Abstract
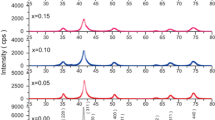
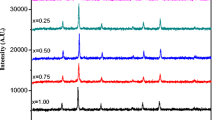
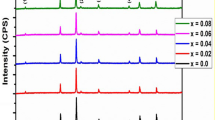
Polycrystalline nano-magnetic pure and Ho3+-substituted Mg–Mn ferrite [Mg0.90Mn0.10Fe(2−x)HoxO4 (x = 0, 0.1, 0.2, and 0.3)] nanoparticles were synthesized by sol–gel combustion method. The physicochemical properties of samples were analyzed using various characterization techniques such X-ray diffractometer, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), Mossbaur spectroscopy, vibrating sample magnetometer, field emission scanning electron microscope (FESEM) to identify the crystalline phase, functional groups, surface morphology, and magnetic behavior. The structural studies revealed that all the compositions showed pure phase formation of ferrite nanoparticles without any secondary phases and exhibited a cubic crystalline structure with \(Fd\stackrel{-}{3}m\) space group. FTIR spectra displayed the high-frequency peak observed at 554 cm−1 belonging to Fe–O bending, which confirmed the formation of pristine and Ho3+ modified spinel Mg–Mn ferrite nanoparticles. FESEM micrographs depicted the pseudo-spherical and granular morphology with agglomerated regions and energy dispersive X-ray spectra showed the elemental compositions present in the prepared nanoparticles confirming the high purity of the synthesized samples. EPR spectra illustrated the magnetic nature of pure and Ho3+-substituted Mg–Mn ferrite nanoparticles and displayed strong inter-dipolar interactions. Mössbauer spectra showed that the quadrupole shift increased with increasing Ho3+ content in the composition. All the compositions exhibited superparamagnetic behavior and it was observed that the value of saturation magnetization decreased with Ho3+ intrusion in the crystal framework of Mg–Mn ferrites as depicted by magnetic hysteresis loops. The observed results of the present study are significant and useful for their effective utilization in biosensing applications.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.P. Reddy, G. Kim, D.S. Yoo, W. Madhuri, N.R. Reddy, K.V.S. Kumar, R.R. Reddy, Characterization and electromagnetic studies on NiZn and NiCuZn ferrites prepared by microwave sintering technique. Mater. Sci. Appl. 3, 628–632 (2012)
G. Kumar, J. Shah, R.K. Kotnala, V.P. Singh, G. Garg, S.E. Shirsath, K.M. Batoo, M. Singh, Superparamagnetic behaviour and evidence of weakening in super-exchange interactions with the substitution of Gd3+ ions in the Mg–Mn nanoferrite matrix. Mat. Res. Exp. 63, 216–225 (2015)
N.H. Hur, E.K. Lee, J.Y. Park, J. Dho, Effects of the grain boundary on thecoercevity of barium ferrite BaFe12O19. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 285, 164–168 (2005)
X. He, G. Song, J. Zhu, Non-stoichiometric NiZn ferrite by sol–gel processing. Mater. Lett. 59, 1941–1944 (2005)
M.G. Naseri, E.B. Saion, Crystallization in spinel ferrite nanoparticles, in Advances in Crystallization Process. (Intech, Croatia, 2012), pp. 349–380
M.F. Kuo, Y.H. Hung, J.Y. Huang et al., Substitution effects on magnetic properties of Mg1.3−xMnxAlyFe1.8−yO4 ferrites. API Adv. 7(5), 2158–3226 (2017)
Z.A. Sahar, S.M. Maryam, S.N. Masoud, Nd2Sn2O7 nanostructures as highly efficient visible light photocatalyst: green synthesis using pomegranate juice and characterization. J. Clean. Prod. 198, 11–18 (2018)
Z. Karimi, Y. Mohammadifar, H. Shokrollahi, S. KhamenehAsl, Gh. Yousef, L. Karimi, Magnetic and structural properties of nano sized Dy-doped cobaltferrite synthesized by co-precipitation. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 361, 150–156 (2014)
N. Rezlescu, E. Rezlescu, C. Pasnicu, M.L. Craus, Effects of the rare-earth ions on some properties of a nickel–zinc ferrite. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 6, 5707–5716 (1994)
