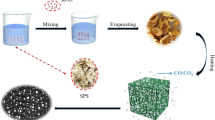
Abstract
Recently, microwave absorbers with strong absorption along with wide absorption band have gained abundant attention due to their low cost, simple fabrication, and sustainability. However, it remains a challenge for pure biomass to achieve this goal without adding other components. Herein, a wheat flour-derived magnetic carbon nanocomposite was prepared and hydrochloric acid was used to fabricate doped PANI on the magnetic porous carbon (MPC), in which PANI was grown on the MPC network. The introduction of NiFe2O4 particles is helpful in balancing permittivity, permeability, and impedance matching. This distinctive PANI structure heightens conductive loss, interfacial polarization, and multiple reflections of the incident EM waves. Overall, the optimal reflection of NiFe2O4/PC/PANI can reach up to -59.3 dB at 2 mm with 20 wt% filler loading and the efficient bandwidth (RL exceeding -10 dB) is as wide as 5.6 GHz (12.4–18 GHz) with a thickness of 1.5 mm. To sum up, this strategy provides a novel scope for the controllable construction of a hierarchical carbon composite and the as-prepared composite possesses a promising potential for exploration of biomass carbon on high-performance microwave absorbers.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Qin, L.M. Zhang, X.R. Zhao et al., Defect induced polarization loss in multi-shelled spinel hollow spheres for electromagnetic wave absorption application. Adv. Sci. 8, 2004640–2004653 (2021)
L.S. Xing, Z.C. Wu, L. Wang et al., Polarization-enhanced three-dimensional Co3O4/MoO2/C flowers as efficient microwave absorbers. J. Mater. Chem. C 8, 10248–10256 (2020)
L.L. Yan, M. Zhang, S.C. Zhao et al., Wire-in-tube ZnO@carbon by molecular layer deposition: accurately tunable electromagnetic parameters and remarkable microwave absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 382, 122860–122870 (2020)
W. Wei, X.G. Liu, W.L. Lu et al., Light-weight gadolinium hydroxide@polypyrrole rare-earth nanocomposites with tunable and broadband electromagnetic wave absorption. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 11, 12752–12760 (2019)
P.B. Liu, S. Gao, Y. Wang et al., Metal-organic polymer coordination materials derived Co/N-doped porous carbon composites for frequency-selective microwave absorption. Compos. Part B 202, 108406–108417 (2020)
Y. Wang, X.C. Di, X. Gao et al., Design of MOF-derived hierarchical Co@C@RGO composite with controllable heterogeneous interfaces as a high-efficiency microwave absorbent. Nanotechnology 31, 395710–395720 (2020)
Y. Wang, X. Gao, L.J. Zhang et al., Synthesis of Ti3C2/Fe3O4/PANI hierarchical architecture composite as an efficient wide-band electromagnetic absorber. Appl. Surf. Sci. 480, 830–838 (2019)
F. Pan, L.Z. Yu, Z. Xiang et al., Improved synergistic effect for achieving ultrathin microwave absorber of 1D Co nanochains/2D carbide MXene nanocomposite. Carbon 172, 506–515 (2021)
Y. Wang, X. Gao, X.M. Wu et al., Facile design of 3D hierarchical NiFe2O4/N-GN/ZnO composite as a high performance electromagnetic wave absorber. Chem. Eng. J 375, 121942–121951 (2019)
Y. Wang, X. Gao, X.M. Wu et al., Facile synthesis of Mn3O4 hollow polyhedron wrapped by multiwalled carbon nanotubes as a high-efficiency microwave absorber. Ceram. Int. 46, 1560–1568 (2020)
H.L. Lv, Y.H. Guo, Z.H. Yang et al., A brief introduction to the fabrication and synthesis of graphene based composites for the realization of electromagnetic absorbing materials. J. Mater. Chem. C 5, 491–512 (2017)
H.H. Zhao, X.Z. Xu, Y.H. Wang et al., Heterogeneous interface induced the formation of hierarchically hollow carbon microcubes against electromagnetic pollution. Small 16, 2003407–2003418 (2020)
X.Y. Wang, Y.K. Lu, T. Zhu et al., CoFe2O4/N-doped reduced graphene oxide aerogels for high-performance microwave absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 388, 124317–124332 (2020)
P.B. Liu, S. Gao, Y. Wang et al., Core–shell Ni@C encapsulated by N-doped carbon derived from nickel–organic polymer coordination composites with enhanced microwave absorption. Carbon 170, 503–516 (2020)
H.X. Zhang, Z.R. Jia, A.L. Feng et al., In situ deposition of pitaya-like Fe3O4@C magnetic microspheres on reduced graphene oxide nanosheets for electromagnetic wave absorber. Compos. Part B 199, 108261–108271 (2020)
B. Wen, H.B. Yang, Y. Lin et al., Controlling the heterogeneous interfaces of S Co Co-doped porous carbon nanosheets for enhancing the electromagnetic wave absorption. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 586, 208–218 (2021)
