Abstract
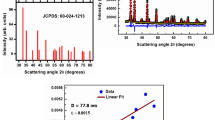
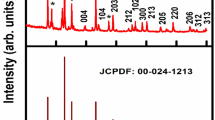
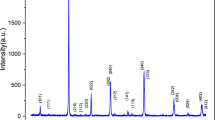
In this communication, structural, dielectric, spectroscopic and electrical characteristics of cerium-modified strontium manganite perovskite of a composition SrMn0.9Ce0.1O3, (SMCO) prepared by a high-temperature solid-state reaction technique have been reported. The preliminary structural analysis of SrMnO3 exhibits hexagonal (P63/mmc) crystal structure, whereas SMCO, synthesized under identical conditions, shows a tetragonal (I4/mmm) structure. The average crystallite size and lattice strain of SMCO using X-ray data were found to be 74 nm and 0.107%, respectively. The surface morphology, study by the scanning electron microscopy (SEM), shows distinct grains of average size of 19.2 μm. The X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) study confirms the oxidation state of Mn and Ce as Mn4+ and Ce4+ and composition of SMCO compound. The grains and the grain boundaries play an important role to explain the conduction mechanism. The bulk resistance (Rb) decreases from 1.020 × 105 Ω at 25 °C to 1.096 × 103 Ω at 500 °C. This behaviour of decrease in resistance with the increase in temperature shows semiconductor (negative temperature coefficient resistance) nature of the material at high temperatures. The variation of the activation energies with temperature suggests that the ac conductivity is thermally activated. The immobile charge carriers at low temperatures and defects and oxygen vacancies at high temperatures are responsible for the thermally activated conduction mechanism. Detailed studies of electrical parameters as a function of frequency at different temperatures using dielectric and impedance spectroscopy of SMCO have provided conduction mechanism and structural properties relationship.












Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
30 September 2021
This article has been retracted. Please see the Retraction Notice for more detail: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-07112-w
References
S. Hashimoto, H. Iwahara, Structural, thermal and electrical properties of Ce-doped SrMnO3. J. Electroceram. 4, 225–231 (2000)
S. Hashimoto, H. Iwahara, Study on the structural and electrical properties of Sr1−xCexMnO3−α (x = 0.1, 0.3) perovskite oxide. Mater. Res. Bull. 35, 2253–2262 (2000)
K.J. Lee, E. Iguchi, Electronic properties of SrMnO3-x. J. Solid State Chem. 114, 242–248 (1995)
C. Jeong, J. Ryu, T. Noh, Y.-N. Kim, H. Lee, Structural analysis and electrode performance of Ce doped SrMnO3 synthesized by EDTA citrate complexing process. Adv. Appl. Ceram. 112, 494–498 (2013)
J. Ryu, R. O’Hayre, H. Lee, Polarization resistance and composite cathode of Ce doped SrMnO3 system for intermediate temperature solid oxide fuel cells. Solid State Ionics 260, 60–64 (2014)
J. Ryu, H. Lee, Local structure and polarization resistance of Ce doped SrMnO3 using extended X-ray fine structure analysis. Appl. Phys. Lett. 105, 111903–111904 (2014)
