Abstract
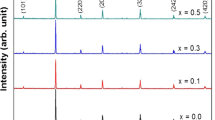
In this study, nano-composites are formed as a mixture of spinel and a perovskite with various percentages to enhance their physical properties and applicability. The composites have the general form (1-x) CoFe2O4 + x Sm0.7La0.3FeO3; 0.0 ≤ x ≤ 1. All the samples including the parents are thoroughly characterized to make sure of their crystallinity, single or double phase formation, and the percentages of the mixed components. Moreover, the crystallite size of the prepared samples, the infrared excitation of their functional groups, and their particle distribution are also comprehensively explored. The inspected samples display the spinel ferrites signature peaks at around 405 and 568 cm−1 with corresponding bond force constants of about 1 × 105 and 2 × 105 dyne/cm, respectively. The magnetic properties of samples at room temperature are discussed with extensive elaboration on the critical size and the magneto-crystalline anisotropy constant. The Stoner–Wohlfarth model has been applied to find the cubic anisotropy constant of CoFe2O4 which agrees pretty well with prior published data.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y.H. Hou et al., Structural, electronic and magnetic properties of partially inverse spinel CoFe2O4: a first-principles study. J. Phys. D. Appl. Phys. (2010). https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/43/44/445003
S. Jauhar, J. Kaur, A. Goyal, S. Singhal, Tuning the properties of cobalt ferrite: a road towards diverse applications. RSC Adv. 6(100), 97694–97719 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ra21224g
T. Yu, Z.X. Shen, Y. Shi, J. Ding, Cation migration and magnetic ordering in spinel CoFe2O4 powder: Micro-Raman scattering study. J. Phys. Condens. Matter. (2002). https://doi.org/10.1088/0953-8984/14/37/101
L.J. Berchmans, V. Leena, K. Amalajyothi, S. Angappan, A. Visuvasam, Preparation of lanthanum ferrite substituted with MG and CA. Mater. Manuf. Process. 24(5), 546–549 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1080/10426910902746739
L. Wu et al., Monolayer assembly of ferrimagnetic CoxFe3-xO 4 nanocubes for magnetic recording. Nano Lett. 14(6), 3395–3399 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1021/nl500904a
J.A. Paulsen, A.P. Ring, C.C.H. Lo, J.E. Snyder, D.C. Jiles, Manganese-substituted cobalt ferrite magnetostrictive materials for magnetic stress sensor applications. J Phys Appl (2005). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1839633
A.B. Stambouli, E. Traversa, Solid oxide fuel cells (SOFCs): A review of an environmentally clean and efficient source of energy. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 6(5), 433–455 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1364-0321(02)00014-X
Y.M. Zhang, Y.T. Lin, J.L. Chen, J. Zhang, Z.Q. Zhu, Q.J. Liu, A high sensitivity gas sensor for formaldehyde based on silver doped lanthanum ferrite. Sensors Actuators, B Chem. 190, 171–176 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2013.08.046
F. Tang Li, Y. Liu, R. Hong Liu, Z. Min Sun, D. Shun Zhao, C. Guang Kou, Preparation of Ca-doped LaFeO3 nanopowders in a reverse microemulsion and their visible light photocatalytic activity”. Mater. Lett. 64(2), 223–225 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2009.10.048
N. Sanpo, C.C. Berndt, C. Wen, J. Wang, Transition metal-substituted cobalt ferrite nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Acta Biomater. 9(3), 5830–5837 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2012.10.037
M. I. A. A. Maksoud et al., Antibacterial, antibiofilm, and photocatalytic activities of metals-substituted spinel cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. Elsevier Ltd. 127 (2019)
M.A. Ahmed, N.G. Imam, M.K. Abdelmaksoud, Y.A. Saeid, Magnetic transitions and butterfly-shaped hysteresis of Sm-Fe-Al-based perovskite-type orthoferrite. J. Rare Earths 33(9), 965–971 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0721(14)60513-5
E.E. Ateia, H. Ismail, H. Elshimi, M.K. Abdelmaksoud, Structural and magnetic tuning of LaFeO3 orthoferrite substituted different rare earth elements to optimize their technological applications, under puplication. J. Inorgan. Organometall. Polym. Mater. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/abd73b
K.S. Rao, G.S.V.R.K. Choudary, K.H. Rao, C. Sujatha, Structural and magnetic properties of ultrafine CoFe2O4 nanoparticles. Procedia Mater. Sci. 10, 19–27 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mspro.2015.06.019
J. Coates, Encyclopedia of Analytical Chemistry -IInterpretation of Infrared Spectra, A Practical Approach. Encycl. Anal. Chem. 1–23, (2004)
O.M. Hemeda, M.M. Barakat, D.M. Hemeda, Structural, electrical and spectral studies on double rare-earth orthoferrites La1-xNdxFeO3. Turkish J. Phys. 27(6), 537–549 (2003). https://doi.org/10.3906/sag-1205-29
B.C. Smith, Fundamentals of Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy, 2nd edn. (CRC Press, Boca Raton, 2011).