W.H. Gu, X.Q. Cui, J. Zheng et al., Heterostructure design of Fe3N alloy/porous carbon nanosheet composites for efficient microwave attenuation. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 67, 265–272 (2021)
P.B. Liu, S. Gao, Y. Wang et al., Core–shell coni@graphitic carbon decorated on B, N-codoped hollow carbon polyhedrons toward lightweight and high-efficiency microwave attenuation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 11, 25624–25635 (2019)
F.Y. Wang, N. Wang, X.J. Han et al., Core–shell FeCo@carbon nanoparticles encapsulated in polydopamine-derived carbon nanocages for efficient microwave absorption. Carbon 145, 701–711 (2019)
X.C. Di, Y. Wang, Y.Q. Fu et al., Wheat flour-derived nanoporous carbon@ZnFe2O4 hierarchical composite as an outstanding microwave absorber. Carbon 173, 174–184 (2021)
Y. Xiong, L.L. Xu, C.X. Yang et al., Implanting FeCo/C nanocages with tunable electromagnetic parameters in anisotropic wood carbon aerogels for efficient microwave absorption. J. Mater. Chem. A 8, 18863–18871 (2020)
H.Q. Zhao, Y. Cheng, Z. Zhang et al., Biomass-derived graphene-like porous carbon nanosheets towards ultralight microwave absorption and excellent thermal infrared properties. Carbon 173, 501–511 (2021)
H.G. Wang, F.B. Meng, J.Y. Li et al., Carbonized design of hierarchical porous carbon/ Fe3O4@Fe derived from loofah sponge to achieve tunable high-performance microwave absorption. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 6, 11801–11810 (2018)
X.F. Zhou, Z.R. Jia, A.L. Feng et al., Synthesis of fish skin-derived 3D carbon foams with broadened bandwidth and excellent electromagnetic wave absorption performance. Carbon 152, 827–836 (2019)
S. Dong, P.T. Hu, X.T. Li et al., NiCo2S4 nanosheets on 3D wood-derived carbon for microwave absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 398, 125588–125599 (2020)
F. Wu, K. Yang, Q. Li et al., Biomass-derived 3D magnetic porous carbon fibers with a helical/chiral structure toward superior microwave absorption. Carbon 173, 918–931 (2021)
Y.Q. Fan, Y.H. Li, Y.L. Yao et al., Hierarchically porous carbon sheets/Co nanofibers derived from corncobs for enhanced microwave absorbing properties. Appl. Surf. Sci. 534, 147510–147519 (2020)
Z.J. Li, H. Lin, S.Q. Ding et al., Synthesis and enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption performances of Fe3O4@C decorated walnut shell-derived porous carbon. Carbon 167, 148–159 (2020)
Y. Wang, X. Gao, Y.Q. Fu et al., Enhanced microwave absorption performances of polyaniline/graphene aerogel by covalent bonding. Compos Part B 169, 221–228 (2019)
M. Zhang, H.L. Ling, S.Q. Ding et al., Synthesis of CF@PANI hybrid nanocomposites decorated with Fe3O4 nanoparticles towards excellent lightweight microwave absorber. Carbon 174, 248–259 (2021)
Y. Wang, X. Gao, H.W. Zhou et al., Fabrication of biomass-derived carbon decorated with NiFe2O4 particles for broadband and strong microwave absorption. Powder Technol. 345, 370–378 (2019)
T.Q. Hou, Z.R. Jia, A.L. Feng et al., Hierarchical composite of biomass derived magnetic carbon framework and phytic acid doped polyanilne with prominent electromagnetic wave absorption capacity. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 68, 61–69 (2021)
H.G. Wang, F.B. Meng, F. Huang et al., Interface modulating CNTs@PANi hybrids by controlled unzipping of the walls of cnts to achieve tunable high-performance microwave absorption. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 11, 12142–12153 (2019)
J. Li, D. Zhou, P.J. Wang et al., Raspberry-like LiFe5O8 nanoparticles embedded on MoS2 microflowers with excellent microwave absorption performance. J. Mater. Chem. A 8, 20337–20345 (2020)
T.P. Ying, J. Zhang, X.G. Liu et al., Corncob-derived hierarchical porous carbon/Ni composites for microwave absorbing application. J. Alloy Compd. 849, 156662–156671 (2020)
Z.C. Wu, K. Tian, T. Huang et al., Hierarchically porous carbons derived from biomasses with excellent microwave absorption performance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 10, 11108–11115 (2018)
J.M. Tang, N. Liang, L. Wang et al., Three-dimensional nitrogen-doped reduced graphene oxide aerogel decorated with Ni nanoparticles with tunable and unique microwave absorption. Carbon 152, 575–586 (2019)
Y. Wang, X.C. Di, X.M. Wu et al., MOF-derived nanoporous carbon/Co/Co3O4/CNTs/RGO composite with hierarchical structure as a high-efficiency electromagnetic wave absorber. J. Alloy Compd. 846, 156215–156225 (2020)
X.C. Zhang, X. Zhang, H.R. Yuan et al., CoNi nanoparticles encapsulated by nitrogen-doped carbon nanotube arrays on reduced graphene oxide sheets for electromagnetic wave absorption. Chem. Eng. J 383, 123208–123216 (2020)