G.H. Jonker, J.H. Van Santen, Ferromagnetic compounds of manganese with perovskite structure. Physica 16, 337–349 (1950)
C. Zener, Interaction between the d-shells in the transition metals. II. Ferromagnetic compounds of manganese with perovskite structure. Phys. Rev. 82, 403–405 (1951)
P.W. Anderson, H. Hasegawa, Considerations on double exchange. Phys. Rev. 100, 675–681 (1955)
P.G. De Gennes, Effects of double exchange in magnetic crystals. Phys. Rev. 118, 41–154 (1960)
K. Kubo, N. Ohata, A quantum theory of double exchange. I. J Phys. Soc. Jpn. 33, 21–32 (1972)
A.J. Millis, P.B. Littlewood, B.I. Shraiman, Double exchange alone does not explain the resistivity of La1−xSrxMnO3. Phys. Rev. Lett. 74, 5144–5147 (1995)
A.J. Millis, B.I. Shraiman, R. Mueller, Dynamic Jahn-Teller effect and colossal magnetoresistance in La1−xSrxMnO3. Phys. Rev. Lett. 77, 175–178 (1996)
H.A. Jahn, E. Teller, Stability of polyatomic molecules in degenerate electronic states. I. Orbital degeneracy. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 161, 220–235 (1937)
H. Röderm, J. Zang, A.R. Bishop, Lattice effects in the colossal magnetoresistance manganites. Phys. Rev. Lett. 76, 1356–1359 (1996)
J.S. Zhou, J.B. Goodenough, Phonon-assisted double exchange in perovskite manganites. Phys. Rev. Lett. 80, 2665–2668 (1998)
A. Trovarelli, Catalytic properties of ceria and CeO2-containing materials. Catal. Rev. Sci. Eng. 38, 439–520 (1996)
B.M. Weckhuysen, M.P. Rosynek, J.H. Lunsford, Destructive adsorption of carbon tetrachloride on lanthanum and cerium oxides. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 1, 3157–3162 (1999)
F. Yang, J. Wei, W. Liu, J. Guo, Y. Yang, Copper doped ceria nanospheres: surface defects promoted catalytic activity and a versatile approach. Mater. Chem. A 2, 5662–5667 (2014)
S. Tsunekawa, T. Fukuda, A. Kasuya, Blueshift in ultraviolet absorption spectra of monodisperse CeO2–x nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. 87, 1318–1321 (2000)
Y.M. Chiang, E.B. Lavik, I. Kosacki, H.L. Tuller, Defect and transport properties of nanocrystalline, CeO2−x. Appl. Phys. Lett. 69, 185–187 (1996)
A. Abdel-Latif, L.A. Al-Hajji, M. Faisal, A.A. Ismail, Doping strontium into neodymium manganites nanocomposites for enhanced visible light driven photocatalysis. Sci. Rep. 9, 13932–13942 (2019)
A.K. Mandal, G. Panchal, S. Chowdhury, A. Jana, R.J. Choudhary, D.M. Phase, Electronic and magnetic properties of stoichiometric and off-stoichiometric SrMnO3 thin films. J. Supercond. Novel Magnet. 33, 1633–1636 (2020)
J.W. Guo, P.S. Wang, Y. Yuan, Q. He, J.L. Lu, T.Z. Chen, S.Z. Yang, Y.J. Wang, R. Erni, M.D. Rossell, V. Gopalan, H.J. Xiang, Y. Tokura, P. Yu, Strain-induced ferroelectricity and spin-lattice coupling in SrMnO3 thin films. Phys. Rev. B 97, 235135–235138 (2018)
A.K. Mandal, G. Panchal, R.J. Choudhary, D.M. Phase, Magnetic and electronic properties of SrMnO3 thin films. AIP Conf. Proc. 1953, 100035 (2018)