C. Pasquini, Near infrared spectroscopy: Fundamentals, practical aspects and analytical applications. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 14(2), 198–219 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1590/S0103-50532003000200006
N. Adhlakha, K.L. Yadav, R. Singh, BiFeO3–CoFe2O4–PbTiO3 composites: structural, multiferroic, and optical characteristics. J. Mater. Sci. 50(5), 2073–2084 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-014-8769-z
C. Berthomieu, E. Nabedryk, W. Mäntele, J. Breton, Characterization by FTIR spectroscopy of the photoreduction of the primary quinone acceptor QA in photosystem II. FEBS Lett. 269(2), 363–367 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1016/0014-5793(90)81194-S
T. Ibusuki, S. Kojima, O. Kitakami, Y. Shimada, Magnetic anisotropy and behaviors of Fe. IEEE Trans. Magn. 37(4), 2223–2225 (2001)
S. Yuvaraj, S. Layek, S.M. Vidyavathy, S. Yuvaraj, D. Meyrick, R.K. Selvan, Electrical and magnetic properties of spherical SmFeO3 synthesized by aspartic acid assisted combustion method. Mater. Res. Bull. 72, 77–82 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2015.07.013
A. Amirabadizadeh, Z. Salighe, R. Sarhaddi, Z. Lotfollahi, Synthesis of ferrofluids based on cobalt ferrite nanoparticles: Influence of reaction time on structural, morphological and magnetic properties. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 434, 78–85 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2017.03.023
M.A. Ahmed, S.F. Mansour, H. Ismael, A comparative study on the magnetic and electrical properties of MFe12O19 (M=Ba and Sr)/BiFeO3 nanocomposites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 378, 376–388 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JMMM.2014.10.173
C. Sudakar, G.N. Subbanna, T.R.N. Kutty, Wet chemical synthesis of multicomponent hexaferrites by gel-to-crystallite conversion and their magnetic properties. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 263(3), 253–268 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-8853(02)01572-X
L. Horng, G. Chern, M.C. Chen, P.C. Kang, D.S. Lee, Magnetic anisotropic properties in Fe3O4 and CoFe2O4 ferrite epitaxy thin films. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 270(3), 389–396 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2003.09.005
A.J. Rondinone, A.C.S. Samia, Z.J. Zhang, Characterizing the magnetic anisotropy constant of spinel cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. Lett. 76(24), 3624–3626 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.126727
M. D’Aquino, Nonlinear magnetization dynamics in thin-films and nanoparticles. Dr. Thesis Electr. Eng. 155, (2004)
T. Hyeon, Chemical synthesis of magnetic nanoparticles. 927–934, (2003)
A. Lehlooh, S.H. Mahmood, J.M. Williams, On the particle size dependence of the magnetic anisotropy energy constant. Phys B: Condens Mater 321, 159–162 (2002)
Q. Song, Z.J. Zhang, Shape control and associated magnetic properties of spinel cobalt ferrite nanocrystals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 126(19), 6164–6168 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1021/ja049931r
L. Kumar, M. Kar, Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials Influence of Al 3 + ion concentration on the crystal structure and magnetic anisotropy of nanocrystalline spinel cobalt ferrite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 323(15), 2042–2048 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2011.03.010
C. D. G. B D Cullity, Introduction to magnetic materials. 2008.
C.N. Chinnasamy et al., Unusually high coercivity and critical single-domain size of nearly monodispersed CoFe2O4 nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. Lett. 83(14), 2862–2864 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1616655
D.S. Mathew, R.S. Juang, An overview of the structure and magnetism of spinel ferrite nanoparticles and their synthesis in microemulsions. Chem. Eng. J. 129(1–3), 51–65 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2006.11.001
K. Maaz, A. Mumtaz, S.K. Hasanain, A. Ceylan, Synthesis and magnetic properties of cobalt ferrite (CoFe2O4) nanoparticles prepared by wet chemical route. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 308(2), 289–295 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2006.06.003
C. Sujatha, K. Venugopal Reddy, K. Sowri Babu, A. Ramachandra Reddy, K.H. Rao, Effect of sintering temperature on electromagnetic properties of NiCuZn ferrite. Ceram. Int. 39(3), 3077–3086 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2012.09.087
E.E. Ateia, M.K. Abdelamksoud, M.A. Rizk, Improvement of the physical properties of novel (1–x) CoFe2O4 + (x) LaFeO3 nanocomposites for technological applications. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 28(21), 16547–16553 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-7567-1
C. Caizer, M. Stefanescu, Nanocrystallite size effect on σs and Hc in nanoparticle assemblies. Phys. B Condens. Matter 327(1), 129–134 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-4526(02)01785-4
L.D. Tung, V. Kolesnichenko, D. Caruntu, N.H. Chou, C.J. O’Connor, L. Spinu, Magnetic properties of ultrafine cobalt ferrite particles. J. Appl. Phys. 93(102), 7486–7488 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1540145
Y.C. Wang, J. Ding, J.B. Yi, B.H. Liu, T. Yu, Z.X. Shen, High-coercivity Co-ferrite thin films on (100)-SiO 2 substrate. Appl. Phys. Lett. 84(14), 2596–2598 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1695438
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ateia, E.E., Abdelmaksoud, M.K. & Ismail, H. A study of the magnetic properties and the magneto-crystalline anisotropy for the nano-composites CoFe2O4/Sm0.7La0.3FeO3. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 32, 4480–4492 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-05189-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-05189-3