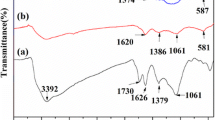
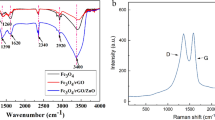
Abstract
Fe3O4 nanodisks with plate and layered hierarchical nanostructure were successfully synthesized by the reduction of the layered α-Fe2O3 nanodisk. The microwave absorb ability could be well modulated by mainly tuning the nanostructure of the Fe3O4 nanodisks. The minimum reflection loss (RL) of layered Fe3O4 nanodisks reaches − 14.8 dB at an extremely low mass fraction (about 10%), which is better than − 10.0 dB obtained using plate Fe3O4 nanodisks. The dielectric loss plays a critical role in the structure-dependent RL ability, caused by the enhanced multiple reflections in the absorber and an increase of the dipoles, interfacial polarization, and the associated relaxation. Such layered Fe3O4 nanodisks open a new avenue to exploit new microwave devices.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Wen, M.H. Cao, G.B. Sun, W.G. Xu, D. Wang, X.Q. Zhang, C.W. Hu, Hierarchical three-dimensional cobalt phosphate microarchitectures: large-scale solvothermal synthesis, characterization, and magnetic and microwave absorption properties. J. Phys. Chem. C 112, 15948 (2008)
J Qu, Y Yu, CY Cao, WG Song (2013) Alpha-Fe2 O3 nanodisks: layered structure, growth mechanism, and enhanced photocatalytic property Chemistry 19: 11172
Q. Zhou, B. Wang, P. Wang, C. Dellago, Y. Wang, Y. Fang, Nanoparticle-based crystal growth via multistep self-assembly CrystEngComm 15, 5114 (2013)
R. Qiu, X.L. Zhang, R. Qiao, Y. Li, Y.I. Kim, Y.S. Kang, CuNi dendritic material: synthesis, mechanism discussion, and application as glucose. Sens. Chem. Mater. 19, 4174 (2007)
D. Chen, J. Ye, Hierarchical WO3 hollow shells: dendrite, sphere, dumbbell, and their photocatalytic properties. Adv. Funct. Mater. 18, 1922 (2008)
G. Sun, B. Dong, M. Cao, B. Wei, C. Hu, Hierarchical dendrite-like magnetic materials of Fe3O4, γ-Fe2O3, and Fe with high performance of microwave absorption. Chem Mater. 23, 1587 (2011)
C.Y. Cao, J. Qu, W.S. Yan, J.F. Zhu, Z.Y. Wu, W.G. Song, Low-cost synthesis of flowerlike alpha-Fe2O3 nanostructures for heavy metal ion removal: adsorption property and mechanism. Langmuir 28, 4573 (2012)
M. Basu, A.K. Sinha, M. Pradhan, S. Sarkar, A. Pal, T. Pal, Monoclinic CuO nanoflowers on resin support: recyclable catalyst to obtain perylene compound Chem. Commun. 46, 8785 (2010)
O.M. Bakr, B.H. Wunsch, F. Stellacci, High-yield synthesis of multi-branched urchin-like gold nanoparticles. Chem. Mater. 18, 3297 (2006)
R.A. Meyer, J.J. Green, Shaping the future of nanomedicine: anisotropy in polymeric nanoparticle design. Wiley Inter. Rev. Nano. Nanobiotech. 8, 191 (2016)
A.N. Yusoff, M.H. Abdullah, S.H. Ahmad, S.F. Jusoh, A.A. Mansor, S.A.A. Hamid, Electromagnetic and absorption properties of some microwave absorbers. J. Appl. Phys. 92, 876 (2002)
D. Chen, G.S. Wang, S. He, J. Liu, L. Guo, M.S. Cao, Controllable fabrication of mono-dispersed RGO–hematite nanocomposites and their enhanced wave absorption properties. J. Mater. Chem. A 1, 5996 (2013)
R.F. Zhuo, L. Qiao, H.T. Feng et al., Microwave absorption properties and the isotropic antenna mechanism of ZnO nanotrees. J. Appl. Phys. 104, 094101 (2008)
J.L. Snoek, Dispersion and absorption in magnetic ferrites at frequncies above one Mc/s. Physica 14, 207 (1948)
X. Ren, H. Yang, J. Tang et al., An effective way to increase the high-frequency permeability of Fe3O4 nanorods. Nanoscale 8, 12910 (2016)