S. Yasmin, S. Choudhury, M.A. Hakim, A.H. Bhuiyan, M.J. Rahman, Structural and dielectric properties of pure and cerium doped barium titanate. J. Ceram. Process. Res. 12, 387–391 (2011)
C.G. Hu, H. Liu, C.S. Lao, L.Y. Zhang, D. Davidovic, Z.L. Wang, Size-manipulable synthesis of single crystalline BaMnO3 and BaTi1/2Mn1/2O3 nanorods/nanowires. J. Phys. Chem. B 110, 14050–14054 (2006)
S. Phokha, S. Pinitsoontorn, S. Maensiri, Structure and magnetic properties of monodisperse Fe3+ doped CeO2 nanospheres. Nano-Micro Lett. 5, 223–233 (2013)
C. Xia, C. Hu, P. Chen, B. Wan, X. He, Y. Tian, Magnetic properties and photoabsorption of the Mn-doped CeO2 nanorods. Mater. Res. Bul. 45, 794–798 (2010)
L. Bi, H.-S. Kim, G.F. Dionne, S.A. Speakman, D. Bono, C.A. Ross, Structural, magnetic, and magneto-optical properties of Co-doped CeO2−δ films. Appl. Phys. 103, 07D138:1–07D138:3 (2008)
X.B. Chen, G.S. Li, Y.G. Su, X.Q. Qiu, L.P. Li, Z.G. Zou, Synthesis and room-temperature ferromagnetism of CeO2 nanocrystals with nonmagnetic Ca2+ doping. Nanotechnology 20, 115606–115613 (2009)
N.S. Ferreira, M.A. Macêdo, Cr-doping induced ferromagnetism in CeO2−δ no powders. Adv. Mater. Res. 975, 42–49 (2014)
N. Sharma, S. Jandaik, S. Kumar, M. Chitkara, I.S. Sandhu, Synthesis, characterization and antimicrobial activity of manganese- and iron-doped zinc oxide nanoparticles. J. Exp. Nanosci. 11, 54–71 (2016)
F. Vaja, O. Oprea, D. Ficai, A. Ficai, C. Guran, Synthesis of CeO2 nanoparticles on the mesoporous silica support via nano casting,". Digest J. Nanomater. Biostruct. 9, 187–195 (2014)
H. Shinjoh, Rare earth metals for automotive exhaust catalysts. J. Alloys Compd. 408–412, 1061–1064 (2006)
M. Sugiura, M. Ozawa, A. Suda, T. Suzuki, T. Kanazawa, Development of innovative three-way catalysts containing ceria-zirconia solid solutions with high oxygen storage/release capacity. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 78, 752–776 (2005)
R.J.H. Voorhoeve, Advanced Materials in Catalysis (Academic Press, New York, 1977), pp. 1–129
J.A. Dean, Lange’s Handbook of Chemistry, 15th edn. (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1998).
N. Pandey, A.K. Thakur, Studies on structural and electrical properties of SrMnO3−δ prepared in oxidizing medium. Adv. Appl. Ceram. 109, 83–90 (2010)
K. Kuroda, N. Ishizawa, N. Mizutani, M. Kato, The crystal structure of α-SrMnO3. J. Solid State Chem. 38, 297–299 (1981)
R.K. Parida, D.K. Pattanayak, B.N. Parida, Impedance, and modulus analysis of double perovskite Pb2BiVO6. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 28(22), 16689–16695 (2017)
J. Ryu, T. Noh, Y.-N. Kim, H. Lee, Lattice relaxation and electrochemical performances of cobalt-doped Sr0.9Ce0.1MnO3−δ composite cathodes for intermediate-temperature solid oxide fuel cells. J. Electrochem. Soc. 163, F657–F662 (2016)
G. Shirane, S. Hoshino, On the phase transition in lead titanate. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 6, 265–270 (1951)