N. Rezlescu, E. Rezlescu, P.D. Popa, C. Corneliu Doroftei, M. Ignat, Scandium substituted nickel–cobalt ferrite nanoparticles for catalyst applications. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 158–159, 70–75 (2014)
N. Lwin, R. Othman, S. Sreekantan, M.N. Ahmad, Fauzi, Study on the structural and electromagnetic properties of Tm-substituted Mg–Mn ferrites by a solution combustion method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 385, 433–440 (2015)
I. Iliev, I. Nedkov, V. Hristova, Influence of scandium substitution on properties of Mn-Mg microwave ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 93, 433–437 (1990)
K. Kamala Bharathi, G. Markandeyulu, C.V. Ramana, Structural, magnetic, electrical, and magnetoelectric properties of Sm- and Ho-substituted nickel ferrites. J. Phys. Chem. C. 115, 554–560 (2011)
I. Somnath, R.K. Sharma, M. Kotnala, A. Singh, P. Kumar, V.P. Dhiman, K. Singh, G. Verma, Kumar, Structural, magnetic and Mössbauer studies of Nd-doped Mg–Mn ferrite nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 444, 77–86 (2017)
M. Ishaque, M.A. Khan, I.A. Hasan, M. Khan, M.A. Iqbal, M.U. Islam, M.F. Warsid, Investigations on structural, electrical and dielectric properties of yttrium substituted Mg-ferrites. Cer. Int. 41(3), 428–4034 (2015)
N. Lwin, M.N.A. Fauzi, S. Sreekantan, R. Othman, Physical and electromagnetic properties of nanosized Gd substituted Mg–Mn ferrites by solution combustion method. Phys B 461, 134–139 (2015)
N. Lwin, M.N.A. Fauzi, S. Sreekantan, R. Othman, A.A. Thant, Effect of Fe deficiency on structural and magnetic properties in low temperature synthesized Mg–Mn ferrite. Int. J. Nano Sci. 10, 1257–1263 (2011)
H.W. Wang, S.C. Kung, Crystallization of nanosized Ni–Zn ferrite powders prepared by hydrothermal method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 270, 230–236 (2004)
P.P. Hankare, V.T. Vader, N.M. Patil, S.D. Jadhav, U.B. Sankpal, M.R. Kadam, Synthesis, characterization and studies on magnetic and electrical properties of Mg ferrite with Cr substitution. Mater. Chem. Phys. 113, 233–238 (2009)
V.M. Khot, A.B. Salunkhe, M.R. Phadatare, N.D. Thorat, S.H. Pawar, Low-temperature synthesis of MnxMg1−xFe2O4 (x = 0–1) nanoparticles: cation distribution, structural and magnetic properties. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 46, 055303 (2013)
R. Jasrotia, P. Puri, V.P. Singh, R. Kumar, Sol–gel synthesized Mg–Ag–Mn nanoferrites for power applications. J. Sol–Gel Sci. Technol. 97, 205–212 (2020)
K.C. Patil, M.S. Hegde, T. Rattan, S.T. Aruna, Chemistry of Nanocrystalline Oxide Materials: Combustion Synthesis, Properties and Applications (World Scientific Publishing Co. Pte. Ltd., Singapore, 2008).
R.J. Carvajal, A. FullPROF, Rietveld Refinement and Pattern Matching Analysis Program Laboratories (Leon Brillouin, [CEA-CNRS], Gif Sur Yvette, 2000).
G. Kumar, R.K. Kotnala, J. Shah et al., Cation distribution: a key to ascertain the magnetic interactions in a cobalt substituted Mg–Mn nanoferrite matrix. J. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 19(25), 16669–16680 (2017)
M.F. Kuo, Y.H. Hung, J.Y. Huang et al., Substitution effects on magnetic properties of Mg1.3-xMnxAlyFe1.8-yO4 ferrites. J. API Adv. 7(5), 2158–3226 (2017)
S.M. Maryam, S. Ali, A. Ahmad et al., Enhanced dye sensitized solar cells efficiency by utilization of an external layer of CaCe2(MoO4)4:Er3+/Yb3+ nanoparticles. J. All. Compd. 769, 732–739 (2018)
R.D. Waldron, Infrared spectra of ferrites. Phys. Rev. B 99, 1727 (1955)
E. Petrova, D. Kotsikau, V. Pankov, A. Fahmi, Influence of synthesis methods on structural and magnetic characteristics of Mg–Zn-ferrite nanopowders. J. Mag. Mag. Mat. 473, 85–91 (2019)
C. Sudakar, G.N. Subbanna, T.R.N. Kutty, Synthesis of acicular hydrogoethite (α-FeOOH·xH2O; 0.1 < x < 0.22) particles using morphology controlling cationic additives and magnetic properties of maghemite derived from hydrogoethite. J. Mater. Chem. 12, 107 (2002)