L.J. Yang, H.L. Lv, M. Li et al., Multiple polarization effect of shell evolution on hierarchical hollow C@MnO2 composites and their wideband electromagnetic wave absorption properties. Chem. Eng. J. 392, 123666–123675 (2020)
T.L. Wang, S.H. Yang, H.Y. Wang et al., Hollow porous CoNi/C composite nanomaterials derived from MOFs for efficient and lightweight electromagnetic wave absorber. Carbon 167, 485–494 (2020)
M.L. Yang, Y. Yang, Y. Li et al., Dramatically enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption of hierarchical CNT/Co/C fiber derived from cotton and metal–organic-framework. Carbon 161, 517–527 (2020)
Y.Y. Shi, L.J. Yu, K. Li et al., Well-matched impedance of polypyrrole-loaded cotton non- woven fabric/polydimethylsiloxane composite for extraordinary microwave absorption. Compos Sci. Technol. 197, 108246–108255 (2020)
J.Q. Tao, J.T. Zhou, Z.J. Yao et al., Multi-shell hollow porous carbon nanoparticles with excellent microwave absorption properties. Carbon 172, 542–555 (2021)
S. Feng, J.C. Deng, L.J. Yu et al., Development of lightweight polypyrrole/cellulose aerogel composite with adjustable dielectric properties for controllable microwave absorption performance. Cellulose 27, 10213–10224 (2020)
Y. Wang, X. Gao, C.H. Lin et al., Metal organic frameworks-derived Fe-Co nanoporous carbon/graphene composite as a high-performance electromagnetic wave absorber. J. Alloys. Compd. 785, 765–773 (2019)
F.X. Li, B.H. Wang, M.M. Ren et al., Preparation and electromagnetic wave absorption properties of carbon nanotubes loaded Fe3O4 composites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 513, 167259–167270 (2020)
J.L. Fan, W.J. Xing, Y. Huang et al., Facile fabrication hierarchical urchin-like C/NiCo2O4/ ZnO composites as excellent microwave absorbers. J. Alloys Compd. 821, 153491–153498 (2020)
Q.X. Yang, Y.Y. Shi, Y. Fang et al., Construction of polyaniline aligned on magnetic functionalized biomass carbon giving excellent microwave absorption properties. Compos Sci. Techno.l 174, 176–183 (2019)
X. Li, E.B. Cui, Z. Xiang et al., Fe@NPC@CF nanocomposites derived from Fe-MOFs/ biomass cotton for lightweight and high-performance electromagnetic wave absorption applications. J. Alloys Compd. 819, 152952–152961 (2020)
Q.W. Zeng, L. Wang, X. Li et al., Double ligand MOF-derived pomegranate-like Ni@C microspheres as high-performance microwave absorber. Appl. Surf. Sci. 538, 148051–148059 (2021)
M.M. Gao, Y. Zhao, S.S. Wang et al., Preparation of pod-like 3D Ni0.33Co0.67Fe2O4@rGO composites and their microwave absorbing properties. Ceram. Int. 45, 7188–7195 (2019)
P.F. Yin, L.M. Zhang, P. Sun et al., Apium-derived biochar loaded with MnFe2O4@C for excellent low frequency electromagnetic wave absorption. Ceram. Int. 46, 13641–13650 (2020)
N.N. Wu, D.M. Xu, Z. Wang et al., Achieving superior electromagnetic wave absorbers through the novel metal–organic frameworks derived magnetic porous carbon nanorods. Carbon 145, 433–444 (2019)
P.B. Liu, Y. Huang, J. Yan et al., Construction of CuS Nanoflakes Vertically Aligned on Magnetically Decorated Graphene and Their Enhanced Microwave Absorption Properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8, 5536–5546 (2016)
Z. Zhang, J.W. Tan, W.H. Gu et al., Cellulose–chitosan framework/polyaniline hybrid aerogel toward thermal insulation and microwave absorbing application. Chem. Eng. J. 395, 125190–125199 (2020)
X.C. Di, Y. Wang, Z. Lu et al., Heterostructure design of Ni/C/porous carbon nanosheet composite for enhancing the electromagnetic wave absorption. Carbon 179, 566–578 (2021)
Y. Wang, X.C. Di, Z. Lu et al., Rational construction of hierarchical Co@C@NPC nanocomposites derived from bimetallic hybrid ZIFs/biomass for boosting the microwave absorption. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 589, 462–471 (2021)
M. Wu, A.K. Darboe, X.S. Qi et al., Optimization, selective and efficient production of CNTs/CoxFe3-xO4 core/shell nanocomposites as outstanding microwave absorbers. J. Mater. Chem. C 8, 11936–11949 (2020)
L. Wang, X.F. Yu, M.Q. Huang et al., Orientation growth modulated magnetic–carbon microspheres toward broadband electromagnetic wave absorption. Carbon 172, 516–528 (2021)
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (61701386 and 21975196), the Young Star Project of Science and Technology of Shaanxi Province (2019KJXX-033).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Di, X., Wang, Y., Lu, Z. et al. Design of biomass-derived magnetic carbon/polyaniline with hierarchical network for superior microwave absorption. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 32, 18790–18807 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-06397-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-06397-1