Y. Xu, Ferroelectric Materials, and Their Applications (North Holland, Amsterdam, 1991).
B.D. Cullity, Elements of X-Ray Diffraction (Addison-Wesley, Reading MA, 1967), p. 388
S.K. Parida, R.N.P. Choudhary, P.G.R. Achary, Structure and ferroelectric properties of lead nickel tungsten titanate: Pb(Ni1/3T1/3W1/3)O3 single perovskite. Ferroelectrics 551, 109–121 (2019)
S.K. Parida, Structural behavior of Cu0.5Ag0.5 and Cu0.5Al0.5 alloys synthesized by co-melting technique. Adv. Sci. Lett. 22(2), 584–587 (2016)
A.B.J. Kharrat, N. Moutiab, K. Khirouni, W. Boujelben, Investigation of electrical behavior and dielectric properties in polycrystalline Pr0.8Sr0.2MnO3 manganite perovskite. Mater. Res. Bull. 105, 75–83 (2018)
S. Phoka, P. Laokul, E. Swatsitang, V. Promarak, S. Seraphinc, S. Maensiri, Mater. Chem. Phys. 115, 423 (2009)
E.K. Goharshadi, S. Samiee, P. Nancarrow, J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 356, 473 (2011)
C.B. Azzoni, M.C. Mozzati, A. Paleari, V. Massarotti, D. Capsoni, M. Bini, Magnetic order in Li-Mnspinels. Z. Nat. Forsch. A 53, 693–698 (1998)
C.D. Wagner, D.A. Zatko, R.H. Raymond, Use of the oxygen KLL Auger lines in identification of surface chemical states by electron spectroscopy for chemical analysis. Anal. Chem. 52, 1445–1451 (1980)
J.W. Murray, J.G. Dillard, R. Giovanoli, H. Moers, W. Stumm, Oxidation of Mn(II): initial mineralogy, oxidation state and ageing. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 49, 463–470 (1985)
Q.-H. Wu, M. Liu, W. Jaegermann, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy of La0.5Sr0.5MnO3. Mater. Lett. 59, 1480–1483 (2005)
N.K. Mohanty, S.K. Satapathy, B. Behera, P. Nayak, R.N.P. Choudhary, Complex impedance properties of LiSr2Nb5O15 ceramic. J. Adv. Ceram. 1, 221–226 (2012)
B.N. Parida, R.K. Parida, A. Panda, Multi-ferroic, and optical spectroscopy properties of (Bi0.5Sr0.5) (Fe0.5Ti0.5)O3 solid solution. J. Alloys Compds. 696, 338–344 (2017)
S.K. Dehury, P.G.R. Achary, R.N.P. Choudhary, Electrical and dielectric properties of bismuth holmium cobalt titanate (BiHoCoTiO6): a complex double perovskite. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 29, 3682–3689 (2018)
M. Greenblatt, Ionic Conductors, Encyclopedia of Inorganic Chemistry (Wiley, New York, 1999), p. 1584
H. Siebert, Anwendungen Der Schwingungsspektroskopie in Der AnorganischenChemie (Springer, Berlin, 1966).
J.T.S. Irvine, D.C. Sinclair, A.R. West, Adv. Mater. 2, 132 (1990)
M. Abbassi, R. Ternane, I. Sobrados, A. Madani, M. Trabelsi-Ayadi, J. Sanz, Ceram. Int. 39, 9215 (2013)
S. Selvasekarapandian, M. Vijaykumar, The ac impedance spectroscopy studies on LiDyO2 Mater. Chem. Phys. 80, 29–33 (2003)
M.B. Hossen, A.K.M.A. Hossain, Complex impedance and electric modulus studies of magnetic ceramic Ni0.27Cu0.10Zn0.63Fe2O4. J Adv Ceram. 4, 217–225 (2015)
A.K. Jonscher, The universal dielectric response. Nature 267, 673–679 (1977)
S.K. Sinha, S.N. Choudhary, R.N.P. Choudhary, Studies of structural, dielectric and electrical behavior of Pb(Mn1/4Co1/4W1/2)O3 ceramics. J. Mater. Sci. 39, 315–318 (2004)
M.B. Bechir, K. Karoui, M. Tabellout, K. Guidara, A.B. Rhaiem (2014) J. Alloys Compd. 588, 551-557 (2014)
P.B. Macedo, C.T. Moynihan, R. Bose, Phys. Chem. Glasses 13, 171 (1972)
S.K. Parida, R.N.P. Choudhary, P.G.R. Achary, Study of structural and electrical properties of polycrystalline Pb(Cd1/3Ti1/3W1/3)O3 tungsten perovskite. Int. J. Microstruct. Mater. Prop. 15, 107–121 (2020)
P.G.R. Achary, R.N.P. Choudhary, S.K. Parida, Structure, electric and dielectric properties of PbFe1/3Ti1/3W1/3O3 single perovskite compound. Process. Appl. Ceram. 14(2), 146–153 (2020)
R. Gao, Q. Zhang, Z. Xu, Z. Wang, C. Fu, G. Chen, X. Deng, C. Fu, W. Cai, A comparative study on the structural, dielectric and multiferroic properties of Co0.6Cu0.3Zn0.1Fe2O4/Ba0.9Sr0.1Zr0.1Ti0.9O3 composite ceramics. Compos. B 166, 204–212 (2019)
R. Gao, X. Qin, Q. Zhang, Z. Xu, Z. Wang, C. Fu, G. Chen, X. Deng, W. Cai, Enhancement of magnetoelectric properties of (1–x)Mn0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4−xBa0.85Sr0.15Ti0.9Hf0.1O3 composite ceramics. J. Alloys Compds. 1(795), 501–512 (2019)
S. Hajra, M. Sahu, V. Purohit, R.N.P. Choudhary, Dielectric, conductivity, and ferroelectric properties of lead-free electronic ceramic: 0.6Bi(Fe0.98Ga0.02)O3–0.4BaTiO3. Heliyon 5, 01654–01663 (2019)
A.J. Moulson, J.M. Herbert, Electroceramics: Materials, Properties, Applications (Chapman & Hall, London, 1990).
