Abstract
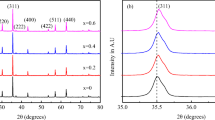
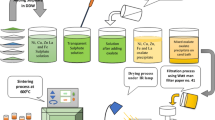
Co2+ ions substituted Ni0.2Mg0.2CoxZn0.6−xFe2O4 (x = 0, 0.15, 0.3, 0.45 and 0.6) nanoferrite was prepared by sol–gel method. The spinel structure of the material was characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD) and fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR). Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) were used to observe the morphology and shape of the prepared nanoferrite particles. The diffraction ring of the sample was observed by selected area electron diffraction (SAED), which is similar with the diffraction ring of spinel structure. The chemical element composition of the sample was analyzed by EDS, which confirmed the presence of Ni, Mg, Zn, Co, Fe, and O elements in the sample. Vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM) was used to measure the magnetic properties of prepared samples. It found that the magnetism of Ni0.2Mg0.2CoxZn0.6−xFe2O4 (x = 0, 0.15, 0.3, 0.45 and 0.6) nanoferrite substituted by Co2+ ions changed from soft magnetic to hard magnetic. The coercivity increased from 4.87 to 523.25 (Oe). Moreover, the Ni0.2Mg0.2CoxZn0.6−xFe2O4 nanoferrite sample has the characteristics of ferromagnetism when x increase to 0.6.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Ali, M.U. Islam, M. Ishaque, H.M. Khan, M.N. Ashiq, M.U. Rana, Structural and magnetic properties of holmium substituted cobalt ferrites synthesized by chemical co-precipitation method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 324, 3773–3777 (2012)
G.V. Williams, T. Prakash, J. Kennedy, S.V. Chong, S. Rubanov, Spin-dependent tunnelling in magnetite nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 460, 229–233 (2018)
M. George, A.M. John, S.S. Nair, P.A. Joy, M.R. Anantharaman, Finite size effects on the structural and magnetic properties of sol-gel synthesized NiFe2O4 powders. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 302, 190–195 (2006)
R.C. Kambale, N.R. Adhate, B.K. Chougule, Y.D. Kolekar, Magnetic and dielectric properties of mixed spinel Ni–Zn ferrites synthesized by citrate–nitrate combustion method. J. Alloys Compds. 491, 372–377 (2010)
P.R. Arjunwadkar, R.R. Patil, D.K. Kulkarni, Effect of sintering temperature on the structural, electrical and magnetic properties of Li0.5Al1.0Fe2O4 ferrite prepared by combustion method. J. Alloys Compds. 463, 403–407 (2008)
M. Irfan, N.A. Niaz, I. Ali, S. Nasir, A. Shakoor, A. Aziz, N. Karamat, N.R. Khalid, Dielectric behavior and magnetic properties of Mn-substituted Ni–Zn ferrites. J. Electron. Mater. 44, 2369–2377 (2015)
D. Ravinder, K. Latha, Dielectric behaviour of mixed Mg–Zn ferrites at low frequencies. Mater. Lett. 41, 247–253 (1999)
M.M. Haquea, M. Huqa, M.A. Hakim, Densifification, magnetic and dielectric behaviour of Cu-substituted Mg–Zn ferrites. Mater. Chem. Phys. 112, 580–586 (2008)
R.B. Pujar, S.S. Bellad, S.C. Watawe, B.K. Chougule, Magnetic properties and microstructure of Zr4+ substituted Mg-Zn ferrites. Mater. Chem. Phys. 57, 264–267 (1999)
V.J. Angadi, B. Rudraswamy, K. Sadhana, S.R. Murthy, K. Praveena, Effect of Sm3+-Gd3+ on structural, electrical and magnetic properties of Mn-Zn ferrites synthesized via combustion route. J. Alloys Compd. 656, 5–12 (2016)
E. Melagiriyappa, H.S. Jayanna, B.K. Chougule, Dielectric behavior and ac electrical conductivity study of Sm3+ substituted Mg–Zn ferrites. Mater. Chem. Phys. 112, 68–73 (2008)
