on zeolitic imidazolate framework-derived carbon nanotubes. J. Mater. Chem. A 6, 12115–12124 (2018)
K. Haddad, A. Abokifa, S. Kavadiya, B. Lee, S. Banerjee, B. Raman, P. Banerjee, C. Lo, J. Fortner, P. Biswas, SnO2 nanostructured thin films for room-temperature gas sensing of volatile organic compounds. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 10, 29972–29981 (2018)
R. Kumar, P.K. Kulriya, M. Mishra, F. Singh, G. Gupta, M. Kumar, Highly selective and reversible NO2 gas sensor using vertically aligned MoS2 flake networks. Nanotechnology 29, 464001 (2018)
Y. Mo, Y. Okawa, M. Tajima, T. Nakai, N. Yoshiike, K. Natukawa, Micro-machined gas sensor array based on metal film micro-heater. Sens. Actuat. B 79, 175–181 (2001)
L.A. Currie, Nomenclature in evaluation of analytical methods including detection and quantification capabilities (IUPAC Recommendations 1995). Pure Appl. Chem. 67, 1699–1723 (1995)
J. Li, Y. Lu, Q. Ye, M. Cinke, J. Han, M. Meyyappan, Carbon nanotube sensors for gas and organic vapor detection. Nano Lett. 3, 929–933 (2003)
N.A. Algadri, Z. Hassan, K. Ibrahim, A.M. Al-Diabat, A high-sensitivity hydrogen gas sensor based on carbon nanotubes fabricated on glass substrate. J. Electron. Mater. 47, 6671–6680 (2018)
M.K. Kumar, S. Ramaprabhu, Nanostructured Pt functionlized multiwalled carbon nanotube-based hydrogen sensor. J. Phys. Chem. B 110, 11291–11298 (2006)
J. Kong, M.G. Chapline, H. Dai, Functionalized carbon nanotubes for molecular hydrogen sensors. Adv. Mater. 13, 1384–1386 (2001)
Acknowledgement
This study was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT of Korea (2021R1C1C1011588).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, K., Park, J., Jung, S.I. et al. Direct integration of carbon nanotubes on a suspended Pt microheater for hydrogen gas sensing. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 32, 19626–19634 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-06484-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-06484-3