J.C. Maxwell, Electricity and Magnetism, vol. 1 (Clarendon Press, Oxford, 1892).
K.B.R. Varma, K.V.R. Prasad, Structural and dielectric properties of Bi2NbxVi−xO5.5 ceramics. J. Mater. Res. 11, 2288–2292 (1996)
P. Keburis, J. Banys, A. Brilingas, J. Prapuolenis, A. Kholkin, M.E.V. Costa, Ferroelectrics 353, 149–158 (2007)
R.P. Pawar, V. Puri, Structural, electrical and dielectric properties of (Sr1−xCax) MnO3 (0 ≤ x ≤ 1.0 ceramics. Ceram. Int. 40, 10423–10430 (2014)
C.G. Koops, On the dispersion of resistivity and dielectric constant of some semiconductors at audio frequencies. Phys. Rev. 83, 121–124 (1951)
M.M.S. Sanad, M.M. Rashad, Tuning the structural, optical, photoluminescence and dielectric properties of Eu2+-activated mixed strontium aluminate phosphors with different rare earth co-activators. J. Mater. Sci. 27, 9034–9043 (2016)
M.M.S. Sanad, M.M. Rashad, E.A. Abdel-Aal, M.F. El-Shahat, Mechanical, morphological and dielectric properties of sintered mullite ceramics at two different heating rates prepared from alkaline monophasic salts. Ceram. Int. 39, 1547–1554 (2013)
M.M.S. Sanad, M.M. Rashad, E.A. Abdel-Aal, M.F. El-Shahat, Synthesis and characterization of nanocrystalline mullite powders at low annealing temperature using a new technique. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 32, 4249–4255 (2012)
M.M.S. Sanad, M.M. Rashad, E.A. Abdel-Aal, M.F. El-Shahat, K. Powers, Effect of Gd3+ ion insertion on the crystal structure, photoluminescence, and dielectric properties of o-Mullite nanoparticles. J. Electron. Mater. 43, 3559–3566 (2014)
M.M.S. Sanad, M.M. Rashad, E.A. Abdel-Aal, K. Powers, Novel cordierite nanopowders of new crystallization aspects and its cordierite-based glass ceramics of improved mechanical and electrical properties for optimal use in multidisciplinary scopes. Mater. Chem. Phys. 162, 299–307 (2015)
Acknowledgements
The authors render special thanks to Dr. U. P. Deshpande, Scientist of UGC-DAE Consortium for Scientific Research, Indore for extending the facility to carry out the X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) study and Prof. K. M. Parida, Director, Centre of Nanoscience and nanotechnology for facilitating FTIR characterization in time.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article has been retracted. Please see the retraction notice for more detail: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-07112-w
About this article
Cite this article
Achary, P.G.R., Behera, S., Choudhary, R.N.P. et al. RETRACTED ARTICLE: Structural, dielectric and electrical properties of cerium-modified strontium manganite ceramics. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 32, 5738–5754 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-05295-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-05295-w