S. Kumar, R. Kumar, P. Thakur, K.H. Chae, B. Angadi, W.K. Choi, Electrical transport, magnetic, and electronic structure studies of Mg0.95Mn0.05Fe2−2xTi2xO4 ± δ (0≤x≤05) ferrites. J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 19, 1–15 (2007)
L. Satyanarayana, K.M. Reddy, S.V. Manorama, Nanosized spinel NiFe2O4: a novel material for the detection of liquefied petroleum gas in air. Mater. Chem. Phys. 82, 21–26 (2003)
F. Kenfack, H. Langbein, Influence of the starting powders on the synthesis of nickel ferrite. Cryst. Res. Technol. 41, 748–758 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1002/crat.200510663
P.K. Chakrabarti, B.K. Nath, S. Brahma, S. Das, K. Gosawami, V. Kumar, P.K. Mukhopadhyay, D. Das, M. Ammer, F. Mazaleyrat, Magnetic and hyperfine properties of nanocrystalline Ni0.2Zn0.6Cu0.2Fe2O4 prepared by a chemical route. J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 18, 5253 (2006)
R.A. Torquato, F.A. Portela, L. Gama, D.R. Cornejo, S.M. Rezende, R.H.G.A. Kiminami, A.C.F.M. Costa, Avaliação da microestrutura e das propriedades magnéticas de ferritas Ni-Zn dopadas com cobre (Evaluation of microstructure and magnetic properties of Ni-Zn ferrite doped with copper). Cerâmica 54, 55–62 (2008)
A. Murugesan, G. Chandrasekaran, Impact of Gd3+ substitution on the structural, magnetic and electrical properties of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 5, 73714–73725 (2015)
H.E. Scherrer, H. Kisker, H. Kronmuller, R. Wurschum, Nanostruct. Mater. 6, 533–538 (1995)
X. Zhao, W. Wang, Y. Zhang, S. Wu, F. Li, J.P. Liu, Synthesis and characterization of gadolinium doped cobalt ferrite nanoparticles with enhanced adsorption capability for congo red. Chem. Eng. J. 250, 164–174 (2014)
R.D. Shannon, C.T. Prewitt, Acta Cryst. 925, 825 (1969)
M.D. Shultz, E.E. Carpenter, S.A. Morrison, S. Calvin, Cation occupancy determination in manganese zinc ferrites using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. J. Appl. Phys. 99, 83–86 (2006)
J. Smit, H.P.J. Wijn, Ferrites (Wiley, New York, 1959).
N. Varalaxmi, K.V. Sivakumar, Structural and dielectric studies of magnesium substituted Ni-Cu-Zn ferrites for microinductor applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. B. 184, 88–97 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mseb.2014.01.003
B.D. Cullity, Elements of X-Ray Diffraction (Addison Wesley Publication Co. Inc., Boston, 1967), p. 96
H.E. Hassan, T. Sharshar, M.M. Hessien, O.M. Hemeda, Effect of c-rays irradiation on Mn-Ni ferrites: structure, magnetic properties and positron annihilation studies. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. B. 304, 72–79 (2013)
K. Standley, Oxide Magnetic Materials (Clarendon, Oxford, 1974), p. 97
A.B. Gadkari, T.J. Shinde, P.N. Vasambekar, Structural analysis of Y3+-doped Mg–Cd ferrites prepared by oxalate co-precipitation method. Mater. Chem. Phys. 114, 505–510 (2009)
K.P. Chae, J.-G. Lee, H.S. Kweon, Y.B. Lee, Synthesis and magnetic properties of AlxCoFe2-xO4 ferrite powders. Phys. Status Solidi. 201, 1883–1888 (2004)
Y. Slimani, M.A. Almessiereb, E. Hannachi, A. Baykal, A. Manikandan, M. Mumtaz, F. Ben Azzouz, Inflfluence of WO3 nanowires on structural, morphological and flflux pinning ability of YBa2Cu3Oy superconductor. Ceram. Int. 45, 2621–2628 (2019)
R. Waldron, Infrared spectra of ferrites. Phys. Rev. 99, 1727 (1955)
R.D. Waldron, Phys. Rev. 99, 1727 (1955)
Q.M. Wei, J.B. Li, Y.J. Chen, Cation distribution and infrared properties of NixMn1−xFe2O4 ferrites. J. Mater. Sci. 36, 5115–5118 (2001)
C.K.Y. Yafet, Phys. Rev. 87, 290–294 (1958)