D. Gherca, A. Pui, V. Nica, O. Caltun, N. Cornei, Eco-environmental synthesis and characterization of nanophase powders of Co, Mg, Mn and Ni ferrites. Cer. Int. 40(7), 9599–9607 (2014)
P. Priyadharsini, A. Pradeep, P.S. Rao, G. Chandrasekaran, Structural, spectroscopic and magnetic study of nanocrystalline Ni–Zn ferrites. Mater. Chem. Phys. 116, 207–213 (2009)
V.J. Angadi, A.V. Anupama, R. Kumar, H.K. Choudhary, S. Matteppanavar, H.M. Somashekarappa, B. Rudraswamy, B. Sahoo, Composition dependent structural and morphological modifications in nanocrystalline Mn–Zn ferrites induced by high energy γ-irradiation. Mater. Chem. Phys. 199, 313–321 (2017)
M. Dhiman, S. Rana, K. Batoo, J.K. Sharma, M. Singh, Synthesis and characterization of Y and Sm doped Mg nanoferrites. Integr. Ferroelectr. 184(1), 151–157 (2017)
B. Kaur, M. Arora, A. Shankar, A.K. Srivastava, R.P. Pant, Induced size effects of Gd3+ ions doping on structural and magnetic properties of Ni–Zn ferrite nanoparticles. Adv. Mat. Lett. 3, 399–405 (2012)
R.P. Pant, M. Arora, B. Kaur, V. Kumar, A. Kumar, Finite size effect on Gd3+ doped CoGdxFe2−xO4 (0.0<x<0.5) particles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 322, 3688–3691 (2010)
S.A. Altshuler, B.M. Kozyrev, Electron Paramagnetic Resonance (Academic Press, London, 1964).
K.H. Wu, Y.C. Chang, H.B. Chen, C.C. Yang, D.N. Horng, Variable temperature electron paramagnetic resonance studies of the NiZn ferrite/SiO2 nanocomposite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 278, 156–163 (2004)
K.H. Wu, W.C. Huang, G.P. Wang, T.R. Wu, Effect of pH on the magnetic and dielectric properties of SiO2/NiZn ferrite nanocomposites. Mater. Res. Bull. 40, 1822–1831 (2005)
K.H. Wu, T.H. Ting, M.C. Li, W.D. Ho, Sol–gel auto-combustion synthesis of SiO2-doped NiZn ferrite by using various fuels. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 298, 25–32 (2006)
M. Khan, J. Duan, Y. Chen, H. Yao, S. Lyu, H. Shou, K. Heng, Q. Xu, Superparamagnetic nickel–substituted manganese ferrite (Mn0.8Ni0.2Fe2O4) nanoplates as anode materials for lithium-ion batteries. J. Alloys Compd. 701, 147–152 (2017)
G. Kumar, J. Shah, R.K. Kotnala, V.P. Singh, Sarveena, G. Garg, S.E. Shirsath, K.M. Batoo, M. Singh, Superparamagnetic behaviour and evidence of weakening in super-exchange interactions with the substitution of Gd3+ ions in the Mg–Mn nanoferrite matrix. Mater. Res. Bull. 63, 216–225 (2015)
X.B. Xie, C. Ni, Z. Lin, D. Wu, X. Sun, Y. Zhang, B. Wang, W. Du, Phase and morphology evolution of high dielectric CoO/Co3O4 particles with Co3O4 nanoneedles on surface for excellent microwave absorption application. Chem. Eng. J. 396, 125205 (2020)
C. Li, J. Sui, Z. Zhang, X. Jiang, Z. Zhang, L. Yu, Microwave-assisted synthesis of tremella-like NiCo/C composites for efficient broadband electromagnetic wave absorption at 2–40 GHz. Chem. Eng. J. 375, 122017 (2019)
G. Kumar, R.K. Kotnala, J. Shah, V. Kumar, A. Kumar, P. Dhiman, M. Singh, Cation distribution: a key to ascertain the magnetic interactions in cobalt substituted Mg–Mn nanoferrite matrix. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 19, 16669 (2017)
R. Sharma, P. Thakur, M. Kumar, N. Thakur, N.S. Negi, P. Sharma, V. Sharma, Improvement in magnetic behaviour of cobalt doped magnesium zinc nano-ferrites via Co-precipitation route. J. Alloy. Compd. 684, 569–581 (2016)
Acknowledgements
M. Dhiman is thankful to Director, Sophisticated Analytical Instrumentation Facility (SAIF), Laboratory, Punjab University for providing material characterization facility.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors hereby declare that we have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dhiman, M., Rana, S., Sanansha et al. Influence of Ho3+ substitution on structural and magnetic properties of Mg–Mn ferrites. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 32, 8756–8766 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-05547-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-05547-9