Abstract
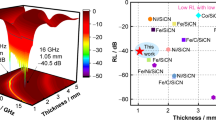
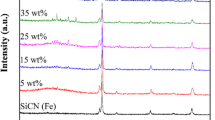
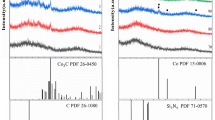
Porous SiCN(Ti) composite ceramics with good microwave absorbing performance were fabricated by pyrolysis of solid polysilazane modified by tetrabutyl titanate. The introduction of Ti not only acted as active filler to react with free carbon in the matrix to form TiC, but also played the role as catalyst to promote the formation of SiC nanowires. Finally, SiCN(Ti) composite ceramics formed a microstructure containing multi-nanophases and multi-nano heterogeneous interfaces when annealing temperature reached 1500 °C. The complex microstructure annealed at 1500 °C made composite ceramics have good matching impedance, as well as greatly increase the interfacial polarization loss and dipole polarization loss. As a result, the TiC/SiC/SiCN composite ceramics showed the excellent performance of electromagnetic wave absorption in X band. The minimum reflection loss (RL) of samples was − 17.1 dB at the thickness of 1.9 mm, and the maximum effective absorption bandwidth (EAB) of composite ceramics was 3.2 GHz when the thickness of sample was 2.1 mm, which exhibited a promising prospect as a structural and microwave absorbing integration material.









Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
16 February 2021
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-05492-7
References
X. Yin, L. Kong, L. Zhang, L. Cheng, N. Travitzky, P. Greil, Electromagnetic properties of Si–C–N based ceramics and composites. Int. Mater. Rev. 59(6), 1743–2804 (2014)
W. Duan, X. Yin, Q. Li, L. Schlier, P. Greil, A review of absorption properties in silicon-based polymer derived ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 36(15), 3681–3689 (2016)
C. Beall, E. Delzell, P. Cole, I. Brill, Brain tumors among electronics industry workers. Epidemiology 7(2), 125–130 (1996)
P. Colombo, G. Mera, R. Riedel, G.D. Soraru, Polymer-derived ceramics: 40 years of research and innovation in advanced ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 93(7), 1805–1837 (2010)
Q. Li, X. Yin, W. Duan, L. Cheng, L. Zhang, Improved dielectric properties of PDCs-SiCN by in-situ fabricated nano-structured carbons. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 37(4), 1243–1251 (2017)
Q. Li, X. Yin, W. Duan, B. Hao, L. Kong, X. Liu, Dielectric and microwave absorption properties of polymer derived SiCN ceramics annealed in N2 atmosphere. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 34(3), 589–598 (2014)
J. Xue, X. Yin, L. Cheng, Induced crystallization behavior and EMW absorption properties of CVI SiCN ceramics modified with carbon nanowires. Chem. Eng. J. 378, 122213 (2019)
F. Ye, L. Zhang, X. Yin, X. Liu, Y. Liu, L. Cheng, SiCN-based composite ceramics fabricated by chemical vapor infiltration with excellent mechanical and electromagnetic properties. Mater. Lett. 111, 169–172 (2013)
H. Wei, X. Yin, X. Li, M. Li, X. Dang, L. Zhang, L. Cheng, Controllable synthesis of defective carbon nanotubes/Sc2Si2O7 ceramic with adjustable dielectric properties for broadband high-performance microwave absorption. Carbon 147, 276–283 (2019)
Y. Zhang, X. Yin, F. Ye, L. Kong, Effects of multi-walled carbon nanotubes on the crystallization behavior of PDCs-SiBCN and their improved dielectric and EM absorbing properties. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 34(5), 1053–1061 (2014)
H. Pan, X. Yin, J. Xue, L. Chen, L. Zhang, In-situ synthesis of hierarchically porous and polycrystalline carbon nanowires with excellent microwave absorption performance. Carbon 107, 36–45 (2016)
W. Duan, X. Yin, F. Ye, Q. Li, M. Han, X. Liu, M. Han, Y. Cai, Synthesis and EMW absorbing properties of nano SiC modified PDC-SiOC. J. Mater. Chem. C 4(25), 5962–5969 (2016)