N.N. Song, H.T. Yang, H.L. Liu et al., Exceeding natural resonance frequency limit of monodisperse Fe(3)O(4) nanoparticles via superparamagnetic relaxation Sci. Rep. 3, 3161 (2013)
X. Liu, C. Cui, T. Li, A. Xia, Y. Lv, Ni@C nanocapsules-decorated SrFe12O19 hexagonal nanoflakes for high-frequency microwave absorption. J. Alloys Compd. 678, 234 (2016)
Y. Yin, M. Zeng, J. Liu et al., Enhanced high-frequency absorption of anisotropic Fe3O4/graphene nanocomposites Sci. Rep. 6, 25075 (2016)
R.C. Che, L.M. Peng, X.F. Duan, Q. Chen, XL Liang (2004) Microwave absorption enhancement and complex permittivity and permeability of Fe encapsulated within carbon nanotubes. Adv. Mater. 16, 401 (2004)
N.N. Song, H.T. Yang, X. Ren et al., Non-monotonic size change of monodisperse Fe(3)O(4) nanoparticles in the scale-up synthesis. Nanoscale 5, 2804 (2013)
W. Li, B. Lv, L. Wang, G. Li, Y. Xu, Fabrication of Fe3O4@C core–shell nanotubes and their application as a lightweight microwave absorbent. RSC Adv. 4, 55738 (2014)
X. Zhang, G. Ji, W. Liu et al., Thermal conversion of an Fe(3)O(4)@metal-organic framework: a new method for an efficient Fe-Co/nanoporous carbon microwave absorbing material. Nanoscale 7, 12932 (2015)
L. Wang, Y. Huang, C. Li, J. Chen, X. Sun, Hierarchical graphene@Fe3O4 nanocluster@carbon@MnO2 nanosheet array composites: synthesis and microwave absorption performance. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 17, 5878 (2015)
M. Zong, Y. Huang, Y. Zhao et al., Facile preparation, high microwave absorption and microwave absorbing mechanism of RGO–Fe3O4 composites. RSC Adv. 3, 23638–23648 (2013)
B. Qu, C. Zhu, C. Li, X. Zhang, Y. Chen, Coupling hollow Fe3O4-Fe nanoparticles with graphene sheets for high-performance electromagnetic wave absorbing material. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8, 3730 (2016)
S. Chikazumi, Physics of Magnetism (Wiley, New York, 1964).
H Yang, L Shen, L Zhao, et al. (2003) Magnetic properties of nanocrystalline Li0.5Fe2.1Cr0.4O4 ferrite. Mater. Lett. 57: 2455
Y. Krupskaya, C. Mahn, A. Parameswaran et al., Magnetic study of iron-containing carbon nanotubes: feasibility for magnetic hyperthermia. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 321, 4067 (2009)
G.X.M. Shishou Kang, S. Shi, Z. Jia, D.E. Nikles, J.W. Harrell, Enhanced magnetic properties of self-assembled FePt nanoparticles with MnO shell. JACS 128(4), 1042 (2006)
S. Roy, I. Dubenko, D.D. Edorh, N. Ali, Size induced variations in structural and magnetic properties of double exchange La0.8Sr0.2MnO3-δ nano-ferromagnet. J. Appl. Phys. 96, 1202 (2004)
N.N. Song, S.Z. Gu, Q. Wu et al., Facile synthesis and high-frequency performance of CoFe2O4 nanocubes with different size. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 451, 793 (2018)
N.N. Song, S.Z. Gu, J. Zhou et al., Achieving a high cutting-off frequency in the oriented CoFe2O4 nanocubes. Appl. Phys. Lett. 111, 133108 (2017)
B. Quan, G. Xu, W. Gu, J. Sheng, G. Ji, Cobalt nanoparticles embedded nitrogen-doped porous graphitized carbon composites with enhanced microwave absorption performance. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 533, 297 (2019)
Z. Xu, Y. Du, D. Liu et al., Pea-like Fe/Fe3C nanoparticles embedded in nitrogen-doped carbon nanotubes with tunable dielectric/magnetic loss and efficient electromagnetic absorption. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 11, 4268 (2019)
N.N. Song, H.T. Yang, F.Y. Li et al., Interspacing dependence of spin-dependent variable range hopping for cold-pressed Fe3O4 nanoparticles. J. Appl. Phys. 113, 184–309 (2013)