X. Wu et al., Enhanced infrared radiation properties of CoFe2O4 by single Ce3+doping with energy-efficient preparation. Ceram. Int. 40, 5905–5911 (2014)
S. Maensiri, C. Masingboon, B. Boonchom, S. Seraphin, A simple route to synthesize nickel ferrite (NiFe2O4) nanoparticles using egg white. Scripta Mater. 56, 797–800 (2007)
P. Priyadharsini, A. Pradeep, P.S. Rao, G. Chandrasekaran, Structural, spectroscopic and magnetic study of nanocrystalline Ni–Zn ferrites. Mater. Chem. Phys. 116, 207–213 (2009)
Y. Köseoğlu, F. Alan, M. Tan, R. Yilgin, M. Öztürk, Low temperature hydrothermal synthesis and characterization of Mn doped cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. Ceram. Int. 38, 3625–3634 (2012)
F. Yan, M.O. Lai, L. Lu, Enhanced multiferroic properties and valence effect of Ru-doped BiFeO3 thin films. J. Phys. Chem. C. 114, 6994–6998 (2010)
G.K. Joshi, S. Deshapande, A. Khot, S.R. Sawant, Ind. J. Phys. A 61, 251 (1987)
G.K. Joshi, S. Deshapande, A. Khot, S.R. Sawant, Solid State Commun. 65, 593 (1988)
J. Wang, C. Zeng, Z. Peng, Q. Chen, Synthesis and magnetic properties of Zn1-xMnxFe2O4 nanoparticles. Phys. B 349, 124–128 (2004)
P. Motavallian, B. Abasht, H. Abdollah-Pour, Zr doping dependence of structural and magnetic properties of cobalt ferrite synthesized by sol-gel based Pechini method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 451, 577–586 (2018)
J.M.D. Coey, Rare-Earth Iron Permanent Magnets (Oxford University Press, New York, 1996).
S.S. Jadhav, S.E. Shirsath, S.M. Patange, K.M. Jadhav, Effect of Zn substitution on magnetic properties of nanocrystalline cobalt ferrites. J. Appl. Phys. 108, 2–6 (2010)
L. Neel, SCR Acad. Sci. 230, 375 (1950)
B.S. Chauhan, R. Kumar, K.M. Jadhav, M. Singh, Magnetic study of substituted Mg–Mn ferrites synthesized by citrate precursor method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 283, 71–81 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2004.04.133
E.E. Ateia, F.S. Soliman, Modifification of Co/Cu nanoferrites properties via Gd3+/ Er3+ doping. Appl. Phys. A. 123, 312 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-017-0948-8
U.R. Ghodake, N.D. Chaudhari, R.C. Kambale, J.Y. Patil, S.S. Suryavanshi, Effect of Mn2+ substitution on structural, magnetic, electric and dielectric properties of Mg–Zn ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 407, 60–68 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2016.01.022
M.M. Eltabey, K.M. El-Shokrofy, S.A. Gharbia, Enhancement of the magnetic properties of Ni–Cu–Zn ferrites by the non-magnetic Al3+-ions substitution. J. Alloys Compds. 509, 2473–2477 (2011)
Y. Yafet, C. Kittel, Phys. Rev. 90, 295 (1952)
S.S. Bellad, R.B. Pujar, B.K. Chougule, Structural and magnetic properties of some mixed Li-Cd ferrites. Mater. Chem. Phys. 52, 166–169 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0254-0584(98)80019-9
T. Ibusuki, S. Kojima, O. Kitakami, Y. Shimada, Magnetic anisotropy and behaviors of Fe nanoparticles. IEEE Trans. Magn. 37, 2223–2225 (2001)
I.P. Muthuselvam, R.N. Bhowmik, Mechanical alloyed Ho3+ doping in CoFe2O4 spinel ferrite and understanding of magnetic nanodomains. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 322, 767–776 (2010)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suo, N., Sun, A., Zhang, Y. et al. Magnetic transformation of Ni–Mg–Zn ferrite substituted by the Co2+ ions from soft magnetic to hard magnetic. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 32, 3286–3302 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-05077-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-05077-w