M. Han, X. Yin, W. Duan, S. Ren, L. Zhang, L. Cheng, Hierarchical graphene/SiC nanowire networks in polymer-derived ceramics with enhanced electromagnetic wave absorbing capability. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 36(11), 2695–2703 (2016)
L. Kong, C. Wang, X. Yin, X. Fan, W. Wang, J. Huang, Electromagnetic wave absorption properties of a carbon nanotube modified by a tetrapyridinoporphyrazine interface layer, J. Mater. Chem. C 5, (2017)
H. Wu, L. Wang, S. Guo, Y. Wang, Z. Shen, Electromagnetic and microwave-absorbing properties of highly ordered mesoporous carbon supported by gold nanoparticles. Mater. Chem. Phys. 133, 965–970 (2012)
L. Kong, X. Yin, M. Han, X. Yuan, Z. Hou, F. Ye, L. Zhang, L. Cheng, Z. Xu, J. Huang, Macroscopic bioinspired graphene sponge modified with in-situ grown carbon nanowires and its electromagnetic properties. Carbon 111, 94–102 (2017)
L. Kong, X. Yin, H. Xu, X. Yuan, T. Wang, Z. Xu, J. Huang, R. Yang, H. Fan, Powerful absorbing and lightweight electromagnetic shielding CNTs/RGO composite. Carbon 145, 61–66 (2019)
H. Wu, L. Wang, Y. Wang, S. Guo, S. Guo, Z. Shen, Enhanced microwave performance of highly ordered mesoporous carbon coated by Ni2O3 nanoparticles. J. Alloy. Compd. 525, 82–86 (2012)
K. Luo, X. Yin, F. Ye, Q. Li, L. Zhang, L. Cheng, Electromagnetic wave absorption properties of ZnO-based materials, modified with ZnAl2O4 nanograins. J. Phys. Chem. C 117(5), 2135–2146 (2013)
Z. Yu, J. Zhan, C. Zhou, L. Yang, R. Li, H. Xia, Synthesis and characterization of SiC(Ti) ceramics derived from a hybrid precursor of titanium-containing polycarbosilane. J. Inorg. Organomet. P 21(3), 412–420 (2011)
T. Ishikawa, T. Yamamura, K. Okamura, Production mechanism of polytitanocarbosilane and its conversion of the polymer into inorganic materials. J. Mater. Sci. 27(24), 6627–6634 (1992)
Y.C. Song, Y. Hasegawa, S.J. Yang, M. Sato, Ceramic fibres from polymer precursor containing Si-O-Ti bonds part I: the formation mechanism and the pyrolysis of the polymer. J. Mater. Sci. 23, 1911–1920 (1988)
Y. Hasegawa, C.X. Feng, Y.C. Song, Z.L. Tan, Ceramic fibres from polymer precursor containing Si-O-Ti bonds. Part II synthesis of the various types of ceramic fibres. J. Mater. Sci. 26, 3657–3664 (1991)
M.A. Schiavon, G.D. Soraru, I. Valeria, P. Yoshida, Synthesis of a polycyclic silazane network and its evolution to silicon carbonitride glass. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 304(1), 76–83 (2002)
H.B. Liu, J.A. Ascencio, M. Perez-Alvarez, M.J. Yacaman, Melting behavior of nanometer sized gold isomers. Surf. Sci. 491, 88–98 (2001)
K. Lu, Z.H. Jin, Melting and superheating of low-dimensional materials. Curr. Opin. Solid St. M. 5(1), 39–44 (2001)
S.S. Ryu, Y.D. Kim, I.H. Moon, Dilatometric analysis on the sintering behavior of nanocrystalline W-Cu prepared by mechanical alloying. J. Alloy. Compd. 335(1), 233–240 (2002)
H.W. Sheng, Z.Q. Hu, K. Lu, Melting and freezing behaviors of Pb nanoparticles embedded in an Al matrix. Nanostruct. Mater. 9(1), 661–664 (1997)
R.O. Dillon, J.A. Woollam, Use of Raman scattering to investigate disorder and crystallite formation in as-deposited and annealed carbon films. Phys. Rev. B 29(6), 3482–3489 (1984)
A.C. Ferrari, J. Robertson, Resonant Raman spectroscopy of disordered, amorphous, and diamondlike carbon. Phys. Rev. B 64(7), 075414 (2001)
A.C. Ferrari, J. Robertson, Interpretation of Raman spectra of disordered and amorphous carbon. Phys. Rev. B 61(20), 14095–14107 (2000)
A.C. Ferrari, Raman spectroscopy of graphene and graphite: Disorder, electron–phonon coupling, doping and nonadiabatic effects. Solid State Commun. 143, 47–57 (2007)
P. Mallet-Ladeira, P. Puech, C. Toulouse, M. Cazayous, N. Ratel-Ramond, P. Weisbecker, G.L. Vignoles, M. Monthioux, A Raman study to obtain crystallite size of carbon materials: A better alternative to the Tuinstra–Koenig law. Carbon 80, 629–639 (2014)