G. Datt, C. Kotabage, A.C. Abhyankar, Ferromagnetic resonance of NiCoFe2O4 nanoparticles and microwave absorption properties of flexible NiCoFe2O4-carbon black/poly(vinyl alcohol) composites. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 19, 20699 (2017)
N.N. Song, Y.J. Ke, H.T. Yang et al., Integrating giant microwave absorption with magnetic refrigeration in one multifunctional intermetallic compound of LaFe(11.6)Si(1.4)C(0.2)H(1.7). Sci. Rep. 3, 2291 (2013)
Y. Yang, X. Liu, Y. Yang et al., Synthesis of nonstoichiometric zinc ferrite nanoparticles with extraordinary room temperature magnetism and their diverse applications. J. Mater. Chem. C 1, 2875 (2013)
W. Xue, G. Yang, S. Bi, J. Zhang, Z.-L. Hou, Construction of caterpillar-like hierarchically structured Co/MnO/CNTs derived from MnO2/ZIF-8@ZIF-67 for electromagnetic wave absorption. Carbon 173, 521 (2021)
Z. Deng, S. He, W. Wang et al., Construction of hierarchical SnO2@Fe3O4 nanostructures for efficient microwave absorption. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 498, 166224 (2020)
X. Zhang, Preparation and microwave absorption properties of polyaniline and magnetite core-shell-structured hybrid. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2018, 1 (2018)
C. Fu, D. He, Y. Wang, X. Zhao, Enhanced microwave absorption properties of polyaniline-modified porous Fe3O4@C nanosheets. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 30, 11907 (2019)
S.W. Phang, N. Kuramoto, Microwave absorption property of polyaniline nanocomposites containing TiO2 and Fe3O4 nanoparticles after FeCl36H2O treatment. Polym. Composites 31, 516 (2010)
Q. Qi, Y. Huang, M. Xu, X. Lei, X. Liu, Synthesis and microwave absorption properties of sandwich-type as a bridge. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 28, 15043 (2017)
W. Yang, X. Yang, X. Li et al., Construction and microwave absorption properties of core@double-shell structured Fe3O4@polyaniline@MnO2 nanospheres. NANO 15, 2050032 (2020)
L. Wang, H. Xing, Z. Liu, Z. Shen, X. Sun, G. Xu, Synthesis and excellent microwave absorption properties of ZnO/Fe3O4/MWCNTs composites. NANO 11, 1650139 (2016)
P. Zhou, M. J-h Chen, P.J. Liu, B. Li, X.-M. Hou, Microwave absorption properties of SiC@SiO2@Fe3O4 hybrids in the 2–18 GHz range. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 24, 804 (2017)
G.B. Sun, X.Q. Zhang, M.H. Cao, B.Q. Wei, A.H.C. Wen, Facile synthesis, characterization, and microwave absorbability of CoO nanobelts and submicrometer spheres. J. Phys. Chem. C 113, 6948 (2009)
C.L. Zhu, M.L. Zhang, Y.J. Qiao, G. Xiao, F. Zhang, A.Y.J. Chen, Fe3O4/TiO2 core/shell nanotubes: synthesis and magnetic and electromagnetic wave absorption characteristics. J. Phys. Chem. C 114, 16229 (2010)
S. Ohkoshi, S. Kuroki, S. Sakurai, K. Matsumoto, K. Sato, S. Sasaki, A millimeter-wave absorber based on gallium-substituted epsilon-iron oxide nanomagnets. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 8392 (2007)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Sciences Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 51872021).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Ren, X., Wang, C. et al. Synthesis of layered Fe3O4 nanodisk and nanostructure dependent microwave absorption property. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 32, 4404–4415 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-05183-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-05183-9