M.R. Ammar, N. Galy, J.N. Rouzaud, N. Toulhoat, C.E. Vaudey, P. Simon, N. Moncoffre, Characterizing various types of defects in nuclear graphite using Raman scattering: Heat treatment, ion irradiation and polishing. Carbon 95, 364–373 (2015)
Z. Yu, H. Min, J. Zhan, L. Yang, Preparation and dielectric properties of polymer-derived SiCTi ceramics. Ceram. Int. 39, 3999–4007 (2013)
R.S. Wagner, W.C. Ellis, Vapor-liquid-solid mechanism of single crystal growth. Appl. Phys. Lett. 4(5), 89–90 (1964)
H. Xu, X. Yin, X. Fan, Z. Tang, Z. Hou, M. Li, X. Li, L. Zhang, L. Cheng, Constructing a tunable heterogeneous interface in bimetallic metal-organic frameworks derived porous carbon for excellent microwave absorption performance. Carbon 148, 421–429 (2019)
T.J. McMahon, Y. Xiao, Electron spin resonance study of the dangling bond in amorphous Si and porous Si. Appl. Phys. Lett. 63(12), 1657–1659 (1993)
A.A. Konchits, M.Y. Valakh, B.D. Shanina, S.P. Kolesnik, I.B. Yanchuka, Effects of ion implantation on electron centers in hydrogenated amorphous carbon films. J. Appl. Phys. 93(10), 5905–5910 (2003)
H. Wei, X. Yin, F. Jiang, Z. Hou, L. Cheng, L. Zhang, Optimized design of high-temperature microwave absorption properties of CNTs/Sc2Si2O7 ceramics. J. Alloy. Compd. 823, 153864 (2020)
Y. Chen, M. Cao, T. Wang, Q. Wan, Microwave absorption properties of the ZnO nanowire-polyester composites. Appl. Phys. Lett. 84(17), 3367–3369 (2004)
R. Zhuo, L. Qiao, H. Feng, J. Chen, D. Yan, Z. Wu, P. Yan, Microwave absorption properties and the isotropic antenna mechanism of ZnO nanotrees. J. Appl. Phys. 104(9), 94101 (2008)
M. Cao, X. Shi, X. Fang, H. Jin, Z. Hou, W. Hou, Y. Chen, Microwave absorption properties and mechanism of cagelike ZnO/SiO2 nanocomposites. Appl. Phys. Lett. 91(20), 203110 (2007)
X. Fang, M. Cao, X. Shi, Z. Hou, W. Song, J. Yuan, Microwave responses and general model of nanotetraneedle ZnO: Integration of interface scattering, microcurrent, dielectric relaxation, and microantenna. J. Appl. Phys. 107(5), 54304 (2010)
X. Fang, X. Shi, M. Cao, J. Yuan, Micro-current attenuation modeling and numerical simulation for cage-like ZnO/SiO2 nanocomposite. J. Appl. Phys. 104(9), 96101 (2008)
T. Yamamura, T. Ishikawa, M. Shibuya, T. Hisayuki, Development of a new continuous Si-Ti-C-O fibre using an organometallic polymer precursor. J. Mater. SCI. 23, 2589–2594 (1988)
P. Amorós, D. Beltrán, C. Guillem, J. Latorre, Synthesis and characterization of SiC/MC/C ceramics (M = Ti, Zr, Hf) starting from totally non-oxidic precursors. Chem. Mater. 14(4), 1585–1590 (2002)
L.P. Zawada, T. Ishikawa, Mechanical behavior of a Si-Ti-C-O fiber-bonded ceramic material. Key Eng. Mater. 164–165, 245–248 (1998)
J. Hapke, G. Ziegler, Synthesis and pyrolysis of liquid organometallic precursors for advanced Si-Ti-C-N composites. Adv. Mater. 7(4), 380–384 (1995)
Acknowledgements
This work is financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51821091 and 51902257), the National Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars (51725205), and the 111 Project (B08040). We would like to thank my mentor professor Xiaowei Yin for his guidance and help.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The original version of this article was revised: The article was originally published in SpringerLink with open access. With the author(s)’ decision to step back from Open Choice, the copyright of the article changed on January 2021 to © The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature 2021.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., Tang, Z., Xue, J. et al. Enhanced microwave absorption properties of polymer-derived SiC/SiCN composite ceramics modified by TiC. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 32, 25895–25907 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-05193-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-05193-7